Question: Question 1: Supply & Demand (10 Marks) A consumer is having pizza for dinner and their marginal benefit per slice is given in the table
Question 1: Supply & Demand (10 Marks)
A consumer is having pizza for dinner and their marginal benefit per slice is given in the table below. If a slice of pizza costs $4 then how many slices should this consumer purchase? If instead, the pizza parlour only charged an entrance fee of $12 how many slices should this consumer eat?
Slice 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th
Marginal Benefit $7 $5 $3 $1 -$1
Consider the below demand and supply schedules for widgets and carefully illustrate this market to scale. Include all labels, intercepts and graphically calculate equilibrium price and quantity.
Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied
$5 10 1
$7 8 2
$9 6 3
Consider the table in b) and assume that the government now introduces a price ceiling of $7 and calculate the impact this policy will have on the market for widgets.
Sketch the market for bicycles. Now assume that the market for bicycles experiences the following shocks: 1) A study links bike riding with prostate cancer (this impacts only 50% of bike users) and 2) A new robotic bike assembly process has been invented (100% of bike firms adopt this new process). Add the impact of this shocks to your market for bicycles sketch.
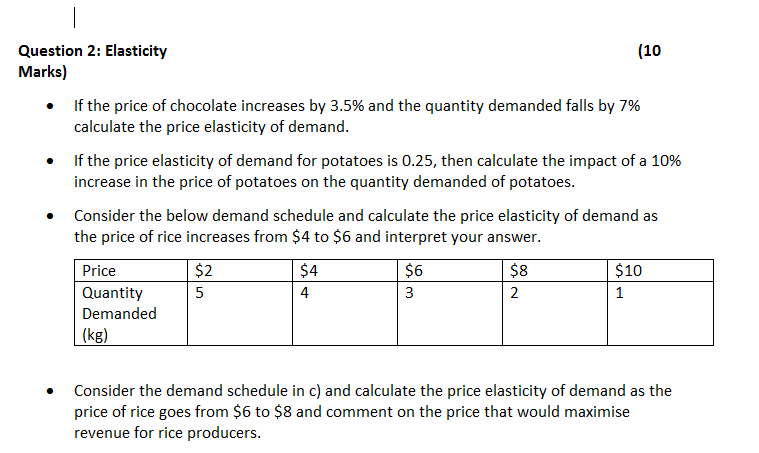
Question 2: Elasticity (10 Marks)
If the price of chocolate increases by 3.5% and the quantity demanded falls by 7% calculate the price elasticity of demand.
If the price elasticity of demand for potatoes is 0.25, then calculate the impact of a 10% increase in the price of potatoes on the quantity demanded of potatoes.
Consider the below demand schedule and calculate the price elasticity of demand as the price of rice increases from $4 to $6 and interpret your answer.
Price $2 $4 $6 $8 $10
Quantity Demanded (kg) 5 4 3 2 1
Consider the demand schedule in c) and calculate the price elasticity of demand as the price of rice goes from $6 to $8 and comment on the price that would maximise revenue for rice producers.
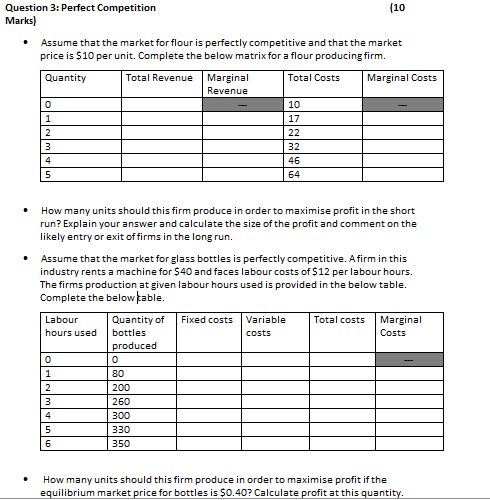
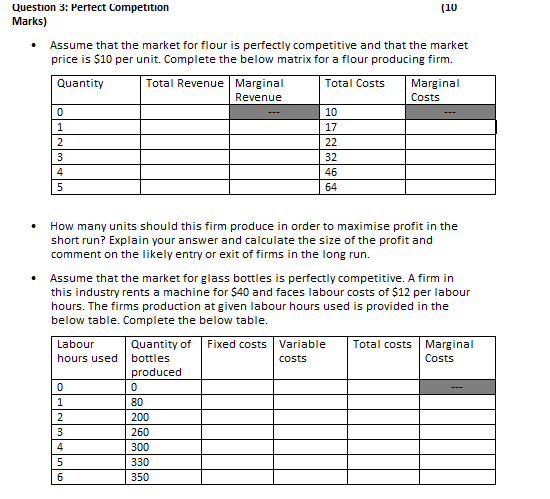
Question 3: Perfect Competition (10 Marks)
Assume that the market for flour is perfectly competitive and that the market price is $10 per unit. Complete the below matrix for a flour producing firm.
Quantity Total Revenue Marginal Revenue Total Costs Marginal Costs
0 --- 10 ---
1 17
2 22
3 32
4 46
5 64
How many units should this firm produce in order to maximize profit in the short run? Explain your answer and calculate the size of the profit and comment on the likely entry or exit of firms in the long run.
Assume that the market for glass bottles is perfectly competitive. A firm in this industry rents a machine for $40 and faces labor costs of $12 per labor hours. The firms production at given labor hours used is provided in the below table. Complete the below table.
Labour hours used Quantity of bottles produced Fixed costs Variable costs Total costs Marginal Costs
0 0 ---
1 80
2 200
3 260
4 300
5 330
6 350
How many units should this firm produce in order to maximise profit if the equilibrium market price for bottles is $0.40? Calculate profit at this quantity.
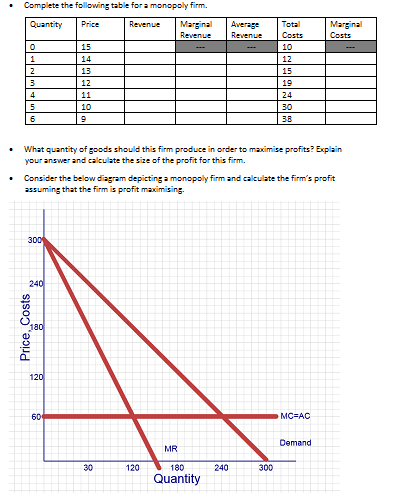
Question 4: Monopoly (10 Marks)
Complete the following table for a monopoly firm.
Quantity Price Revenue Marginal Revenue Average Revenue Total Costs Marginal Costs
0 15 --- --- 10 ---
1 14 12
2 13 15
3 12 19
4 11 24
5 10 30
6 9 38
What quantity of goods should this firm produce in order to maximise profits? Explain your answer and calculate the size of the profit for this firm.
Consider the below diagram depicting a monopoly firm and calculate the firm's profit assuming that the firm is profit maximising.
\f\f\f\f
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


