Question: Question 2: Defining Vectors (7 points) Define class Vector for n-dimensional vectors as follows: . Vector(1) Creates a new vector with dimension len (1) fromis1
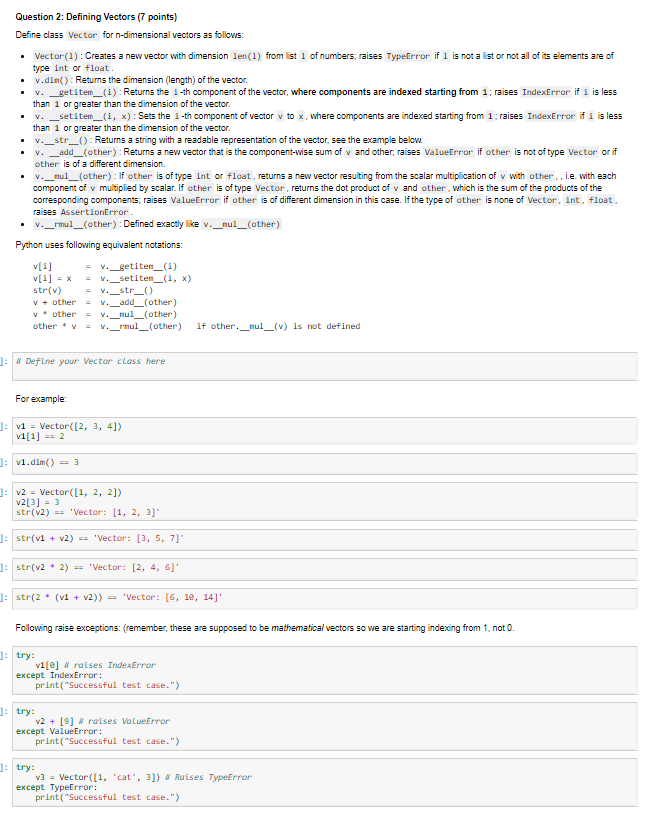
Question 2: Defining Vectors (7 points) Define class Vector for n-dimensional vectors as follows: . Vector(1) Creates a new vector with dimension len (1) fromis1 of numbers; raises TypeError if 1 is not a ist or not all of its elements are of type int or float v.-get item-(i): Returns the i-th oomponent of the vector, where components are indexed starting from 1 ; raises IndexError if i is less . v. setitem_(i, x) : Sets the i-th component of vector v to x, where components are indexed starting from 1 raises IndexError if i is less . v._str__) Returns a string with a readable representation of the vector, see the example below v.din() Returns the dimension (length) of the vector, than 1 or greater than the dimension of the vector. than 1 or greater than the dimension of the vector. . v. add_(other) Returns a new vector that is the component-wise sum of v and other, raises ValueError if other is not of type Vector or if other is of a different dimension. . v._nul_(other) If other is of type int or float, returns a new vector resulting from the scalar multiplication of v with other , i.e. with each component of multipled by scalar. If other is of type Vector,returns the dot product of and other, which is the sum of the products of the corresponding components; raises ValueError if other is of different dimension in this case. If the type of other is none of Vector, int, float raises AssertionError rmul (other) : Defined exactly like w.-nul--(other) Python uses following equivalent notations v[4] -v._getiten () v.-str-( ) v.-add--(other) str(v) = v + other other * v ; v. rnul_(other) if other. mul (v) is not defined j: | # Define your Vector class here For example: v1 -Vector([2, 3, 4]) v1[1] 2 j: | v1.dim( ) 3 j: v2 = Vector( [1, 2, 21) v2[3]3 str(v2) 'Vector: [1, 2, 3] j: | str(v1 + v2) ='Vector: [3, 5, 7]. str(v22) Vector: [2, 4, 6] j: | str(2 * (v1 + v2)) 'Vector : [6, 1e, 14]. Following raise exceptions: (remember, these are supposed to be mathematical vectors so we are starting indexing from 1, not 0. try except IndexError: v1[e] raises IndexError print( "Successful test case.") try v2 + [9] raises VaLueError except ValueError: print( "Successful test case.") try V3 -Vector([1, 'cat', 3]) Raises TypeError except TypeError print( "Successful test case.") Question 2: Defining Vectors (7 points) Define class Vector for n-dimensional vectors as follows: . Vector(1) Creates a new vector with dimension len (1) fromis1 of numbers; raises TypeError if 1 is not a ist or not all of its elements are of type int or float v.-get item-(i): Returns the i-th oomponent of the vector, where components are indexed starting from 1 ; raises IndexError if i is less . v. setitem_(i, x) : Sets the i-th component of vector v to x, where components are indexed starting from 1 raises IndexError if i is less . v._str__) Returns a string with a readable representation of the vector, see the example below v.din() Returns the dimension (length) of the vector, than 1 or greater than the dimension of the vector. than 1 or greater than the dimension of the vector. . v. add_(other) Returns a new vector that is the component-wise sum of v and other, raises ValueError if other is not of type Vector or if other is of a different dimension. . v._nul_(other) If other is of type int or float, returns a new vector resulting from the scalar multiplication of v with other , i.e. with each component of multipled by scalar. If other is of type Vector,returns the dot product of and other, which is the sum of the products of the corresponding components; raises ValueError if other is of different dimension in this case. If the type of other is none of Vector, int, float raises AssertionError rmul (other) : Defined exactly like w.-nul--(other) Python uses following equivalent notations v[4] -v._getiten () v.-str-( ) v.-add--(other) str(v) = v + other other * v ; v. rnul_(other) if other. mul (v) is not defined j: | # Define your Vector class here For example: v1 -Vector([2, 3, 4]) v1[1] 2 j: | v1.dim( ) 3 j: v2 = Vector( [1, 2, 21) v2[3]3 str(v2) 'Vector: [1, 2, 3] j: | str(v1 + v2) ='Vector: [3, 5, 7]. str(v22) Vector: [2, 4, 6] j: | str(2 * (v1 + v2)) 'Vector : [6, 1e, 14]. Following raise exceptions: (remember, these are supposed to be mathematical vectors so we are starting indexing from 1, not 0. try except IndexError: v1[e] raises IndexError print( "Successful test case.") try v2 + [9] raises VaLueError except ValueError: print( "Successful test case.") try V3 -Vector([1, 'cat', 3]) Raises TypeError except TypeError print( "Successful test case.")
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


