Question: [Q3] (Section 3.2: Newton's Method Error Analysis; Related to Theorem 1) Let f: R - R be analytic. The key step in proving Newton's method
![[Q3] (Section 3.2: Newton's Method Error Analysis; Related to Theorem 1)](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6673cd82c69d5_2826673cd82aba7f.jpg)
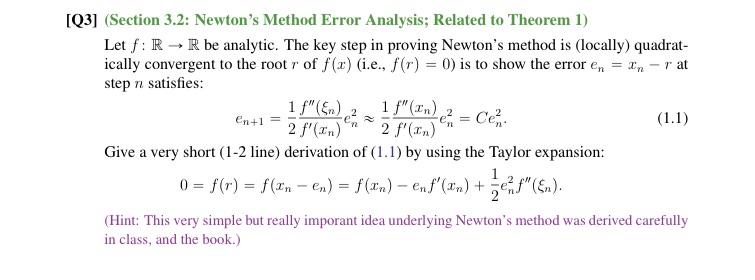
[Q3] (Section 3.2: Newton's Method Error Analysis; Related to Theorem 1) Let f: R - R be analytic. The key step in proving Newton's method is (locally) quadrat- ically convergent to the root r of f(x) (i.e., f(r) = 0) is to show the error en = In - r at step n satisfies: 1 f" ({n) 1 f" (In) en+1= -2 2 f' (In) 2 f'(In ) = Cen. (1.1) Give a very short (1-2 line) derivation of (1.1) by using the Taylor expansion: 0 = f(r) = f(In - en) = f(In) - enf'(In ) + re Dent" (En). (Hint: This very simple but really imporant idea underlying Newton's method was derived carefully in class, and the book.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


