Question: Python question 2. Consider the 2-link robot arm in Figure 1 with link oflength L1 fixed at the origin and connected to the second link
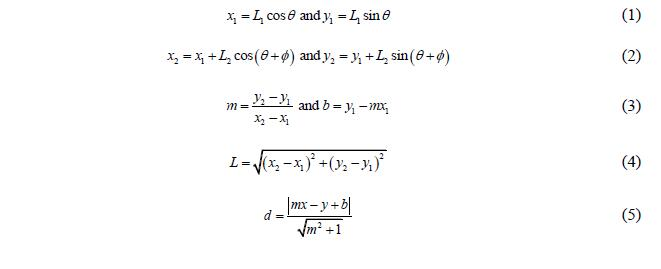
Python question
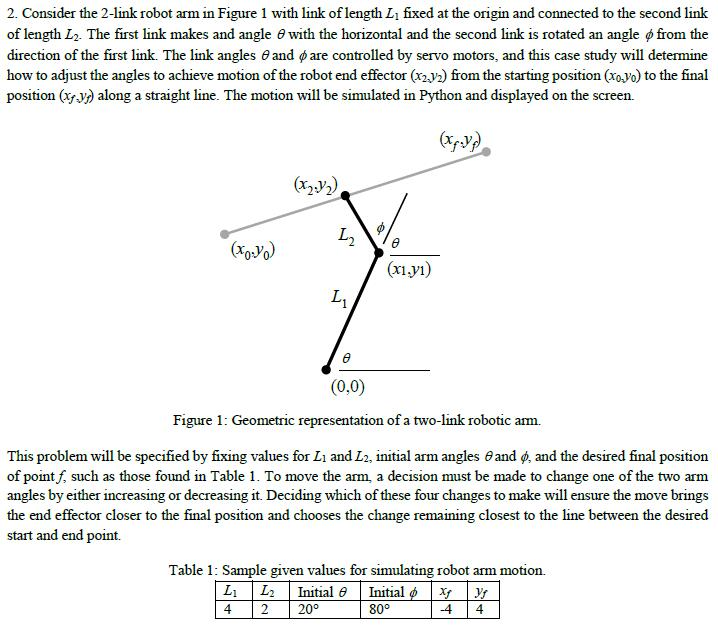
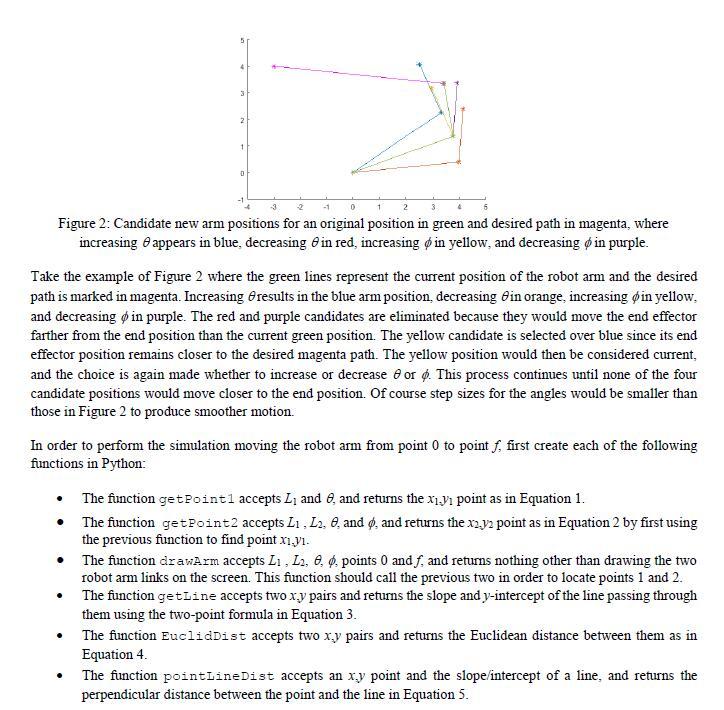
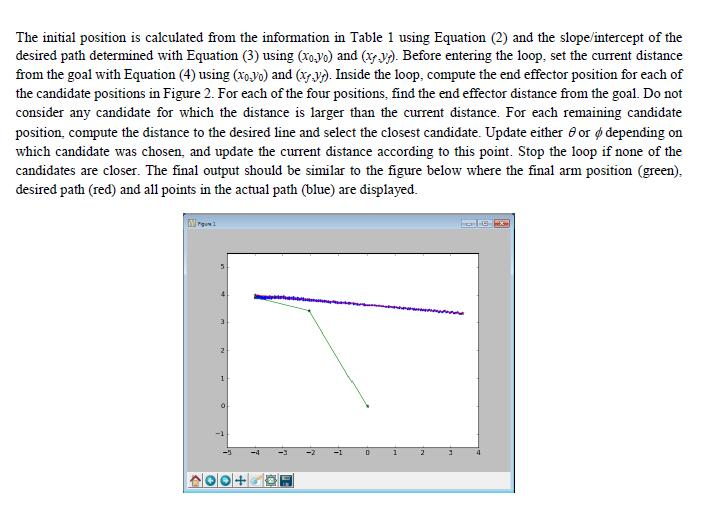
2. Consider the 2-link robot arm in Figure 1 with link oflength L1 fixed at the origin and connected to the second link of length L2. The first link makes and angle with the horizontal and the second link is rotated an angle from the direction of the first link. The link angles 6 and pare controlled by servo motors, and this case study will determine how to adjust the angles to achieve motion of the robot end effector y2 from the starting position (oyo to the final position (yy along a straight line. The motion will be simulated in Python and displayed on the screen. (0,0) Figure 1: Geometric representation of a two-link robotic arm. This problem will be specified by fixing values for Li and L2, initial arm angles Gand and the desired final position of point f, such as those found in Table 1. To move the arm, a decision must be made to change one of the two arm angles by either increasing or decreasing it. Deciding which of these four changes to make will ensure the move brings the end effector closer to the final position and chooses the change remaining closest to the line between the desired start and end point. Table 1: Sample given values for simulating robot arm motion. L1 L2 Initial Initial xt yy 200 80 2. Consider the 2-link robot arm in Figure 1 with link oflength L1 fixed at the origin and connected to the second link of length L2. The first link makes and angle with the horizontal and the second link is rotated an angle from the direction of the first link. The link angles 6 and pare controlled by servo motors, and this case study will determine how to adjust the angles to achieve motion of the robot end effector y2 from the starting position (oyo to the final position (yy along a straight line. The motion will be simulated in Python and displayed on the screen. (0,0) Figure 1: Geometric representation of a two-link robotic arm. This problem will be specified by fixing values for Li and L2, initial arm angles Gand and the desired final position of point f, such as those found in Table 1. To move the arm, a decision must be made to change one of the two arm angles by either increasing or decreasing it. Deciding which of these four changes to make will ensure the move brings the end effector closer to the final position and chooses the change remaining closest to the line between the desired start and end point. Table 1: Sample given values for simulating robot arm motion. L1 L2 Initial Initial xt yy 200 80
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


