Question: Provide solutions in Haskell. The types file CS 381 Homework 5 - Types You may work in groups of up to three people on this
Provide solutions in Haskell.



The types file
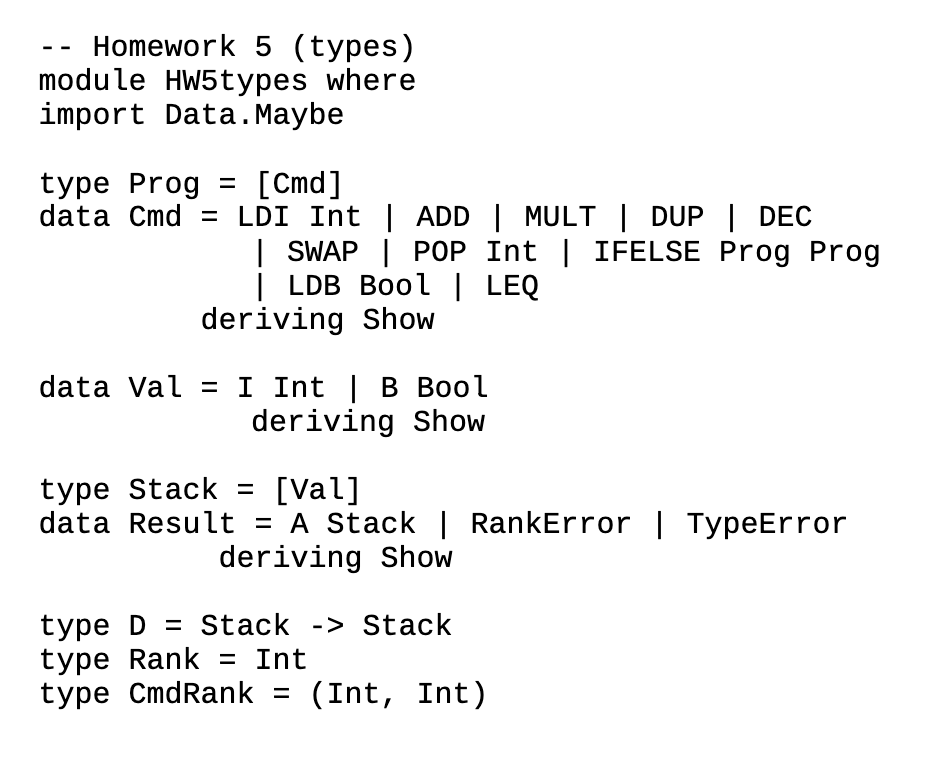
CS 381 Homework 5 - Types You may work in groups of up to three people on this assignment. You will need to sign-up for a group in Canvas at least 24 hours before the due date of the assignment. A Rank-Based Type System for a Stack Language 2 We exlend Stack Language 2 from Homework 4 by adding the following three operations - DEC - decrements the topmost element (must be Int) on the stack - SWAP exchanges the two topmost elements on the stack - POPk-pops k elements off the stack The abstract syntax of the extended language is as follows. type Prog =[Cmd] data Cmd= LDI Int | LDB Bool | LEQ | ADD | MULT | DUP | IFELSE Prog Prog | DEC | SWAP | POP Int deriving Show Again the types of the values on the Stack are Bool and Int. You should dynamically type check all operations during run time. Instead of using Either as in homework 4 you can define data Val=IlntB Bool data Stack =[Val] You can assume that the initial contents of the stack will be in the form [15, B True] etc. Use the data types defined in IIW5types.hs. We will also define a rank type system for this language that assigns ranks to stacks and operations to ensure that a program does not result in a rank mismatch. A rank mismatch occurs when there are not enough elements on the stack to perform an operation in a program. For example, executing the program p1=[ADD] with the stack =[I 1] will result in a rank mismatch and would return RankError. The rank of a stack is given by the number of its elements. The rank of a single stack operation is given by a pair of numbers (n,m) where n indicates the number of elements operation takes off the top of the stack and m is the number of elements the operation puts onto the stack. The rank for a stack program is defined to be the rank of the stack that would be obtained if the program was run on an empty stack. The rank of a stack program p1 run with stack s1 is the rank of the stack s1 after the execution of program p1. A rank error occurs in a stack program when an operation with rank (n,m) is executed on a stack with rank k
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


