Question: Provide 1 SAMPLE PROBLEM in each topic that is listed below: NOTE: PLEASE USE EXCEL FOR SOLVING THE SAMPLE PROBLEM THAT YOU'VE PROVIDE Extreme Value

Provide 1 SAMPLE PROBLEM in each topic that is listed below:
NOTE: PLEASE USE EXCEL FOR SOLVING THE SAMPLE PROBLEM THAT YOU'VE PROVIDE
Extreme Value Distributions Statistics & Sampling Variability
Sampling Distribution of a Sample Mean
Sampling Distribution of a Sample Proportion
t- and F-Distributions
reference below
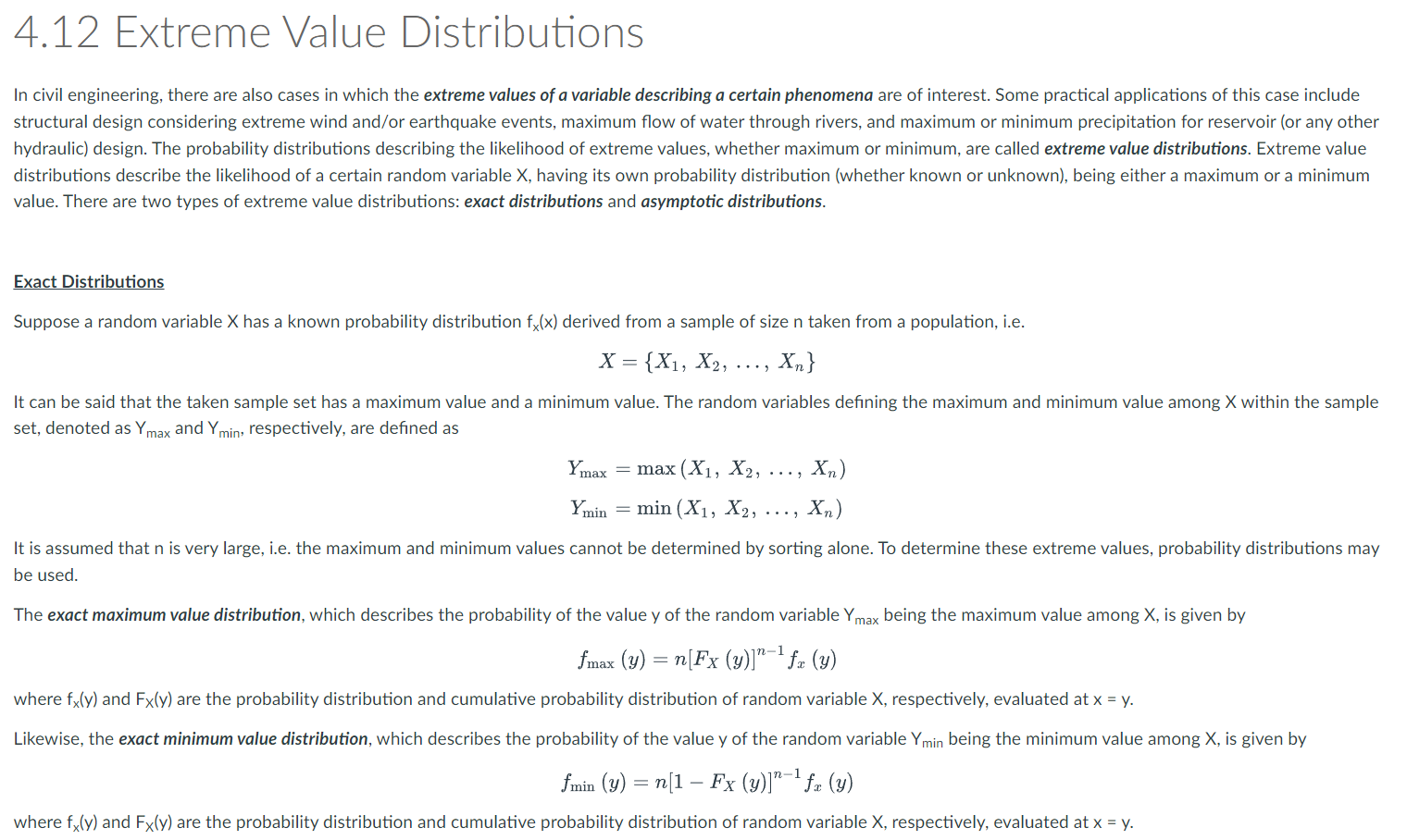

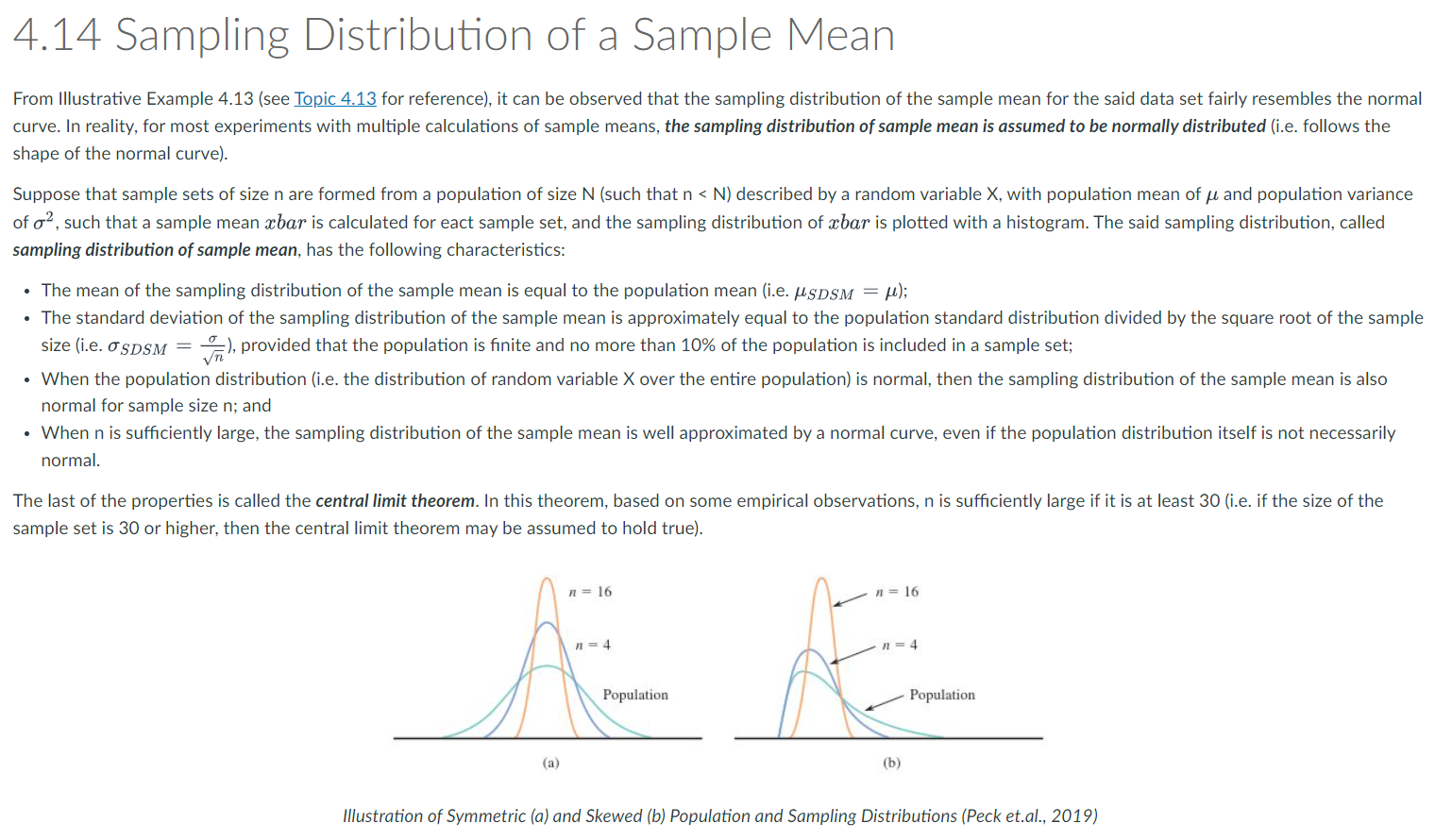
4.12 Extreme Value Distributions In civil engineering, there are also cases in which the extreme values ofa variable describing a certain phenomena are of interest. Some practical applications of this case include structural design considering extreme wind and/or earthquake events, maximum ow of water through rivers, and maximum or minimum precipitation for reservoir (or any other hydraulic) design. The probability distributions describing the likelihood of extreme values, whether maximum or minimum, are called extreme value distributions. Extreme value distributions describe the likelihood of a certain random variable X, having its own probability distribution (whether known or unknown), being either a maximum or a minimum value. There are two types of extreme value distributions: exact distributions and asymptotic distributions. Exact Distributions Suppose a random variable X has a known probability distribution fx(x) derived from a sample of size n taken from a population, i.e. X :{X1, X2, ..., X} It can be said that the taken sample set has a maximum value and a minimum value. The random variables dening the maximum and minimum value among X within the sample set, denoted as Y,\"ax and Ymin, respectively, are dened as Ymax :max(X15X25 \"'9 X71) Ymin =min(X1, X25 "'1 X71) It is assumed that n is very large, i.e. the maximum and minimum values cannot be determined by sorting alone. To determine these extreme values, probability distributions may be used. The exact maximum value distribution, which describes the probability of the value v of the random variable 'r'mx being the maximum value among X, is given by final (19') = \"lFlelln_1fx(yl where fxly) and Fx(y) are the probability distribution and cumulative probability distribution of random variable X, respectively, evaluated at x = y. Likewise, the exact minimum value distribution, which describes the probability of the value y of the random variable Ymin being the minimum value among X, is given by fmin (y) = n[1 FX (allnilfm (y) where fxly) and Fx(y) are the probability distribution and cumulative probability distribution of random variable X, respectively, evaluated at x = y. Illustrative Example 4.9: Refer to Example 4.17 of our reference text by Ang & Tang (2007). Asymptotic Distributions The asymptotic extreme value distributions are extreme value distributions of random variables as the sample size n approaches infinity. There are three types of asymptotic distributions: . Type 1: Gumbel distribution (double exponential form) . Type II: Fisher-Tippett distribution (single exponential form) . Type Ill: Weibull distribution (exponential form with upper or lower bound) Type I (Gumbel Distribution) The Type I asymptotic extreme value (Gumbel) distribution, which describes the probability of the value y of the random variable Ymax being the maximum value among X, is given by fmax (y) = an . exp [-an (y - Un)] . explexp [-an (y - un)]} where un is the most probable value of Ymax and On is an inverse measure of dispersion of Ymax (related to variance or standard deviation). If the random variable X is a standard normal random variable, then Un = V2 Inn - In(In n) +In 47 ; an = V2 Inn 2v2 In n The mean and variance of the random variable described by the Type I asymptotic distribution are H = Un + an' Y = 0.577216 02 =4.13 Stahstics & Sampling Variability Part 3: Sampling Distributions Module 4: Introduction to Probability Theory (Part Suppose a population of N objects or members has a characteristic represented by a random variable X with population mean of pi and population variance of 02. with values still unknown. To estimate these parameters, a sample of n objects (such that n
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


