Question: public static void printsparsetable(int start, int end) { if (start int f = fibby(start); System.out.println(start + + f); printsparsetable(f, end); } I need
public static void printsparsetable(int start, int end) {
if (start
int f = fibby(start);
System.out.println(start + " " + f);
printsparsetable(f, end);
}
I need part 2b please
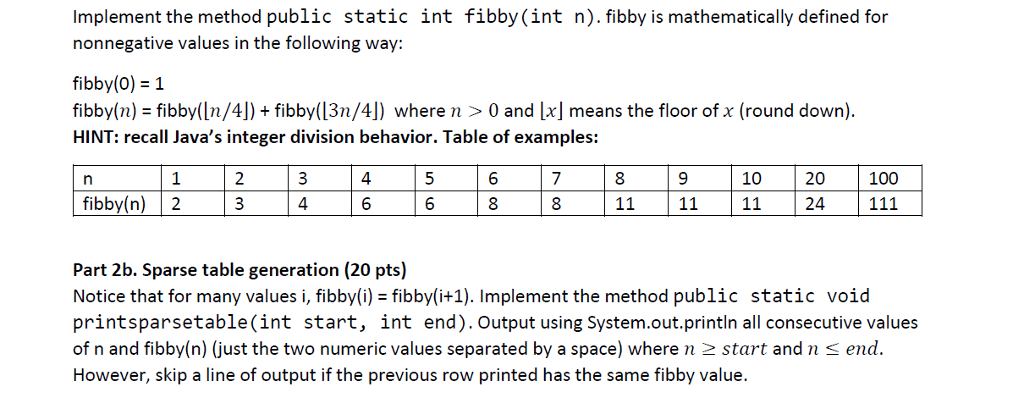
Implement the method public static int fibby (int n). fibby is mathematically defined for nonnegative values in the following way: fibby(0) = 1 fibby(n) = fibby([n/4]) + fibby([3n/4]) where n >0 and [x] means the floor of x (round down). HINT: recall Java's integer division behavior. Table of examples: n fibby(n) 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 6 5 6 6 8 7 8 8 11 9 11 10 11 20 24 100 111 Part 2b. Sparse table generation (20 pts) Notice that for many values i, fibby(i) = fibby(i+1). Implement the method public static void printsparsetable(int start, int end). Output using System.out.println all consecutive values of n and fibby(n) (just the two numeric values separated by a space) where n > start and n send. However, skip a line of output if the previous row printed has the same fibby value
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


