Question: python code r* is called a root. The Newton-Raphson is an algorithm to find roots that uses a function and its derivative o estimate (rn)
python code


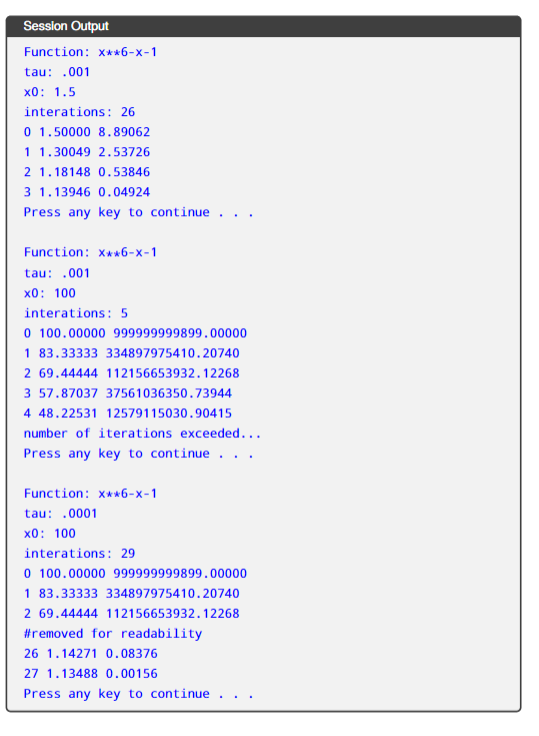

r* is called a root. The Newton-Raphson is an algorithm to find roots that uses a function and its derivative o estimate (rn) To remind you, a derivative is a function that characterizes the way a function changes as inputs change. Line 4 is the typical definition. Line 5 is a usual approximation of the derivative used in many devices. h is tiny, positive 2h (zn, f(%)) Figure 1: The root is . Our approximation rn moves toward the root as long as we're larger than our threshold. Observe in the graphic that f(b) is positive and f(a) is negative insuring that there exists a root r*, f(a*) The following listing shows two versions of the Newton-Raphson for: The first uses the explicit derivative (which isn't very scalable) done by hand. The second uses the approximation. With A functions we can easily approximate the derivative and use the algorithm without any changes
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


