Question: Pseudo code below: # Constructing the polynomial x^2 + y^2 x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 10) y = np.linspace(-1, 1, 10) x, y = np.meshgrid(x,
Pseudo code below:
# Constructing the polynomial x^2 + y^2
x = np.linspace(-1, 1, 10)
y = np.linspace(-1, 1, 10)
x, y = np.meshgrid(x, y, copy=False)
Z = x**2 + y**2 + np.random.rand(*x.shape)*0.01
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
surf = ax.plot_surface(x, y, Z, cmap=cm.coolwarm,
linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
plt.title('Original Surface')
X = x.flatten()
Y = y.flatten()
# Create the matrix A
A = #TODO
b = #TODO
# Solve for theta
Q = #TODO
Q1 = #TODO
theta = #TODO
print("Estimated parameters are theta = [%8.2f %8.2f %8.2f %8.2f %8.2f %8.2f]" %(theta[0],theta[1],theta[2],theta[3],theta[4],theta[5]))
# Compute the estimated polynomial
Zest = theta[0] + theta[1]*x + theta[2]*y + theta[3]*x**2 + theta[4]*x*y+ theta[5]*y**2
fig1 = plt.figure()
ax = fig1.gca(projection='3d')
surf = ax.plot_surface(x, y, Zest, cmap=cm.coolwarm,
linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
c=plt.title('Estimated Surface')
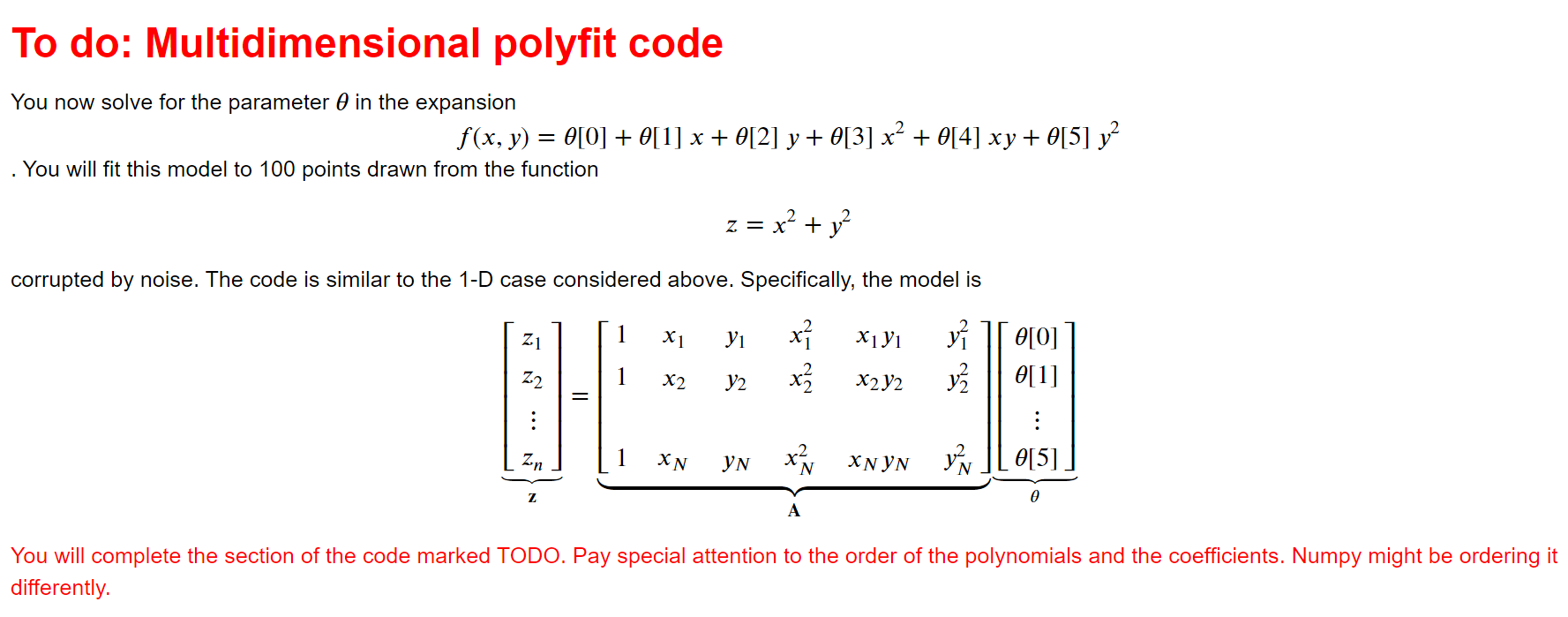
To do: Multidimensional polyfit code You now solve for the parameter in the expansion (x, y) = 0[0] + 0[1] x + 0[2] y + 0[3] x + 0[4] xy + 0[5] y . You will fit this model to 100 points drawn from the function z = x + y corrupted by noise. The code is similar to the 1-D case considered above. Specifically, the model is x7 X1Y1 } e[0] x X2Y2 0[1] Z1 Z2 Zn Z || X1 x2 XN 1 Y2 YN XXN YN Y0[5]. A 0 You will complete the section of the code marked TODO. Pay special attention to the order of the polynomials and the coefficients. Numpy might be ordering it differently.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To solve for the parameters in the expansion fx y c0 c1 x c2 y c3 x2 c4 xy c5 y2 where c is the para... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


