Question: public class TestList { static final int N = 4; public static void main(String[] args) { testSLList (); testDLList (); testStackQueue (); } static void

![static void main(String[] args) { testSLList(); testDLList(); testStackQueue(); } static void testSLList()](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f05db095c78_65666f05db0183a0.jpg)
public class TestList {
static final int N = 4;
public static void main(String[] args) {
testSLList();
testDLList();
testStackQueue();
}
static void testSLList() {
System.out.println("Singly-Linked List");
SLList list1 = new SLList();
for (int i = 0; i N; i++)
list1.append(new SLNode(i));
for (double d = N; d N; d++)
list1.append(new SLNode(d));
System.out.println(list1);
SLNode temp = list1.search(0);
System.out.println(temp);
list1.insertAfter(temp, new SLNode(1000));
System.out.println(list1);
list1.removeAfter(temp);
System.out.println(list1);
System.out.println();
}
static void testDLList() {
System.out.println("Doubly-Linked List");
DLList list2 = new DLList();
for (int i = 0; i N; i++)
list2.append(new DLNode(i));
for (double d = N; d N; d++)
list2.append(new DLNode(d));
System.out.println(list2);
DLNode temp = list2.search(0);
System.out.println(temp);
list2.insertAfter(temp, new DLNode(2000));
System.out.println(list2);
list2.remove(temp);
System.out.println(list2);
System.out.println();
}
public static void testStackQueue() {
System.out.println("Stack");
SLList stack1 = new SLList();
final int M = 10;
for (int i = 1; i
System.out.print("push " + i + ": ");
stack1.push(i);
System.out.println(stack1);
}
for (int i = 1; i
System.out.print(stack1.pop() + " pop: ");
System.out.println(stack1);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Quene");
SLList queue1 = new SLList();
for (int i = 1; i
System.out.print("enqueue " + i + ": ");
queue1.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(queue1);
}
for (int i = 1; i
System.out.print(queue1.dequeue() + " dequeue: ");
System.out.println(queue1);
}
System.out.println();
}}



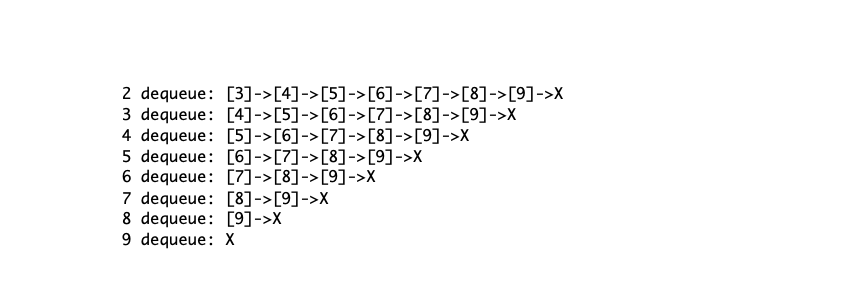
SUBMISSION 1. CREATE a class that is your last name place code in Testlist in it and place SLNode, SLlist, DLNode and DLList as static classes inside the last-name class. 2. CREATE a PDF file containing your output DIRECTION Create Java classes to implement Singly-Linked List, Doubly-Linked List, Stacks and Queues, and a program to test them. C. Part 1: Implement the pseudo-code in zyBooks with Java for Singly-Linked Lists with Object Oriented Programming: 1) Define class SLNode. a. Define local variables b. Define constructor SL Node(Object o) Define toString method public String tastring() that returns the String "I" + data.toString() + "]" 2) Define class SlList a. Define local variables b. Define constructor Sulisto c. Define public void appendCSL Node newdade d. Define prepend Define insertAfter Define removeAfter g. Define public SLNode search(Object key) h. Define public String tostring() that returns a String by traversing the list and getting the toString of each of the nodes: separate each node with "->", and end the last node with "->X" i. If list is empty print "X" ii. Separate two node with "->" iii. After the last node print "->X" Example: X [0]->X [0]->[1]->X e. f. a. Part 2: Implement the pseudo-code in zyBooks for Doubly-Linked Lists with Java with Object Oriented Programming: 3) Define class DLNode Define local variables b. Define constructor DL. Node(Object o) Define to String method public String tastring that returns the String "[" + data.toString() + "]" 4) Define class Di List C. a. Define local variables b. Define constructor DlListo) c. Define public void appendCDL Node newdede) d. Define prepend/ Define insertAfter0 f. Define remove() - fix the code so it will not crash if no elements g. Define public DL. Node search(Object key) h. Define public String tastring that returns a String by traversing the list and getting the toString of each of the nodes: i. If list is empty print X ii. Before the first node print X" iv. After the last node print"->X Example: X XX X [0]->X X[0][1]->X i. Define public String reverseString that returns a String similar to toString but traverses in reverse. Part 3: Implement the pseudo-code in zyBooks for Stacks and Queues with Java with Object Oriented Programming within the Sllist class 5) Add the following to the SLlist class a. Define void stackRush (SLNode newItem b. Define SL. Node stackPon() c. Define queuePusho d. Define queuePop Normally, we just want to push and pop Objects directly, and not SL Nodes. Create the following: e. Define void push(Object newdata) f. Define Object pop() Define enqueue h. Define dequeue Part 4: Test your code: 6) Use the following code to test your results. Copy the output and turn in as PDF. Part 5: Modifying insertAfter 7) Notice that with insertAfter you cannot insert a node at the beginning of the list. Modify the code so that a new method insertAfterNew0 will allow insertion at the front of the list if curNode is NULL. a. Define public void insertAfterNewC SL Node surdade, SL Node Dewflade) for class SlList b. Define public void insertAfterNewCDL Node surdade, DL Node Dewllade) for class Di List Hint: use previously defined methods. SAMPLE OUTPUT Singly-Linked List [0]->[1]->[2]->[3]->[4.0]->[5.0]->[6.0]->[7.0]->X [0] [0]->[1000]->[1]->[2]->[3]->[4.0]->[5.0]->[6.0]->[7.0]->X [0]->[1]->[2]->[3]->[4.0]->[5.0]->[6.0]->[7.0]->X Doubly-Linked List X[1][2][3][4.0][5.0][6.0][7.0]->X [0] X[2000][1][2][3][4.0][5.0][6.0][7.0]->X X[1][2][3][4.0][5.0][6.0][7.0]->X Stack push 1: [1]->X push 2: [2]->[1]->X push 3: [3]->[2] ->[1]->X push 4: [4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X push 5: [5]->[4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X push 6: [6]->[5] ->[4]->[3]->[2] ->[1]->X push 7: [7]->[6] ->[5] ->[4]->[3]->[2] ->[1]->X push 8: [8]->[7]->[6]->[5]->[4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X push 9: [9]->[8]->[7]->[6] ->[5]->[4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X 9 pop: [8]->[7]->[6]->[5]->[4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X 8 pop: [7]->[6]->[5] ->[4]->[3]->[2] ->[1]->X 7 pop: [6] ->[5] ->[4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X 6 pop: [5] ->[4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X 5 pop: [4]->[3] ->[2]->[1]->X 4 pop: [3]->[2] ->[1]->X 3 pop: [2]->[1]->X 2 pop: [1]->X 1 pop: X Quene enqueue 1: [1]->X enqueue 2: [1]->[2]->X enqueue 3: [1]->[2]->[3] ->X enqueue 4: [1]->[2]->[3] ->[4]->X enqueue 5: [1]->[2] ->[3] ->[4]->[5] ->X enqueue 6: [1]->[2]->[3]->[4]->[5] ->[6] ->X enqueue 7: [1]->[2]->[3] ->[4]->[5]->[6] ->[7]->X enqueue 8: [1]->[2]->[3] ->[4]->[5] ->[6] ->[7]->[8]->X enqueue 9: [1]->[2]->[3]->[4]->[5]->[6]->[7]->[8]->[9]->X 1 dequeue: [2]->[3]->[4]->[5] ->[6] ->[7]->[8]->[9] ->X 2 dequeue: [3]->[4]->[5] ->[6] ->[7]->[8]->[9] ->X Singly-Linked List [0]->[1]->[2]->[3]->[4.0]->[5.0]->[6.0]->[7.0]->X [0] [0]->[1000]->[1]->[2]->[3]->[4.0]->[5.0]->[6.0]->[7.0]->X [0]->[1]->[2]->[3]->[4.0]->[5.0]->[6.0]->[7.0]->X Doubly-Linked List X[1][2][3][4.0][5.0][6.0][7.0]->X [0] X[2000][1][2][3][4.0][5.0][6.0][7.0]->X X[1] [2][3][4.0][5.0][6.0][7.0] ->X Stack push 1: [1]->X push 2: [2]->[1]->X push 3: [3]->[2]->[1]->X push 4: [4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X push 5: [5]->[4]->[3] ->[2] ->[1]->X push 6: [6]->[5]->[4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X push 7: [7]->[6] ->[5] ->[4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X push 8: [8]->[7]->[6] ->[5]->[4] ->[3]->[2]->[1]->X push 9: [9]->[8] ->[7]->[6] ->[5] ->[4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X 9 pop: [8]->[7]->[6] ->[5]->[4]->[3]->[2] ->[1]->X 8 pop: [7]->[6]->[5]->[4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X 7 pop: [6] ->[5]->[4]->[3]->[2]->[1]->X 6 pop: [5] ->[4] ->[3]->[2]->[1]->X 5 pop: [4]->[3]->[2] ->[1]->X 4 pop: [3]->[2] ->[1]->X 3 pop: [2]->[1]->X 2 pop: [1]->X 1 pop: X Quene enqueue 1: [1]->X enqueue 2: [1]->[2] ->X enqueue 3: [1]->[2]->[3]->X enqueue 4: [1]->[2] -> [3]->[4]->X enqueue 5: [1]->[2] -> [3]->[4]->[5]->X enqueue 6: [1]->[2]->[3]->[4]->[5]->[6]->X enqueue 7: [1]->[2]->[3]->[4] ->[5] ->[6] ->[7]->X enqueue 8: [1]->[2]->[3]->[4]->[5]->[6] ->[7]->[8] ->X enqueue 9: [1]->[2]->[3]->[4]->[5] ->[6]->[7]->[8]->[9]->X 1 dequeue: [2]->[3]->[4]->[5] ->[6]->[7]->[8]->[9] ->X 2 dequeue: [3]->[4]->[5]->[6] ->[7]->[8]->[9]->X 3 dequeue: [4]->[5]->[6]->[7]->[8]->[9]->X 4 dequeue: [5]->[6]->[7]->[8]->[9]->X 5 dequeue: [6] -> [7]->[8] ->[9] ->X 6 dequeue: [7]->[8] ->[9] ->X 7 dequeue: [8]->[9]->X 8 dequeue: [9] ->X 9 dequeue: X
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


