Question: Python The function square_wave (x) is defined by [ text { square_wave }(x)=left{begin{array}{ll} -pi / 4 & x2 pi end{array} ight. ] Compute an approximation
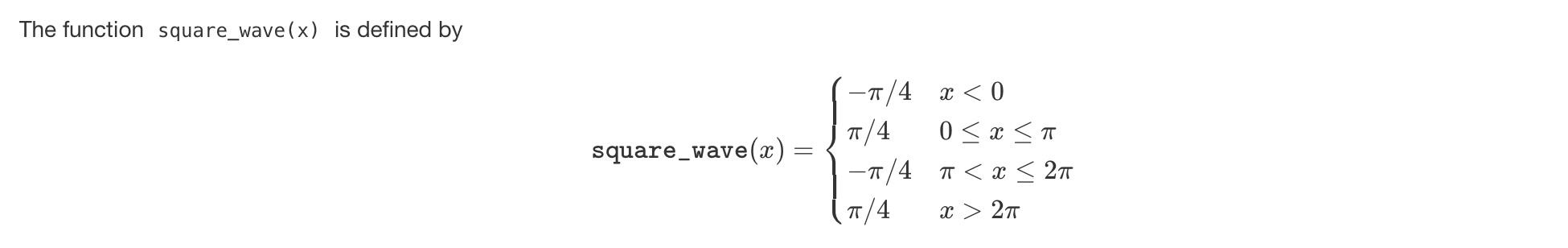
![}(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} -\pi / 4 & x2 \pi \end{array} ight. \] Compute an](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f2ca1bd3689_48366f2ca1b5b997.jpg) Python
Python
The function square_wave (x) is defined by \[ \text { square_wave }(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} -\pi / 4 & x2 \pi \end{array} ight. \] Compute an approximation to I=0sinc(t)dt, where sinc(x)={1xsin(x)x=0x=0 do this by using the code for the rectangle rule Then, on the same axes, plot partial_sum (x,100), square_wave (x), and the lines y=2I for 0.2x2+0.2. You should see that the straight lines y=2I show exactly how much the partial sums of the Fourier series differ from the square wave near to the points where the square wave changes value
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


