Question: Q 6 . When y = 1 , what is the gradient of the loss function w . r . t . W 1 1
Q When what is the gradient of the loss function wrt Write your answer to three decimal places.
Note: Please use the computation graph method. One can calculate the gradient directly using chain rules, but if the computation graph is not used at all, it will not score properly. Try to fill the red boxes above. This question does not need coding and the answer can be easily obtained analytically.
Hint: You may use the property of
Correct
Your answer is correct.
delL
delW
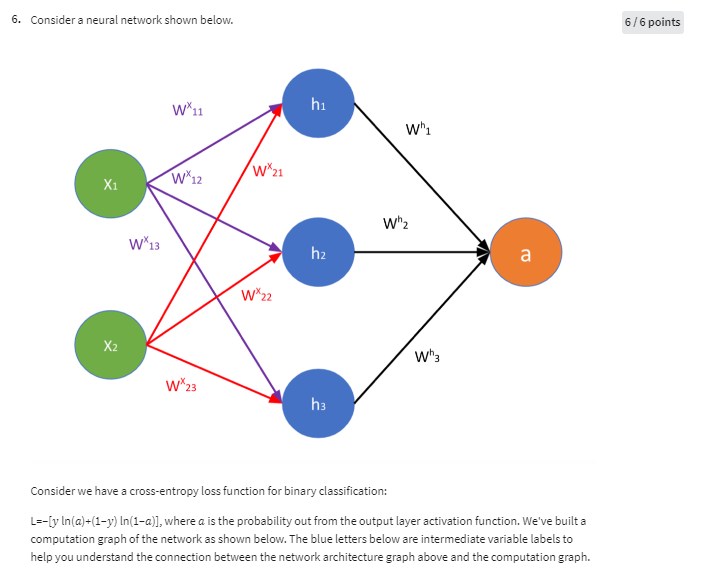
Consider a neural network shown below.
points
Consider we have a crossentropy loss function for binary classification:
where is the probability out from the output layer activation function. We've built a computation graph of the network as shown below. The blue letters below are intermediate variable labels to help you understand the connection between the network architecture graph above and the computation graph.With the same condition and the learning rate what is the updated weight new Write
your answer to three decimal places.
Note: Please use the computation graph method. One can calculate the gradients directly using chain rules, but if
the computation graph is not used at all, it will not score properly. Try to fill the red boxes in the computation
graph. This question does not need coding and the answer can be easily obtained analytically.
Hint: You may use the property of
Calculate new weight using the old weight and learning learning as follows:
larrW
Incorrect
Your answer is incorrect.
What larrW Consider a neural network shown below.
points
Consider we have a crossentropy loss function for binary classification:
where is the probability out from the output layer activation function. We've built a computation graph of the network as shown below. The blue letters below are intermediate variable labels to help you understand the connection between the network architecture graph above and the computation graph.Consider a neural network shown below. points Consider we have a crossentropy loss function for binary classification: Lylnaylna where a is the probability out from the output layer activation function. We've built a computation graph of the network as shown below. The blue letters below are intermediate variable labels to help you understand the connection between the network architecture graph above and the computation graph. With the same condition y and the learning rate eta what is the updated weight Wnew Write your answer to three decimal places. Note: Please use the computation graph method. One can calculate the gradients directly using chain rules, but if the computation graph is not used at all, it will not score properly. Try to fill the red boxes in the computation graph. This question does not need coding and the answer can be easily obtained analytically. Hint: You may use the property of delsigma zdelzsigma sigma I need answer to be rounded to decimal points
Q Answer is
i need answer of Q
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


