Question: python In this question, you will implement a binary tree according to the following specifications: Implement a Python class named binary_tree that provides the following
python

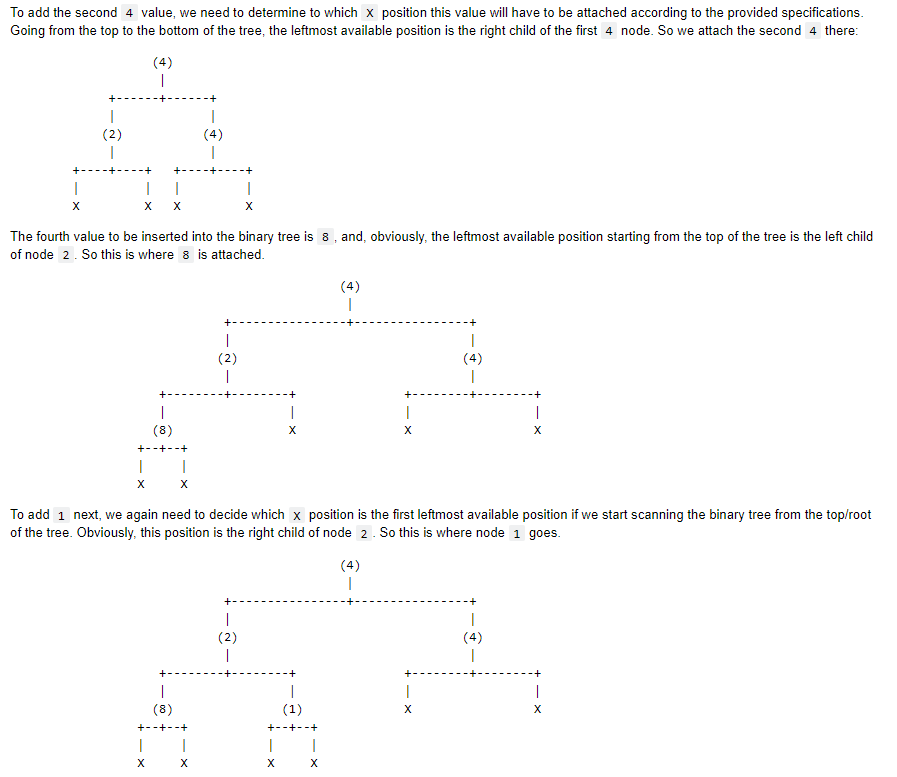


In this question, you will implement a binary tree according to the following specifications: Implement a Python class named binary_tree that provides the following APIs: 1. binary_tree() creates and returns an empty binary tree. Each node of the binary tree should be created as an instance of the bt_node class, whose (partial/incomplete) implementation has been provided to you below. The root of the binary must be stored in an instance variable named root. When the tree is empty, the root value must be None. In addition, the bt_node class must support the == operation. 2. binary_tree.insert( self, item ) should unconditionally insert the provided item in the binary tree. This function should insert the new item into the first leftmost position available that is closest to the root of tree. Hint Consider using iteration/looping to implement this functionality! Example: Consider the following code snippet that adds some values to the binary tree, b: b = binary_tree) for v in [4, 2, 4, 8, 1, 5]: # b.insert( v ) Once the root node with value 4 is inserted into the binary tree, we have both of root's children empty. Empty child node positions will be indicated with x characters in the figures below. One node 4 becomes the root of the binary tree being built, we will have the following structure: (4) T 1 Since we need to insert 2 next, we need to attach a new bt_node with value 2 as the left child of 4, since that position is the first available leftmost position with respect to the root of the tree. So now the binary tree will look as follows: 1 (2) 1 1 -+ | To add the cond 0 dotto bial illbon to batt badooordinate the residedanification To add the second 4 value, we need to determine to which x position this value will have to be attached according to the provided specifications. Going from the top to the bottom of the tree, the leftmost available position is the right child of the first 4 node. So we attach the second 4 there: (4) | -+ (2) 1 -+----+ 1 (4) 1 ---+ | + 1 The fourth value to be inserted into the binary tree is 8, and, obviously, the leftmost available position starting from the top of the tree is the left child of node 2. So this is where 8 is attached. 1 + (2) | 1 (4) 1 cos | 1 1 X | (8) +--+--+ I | X To add 1 next, we again need to decide which x position is the first leftmost available position if we start scanning the binary tree from the top/root of the tree. Obviously, this position is the right child of node 2. So this is where node 1 goes. +- | (2) 1 | + + | -+ | 1 (1) +--+--+ I | (4) + 1 (2) | (4) + + + + 1 X (8) +--+--+ 1 1 (1) +--+--+ | (5) +--+--+ 1 X This method ensures that we always keep what-is-called a complete binary tree. 3. Your implementation should support the in operator so that x in b where x is a value inserted into the binary_tree instance, b, using binary_tree.insert() method returns True . Similarly, e in b should return false if element e is not in binary tree instance, b. 4. binary_tree. _iter__( self ) : returns an iterator for the binary tree. The iterator must return the items in breadth-first order, meaning the items must be returned from top to bottom, and left-to-right order. Therefore, the iterator should always return the root node first, then the left child of the root node followed by the right child of the root node, and this behavior should continue in the same manner for the remaining descendants of the root node. This iterator must be implemented in the class bt_iterator. See the incomplete definition for this class below. You must implement your entire code without using any external libraries/modules. In other words, your code should have absolutely no functioning import statements in it! That is, even if your code works perfectly with import statements despite this requirement, your grade for this exam will unfortunately be zero. The instructor will check for the use of import statements in your code in an automated fashion that you will not have access to So please do not take a chance with this. You must keep the %%file magic directive at the top of the following code cell. Do not remove this directive, as it will lead to the automatic failure of all test cases, which themselves will cause you to get a zero grade, even if your program happens to satisfy the remaining specifications. te that any deviation from any of these specifications will cost you points. Failure to abide by the strict programming rules mentioned here will result in zero ade automatically. For example, even if your code uses a single import statement, you will get a grade of zero for your work, and such a case will also be sed for any sort of appeal later! - %%file binary_tree.py class bt_node: Defines a node in the binary tree def _init__( self, value, left=None, right=None ): self.value = value self.left = left self.right right # YOUR CODE HERE raise NotImplementedError() class bt_iterator: Iterator for a binary_tree instance # YOUR CODE HERE raise Not ImplementedError() class binary_tree: Implements a binary tree def init__( self ): # YOUR CODE HERE raise Not ImplementedError() def insert( self, value ): BE # YOUR CODE HERE raise Not ImplementedError() def iter__( self ): # YOUR CODE HERE raise Not ImplementedError() # YOUR CODE HERE raise Not ImplementedError() # YOUR CODE HERE raise Not ImplementedError() # TEST 1 from binary_tree import binary_tree student_answer binary_tree assert student_answer.root is None # TEST 2 # from binary_tree import bt_node, binary_tree b = binary_tree() b.insert( 9 ) assert b.root == bt_node( 9 ) # TEST 3 # from binary_tree import binary_tree b binary_tree() for v in [4, 2, 4, 8, 1, 5]: # b.insert( v ) student_answer sorted( [v for v in b] ) correct answer [1, 2, 4, 4, 5, 8] assert student_answer == correct answer # TEST 3 from binary_tree import binary_tree binary_tree) b.insert( 4 ) b.insert( 2 ) b.insert( 4 ) b.insert( 8 ) b.insert( 1 ) b.insert( 5 ) assert 4 in b assert 2 in b assert 8 in b assert 1 in b assert 5 in b
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


