Question: Python Question A2: Defining Vectors (9 points) Define class Vector for n-dimensional vectors as follows: Question A2: Defining Vectors (9 points) Define class Vector for
Python Question A2: Defining Vectors (9 points)
Define class Vector for n-dimensional vectors as follows:

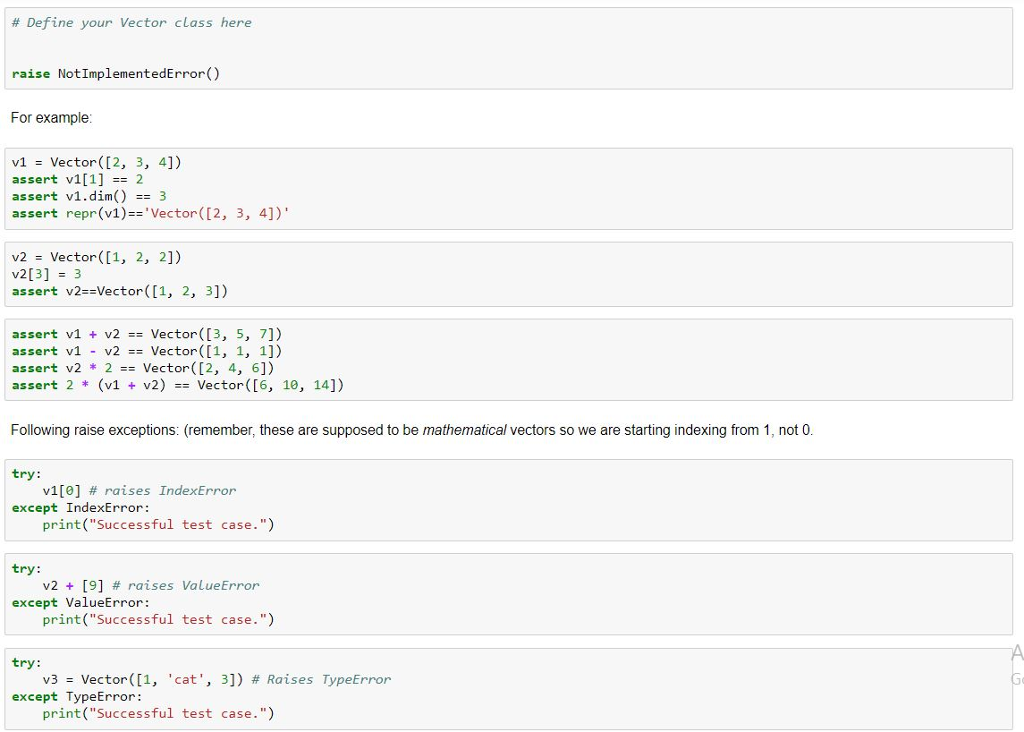
Question A2: Defining Vectors (9 points) Define class Vector for n-dimensional vectors as follows Vector(1) Creates a new vector with dimension len (1) from list 1 of numbers, raises TypeError if 1 is not a list or not all of its elements are of type int or float v.dim) Returns the dimension (length) of the vector . v. getitem i):Returns the i -th component of the vector, where components are indexed starting from 1; raises IndexError if i is less . v.-set item-(?, x):Sets the 1-th component of vector v to x, where components are indexed starting from 1, raises IndexError if i isless . v._repr) Returns the canonical string representation of the vector, see the example below than 1 or greater than the dimension of the vector than 1 or greater than the dimension of the vector v. add_(other) Returns a new vector that is the component-wise sum of v and other, raises ValueError if other is not of type Vector or if other is of a different dimension v. sub (other) Returns a new vector that is the component-wise substraction of v and other, raises ValueError if other is not of type Vector or if other is of a different dimension v._mul_(other) If other is of type int or float, returns a new vector resulting from the scalar multiplication of v with other,, i.e. with each component of v multiplied by scalar. If other is of type Vector, returns the dot product of v and other, which is the sum of the products of the corresponding components, raises ValueError if other is of different dimension in this case. If the type of other is none of Vector, int, float raises AssertionError . v._rmul_(other) Defined exactly like v._mul_(other) v. equal(self, other) Returns True if the values of the vector equals the values of other and are in the same order Python uses the following equivalent notations v other . add (other) v otherv. sub (other) v * other = v.-, mul--(other) other * v - v.--rmul--(other) ?f ys-other v.-, equal,-(other) other ._mul_(v) is not defined
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


