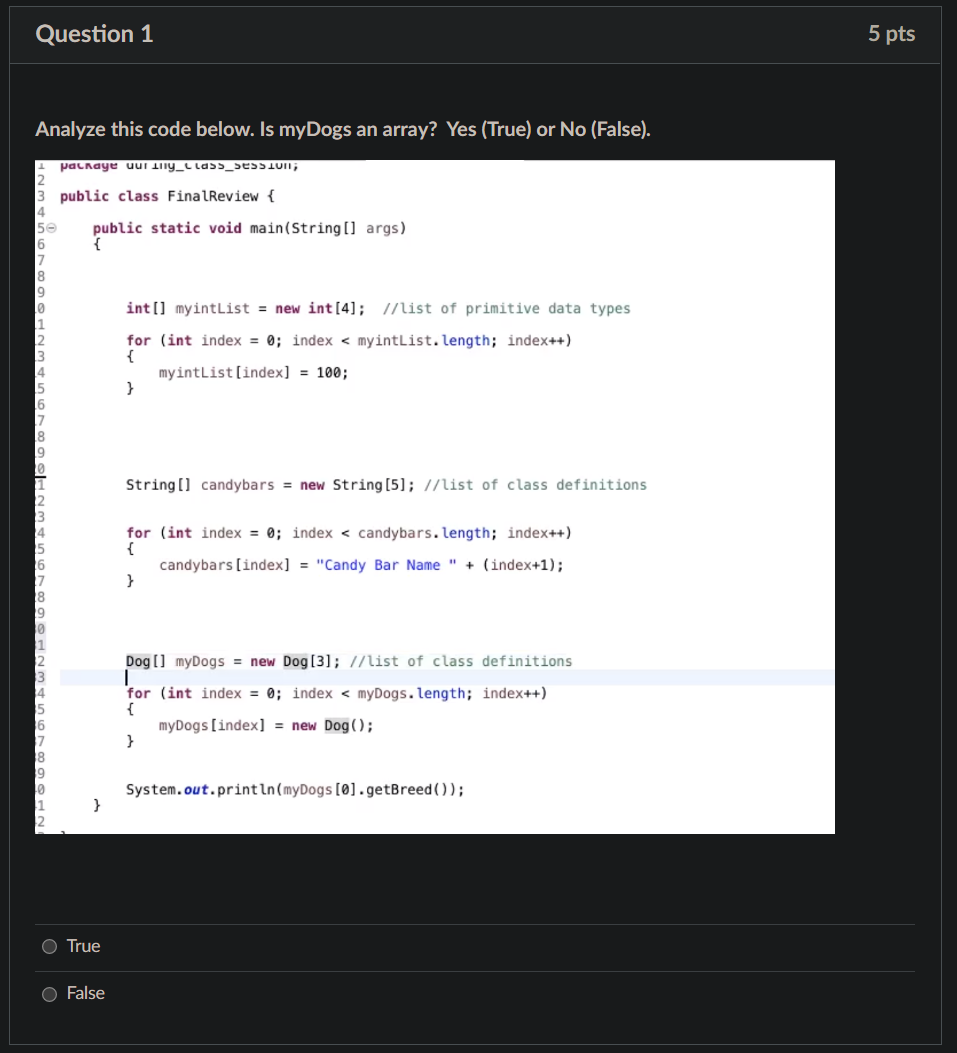
Question: Question 1 Analyze this code below. Is myDogs an array? Yes (True) or No (False). package uur ty_class_session; public class FinalReview { O O
![public public static void main(String[] args) } True False int[] myint List](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/01/65ba1beb218f1_65965ba1beb01d21.jpg)
![= new int [4]; //list of primitive data types for (int index=](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/01/65ba1beba23f5_65965ba1beb5f5a6.jpg)
![0; index < < myintList.length; index++) { myintList [index] = 100; }](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/01/65ba1bec12102_65965ba1bebd58d3.jpg)
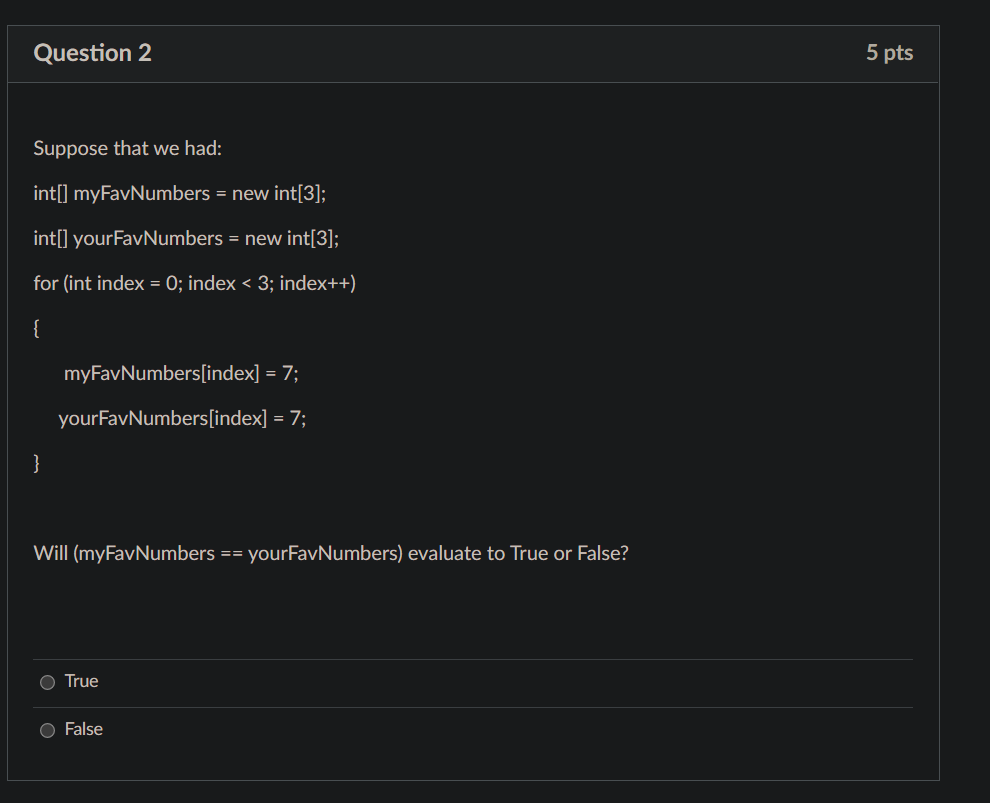
Question 1 Analyze this code below. Is myDogs an array? Yes (True) or No (False). package uur ty_class_session; public class FinalReview { O O public public static void main(String[] args) } True False int[] myint List = new int [4]; //list of primitive data types for (int index= 0; index < < myintList.length; index++) { myintList [index] = 100; } String[] candybars = new String [5]; //list of class definitions for (int index = 0; index < candybars. length; index++) { candybars [index] = "Candy Bar Name " + (index+1); } Dog [1] myDogs = new Dog [3]; //list of class definitions for (int index= 0; index < < myDogs.length; index++) { myDogs [index] = new Dog(); } System.out.println (myDogs [0].getBreed()); 5 pts Question 2 Suppose that we had: int[] myFavNumbers = new int[3]; int[] yourFavNumbers = new int[3]; for (int index = 0; index < 3; index++) { } myFavNumbers[index] = 7; yourFavNumbers[index] = 7; Will (myFavNumbers == yourFavNumbers) evaluate to True or False? True O False 5 pts package during_class_session; public class Flower } private String NameofFlower; private double PriceofFlower; public Flower() { this.setNameofFlower("No name yet"); this.setPriceofFlower (0.0); } public Flower (String nameofFlower_initial, double priceofFlower_initial) { this.setNameofFlower (nameofFlower_initial); this.setPriceofFlower (priceofFlower_initial); } public String getNameofFlower() { return Name of Flower; } public void setNameofFlower (String nameofFlower) { NameofFlower = nameofFlower; public double getPriceofFlower() { return PriceofFlower; } public void setPriceofFlower (double priceofFlower) { PriceofFlower = priceofFlower; } } public String getNameofFlower() { return NameofFlower; } public void setNameofFlower (String nameofFlower) { NameofFlower = nameofFlower; Upload Choose a File } public double getPriceofFlower() { return Priceof Flower; } public void setPriceofFlower (double priceofFlower) { PriceofFlower = priceofFlower; } 1. Import it into Eclipse. Open the file in Eclipse 2. Edit the file to add comments to identify the instance variables, constructors headings and method headings 3. Edit the file to build and add the UML in the Header comment of the code. You must follow the format taught to you in the Ch. 8 Objects lesson. You must do a very thorough job and be sure to pay attention to the details. 4. Save your Flower.java file. 5. Upload your updated Flower.java file here. Question 4 Plan around 30 minutes for this question. Write a statement for each of the following. You may enter your answers below. Only statements are needed. No full program is needed. 1. (5 points) Create an int x and initialize it to 5. 2. (5 points) Write a statement to change the value of x to 25 3. (10 points) Write a statement to check if x is a an even number (x %2) will return 0 if x is an even number and will return 1 if x is an odd number as the % operator provides the remainder. 4. (10 points) Write a statement to create an array of 6 double values. You do not need to worry about the actual 6 data values - just create an array. 5. (10 points) Write a statement to create an array called StoreList designed to hold 2 Store Names of Strings 6. (10 points) Create an array called myFlowerList designed to hold 3 flowers of the data type Flower you set up above. 7.(10 points) Write a for loop that will start at index 0 of the myFlowerList and for each element of myFlowerList, create a new instance of Flower. To create a new instance, remember we use new Flower(); you need to finish the loop and make sure each data element is a new instance of flower Edit View Insert Format Tools Table BI U 12pt p Paragraph A T V 60 pts () 0 words
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


