Question: QUESTION 1 10 points Save Answer What human activity accounts for the increase in the atmospheric CO2 in the last 200 years? O Carbon losses

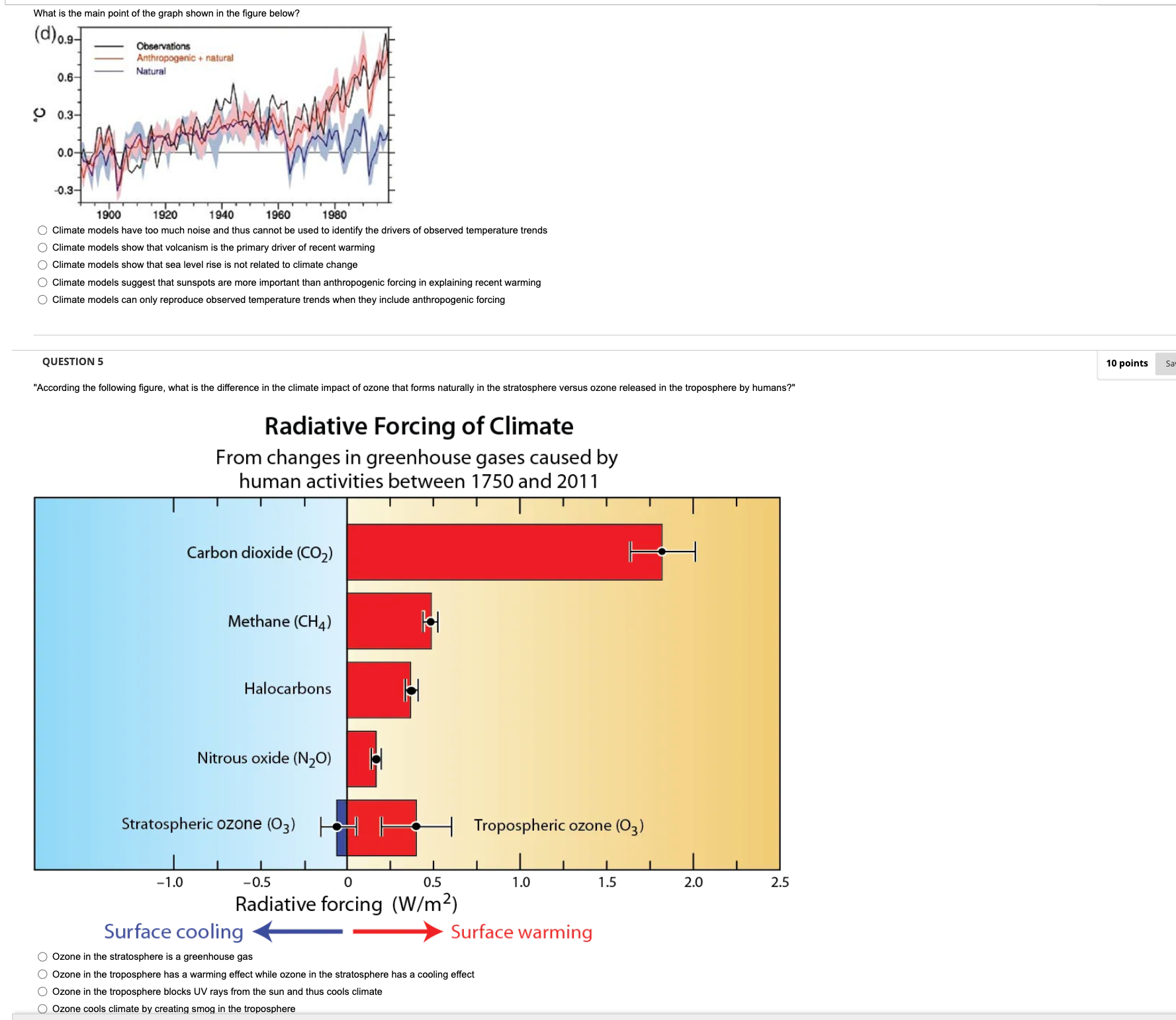
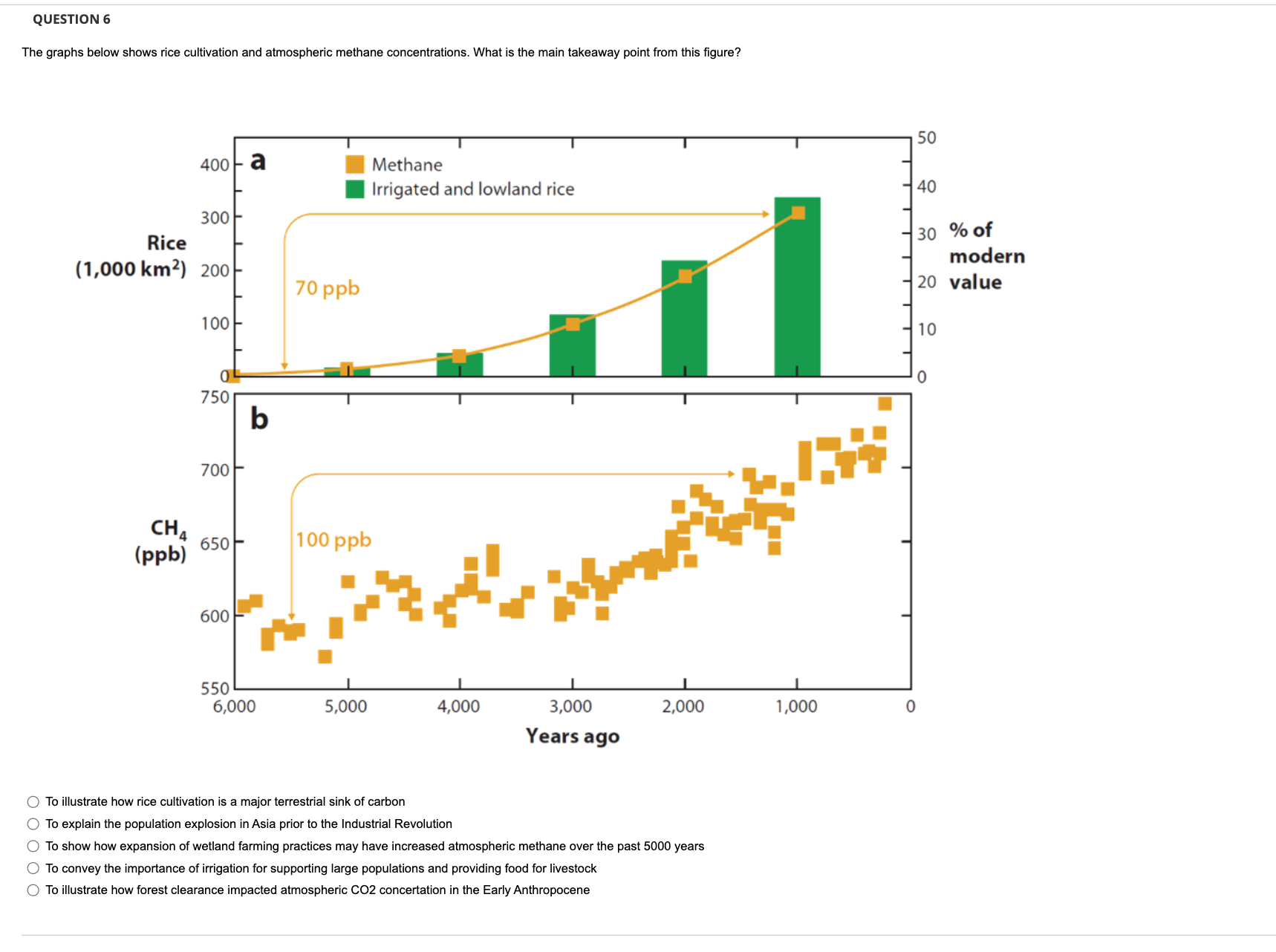
QUESTION 1 10 points Save Answer What human activity accounts for the increase in the atmospheric CO2 in the last 200 years? O Carbon losses from forests to clear land for agriculture O "Burning of carbon in coal, oil, and natural gas" O Production of cement O All of the above QUESTION 2 10 points Save Answer Which of the following statements is TRUE about the societal consequences of climate change? O Rapid climate change is always accompanied by societal collapse Human choices and adaptation play a key role in societal responses to climate change O "While societies readily adapt to wet and cold conditions, they rarely adapt to dry and hot conditions" O Technological innovation plays no role in our ability to adapt to climate change QUESTION 3 10 points Save Answer What is the key environmental impact of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)s? O CFCs combine with reactive nitrogen to form radiocarbon O CFCs cause ocean acidification O CFCs destroy ozone in the stratosphere O CFCs release causes ice sheets to thaw more quickly O CFC s change the earth s albedo by reflecting sunlightWhat is the main point of the graph shown in the figure below? (d) o.9- Observations Anthropogenic + natural 0.6- Natural 0 0.3- 0.3-/ 1900 1920 1940 1960 1980 Climate models have too much noise and thus cannot be used to identify the drivers of observed temperature trends O Climate models show that volcanism is the primary driver of recent warming Climate models show that sea level rise is not related to climate change O Climate models sugg t than anthropogenic forcing in explaining recent warming Climate models can only reproduce observed temperature trends when they include anthropogenic forcing QUESTION 5 10 points 'According the following figure, what is the difference in the climate impact of ozone at forms naturally in the stratosphere versus ozone released in the troposphere by humans?" Radiative Forcing of Climate From changes in greenhouse gases caused by human activities between 1750 and 2011 Carbon dioxide (CO2) Methane (CH4) Halocarbons Nitrous oxide (N20) Stratospheric ozone (03) Tropospheric ozone (03) -1.0 0.5 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 Radiative forcing (W/m2) Surface cooling Surface warming Ozone in the stratosphere is a greenhouse gas O Ozone in the tropo a warming effect while ozone in the stratosphere has a cooling effect Ozone in the troposphere blocks UV rays from the sun and thus cools climate Ozone cools climate by creating smog in the troposphereQUESTION 6 The graphs below shows rice cultivation and atmospheric methane concentrations. What is the main takeaway point from this gure? 50 400 a I Methane I Irrigated and lowland rice 40 300 Rice 30 %Of modern 1 000 km2 ( ' ) 200 20 value 100 10 750 700 CH4 (PPb) 650 6,000 5.000 4.000 3.000 2,000 1,000 0 Years ago 0 To illustrate how rice cultivation is a maior terrestrial sink of carbon C) To explain the population explosion in Asia prior to the Industrial Revolution C) To show how expansion of wetland farming practices may have increased atmospheric methane over the past 5000 years 0 To convey the importance of irrigation for supporting large populations and providing lood tor livestock 0 To illustrate how forest clearance impacted atmospheric COZ oonoertation in the Early Anthropocene
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


