Question: python please! node class starter code class Node: def __init__(self, data, next_node): self.data = data self.next_node = next_node class HashTable: def __init__(self, n, hash_func): #
python please!
node class starter code
class Node: def __init__(self, data, next_node): self.data = data self.next_node = next_node class HashTable: def __init__(self, n, hash_func): # TODO pass def get(self, key): # TODO pass def insert(self, key, value): # TODO pass def remove(self, key): # TODO pass hash_mod = lambda key, n: key % n n = 10
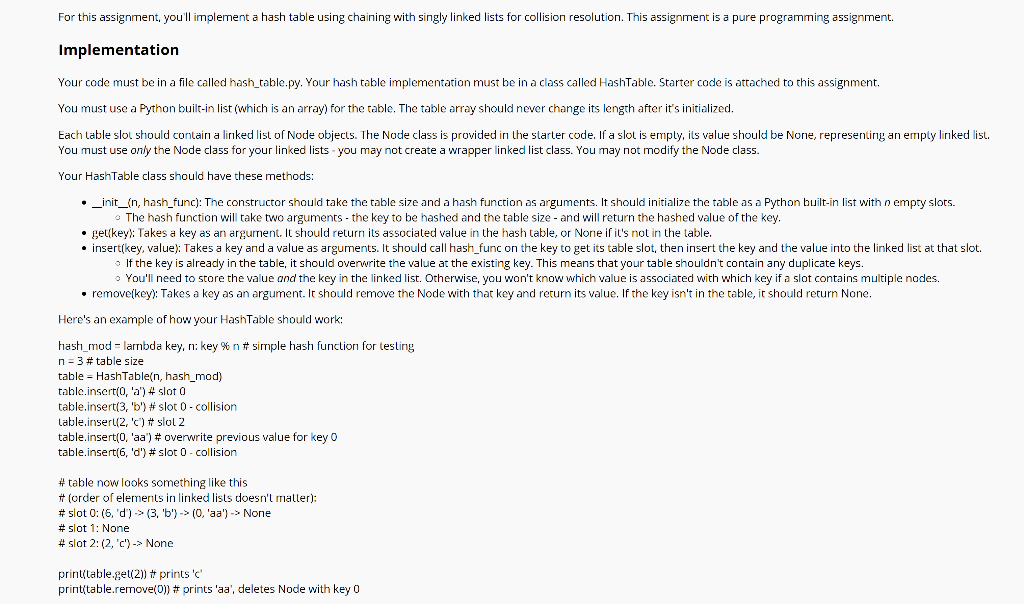
For this assignment, you'll implement a hash table using chaining with singly linked lists for collision resolution. This assignment is a pure programming assignment. Implementation Your code must be in a file called hash_table.py. Your hash table implementation must be in a class called HashTable. Starter code is attached to this assignment. You must use a Python built-in list (which is an array) for the table. The table array should never change its length after it's initialized. Each table slot should contain a linked list of Node objects. The Node class is provided in the starter code. If a slot is emply, its value should be None, representing an empty linked list. You must use only the Node class for your linked lists - you may not create a wrapper linked list class. You may not modify the Node class. Your HashTable class should have these methods: _init_{n, hash_func): The constructor should take the table size and a hash function as arguments. It should initialize the table as a Python built-in list with n empty slots. The hash function will take two arguments - the key to be hashed and the table size - and will return the hashed value of the key. .get(key): Takes a key as an argurnent. It should return its associated value in the hash table, or None if it's not in the table. insert(key, value): Takes a key and a value as arguments. It should call hash_func on the key to get its table slot, then insert the key and the value into the linked list at that slot. If the key is already in the table, it should overwrite the value at the existing key. This means that your table shouldn't contain any duplicate keys. You'll need to store the value and the key in the linked list. Otherwise, you won't know which value is associated with which key if a slot contains multiple nodes. remove(key): Takes a key as an argument. It should remove the Node with that key and return its value. If the key isn't in the table, it should return None. Here's an example of how your HashTable should work: hast_mod = lambda key, n: key %n #simple hash function for testing n = 3 # table size table - HashTablen, hash_mod) table.insert(0, 'a') #4 slot 0 table.insert(3, 'b') slot 0-collision Lable.inserl(2, 'c') #slol 2 table.insert(0, 'aa') #overwrite previous value for key O table.insert(6, 'd') #slot 0-collision #table now looks something like this #order of elements in linked lists doesn't matter): #slot 0:6, 'd')-> (3, 'b')-> (0, 'aa')-> None # slot 1: None #slot 2: (2, 'c') - None print(table.gel(2)) # prints' printtable.remove(0)) # prints 'aa', deletes Node with key 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


