Question: After making some wise short-term investments at a race track, Chris Low had some additional cash to invest in a business. The most promising opportunity
After making some wise short-term investments at a race track, Chris Low had some additional cash to invest in a business. The most promising opportunity at the time was in building supplies, so Low bought a business that specialized in sales of one size of nail. The annual volume of nails was 2,000 kegs, and they were sold to retail customers in an even flow. Low was uncertain how many nails to order at any time. Initially, only two costs concerned him: order-processing costs, which were $60 per order without regard to size, and warehousing costs, which were $1 per year per keg space. This meant that Low had to rent a constant amount of warehouse space for the year, and it had to be large enough to accommodate an entire order when it arrived. Low was not worried about maintaining safety stocks, mainly because the outward flow of goods was so even. Low bought his nails on a delivered basis.
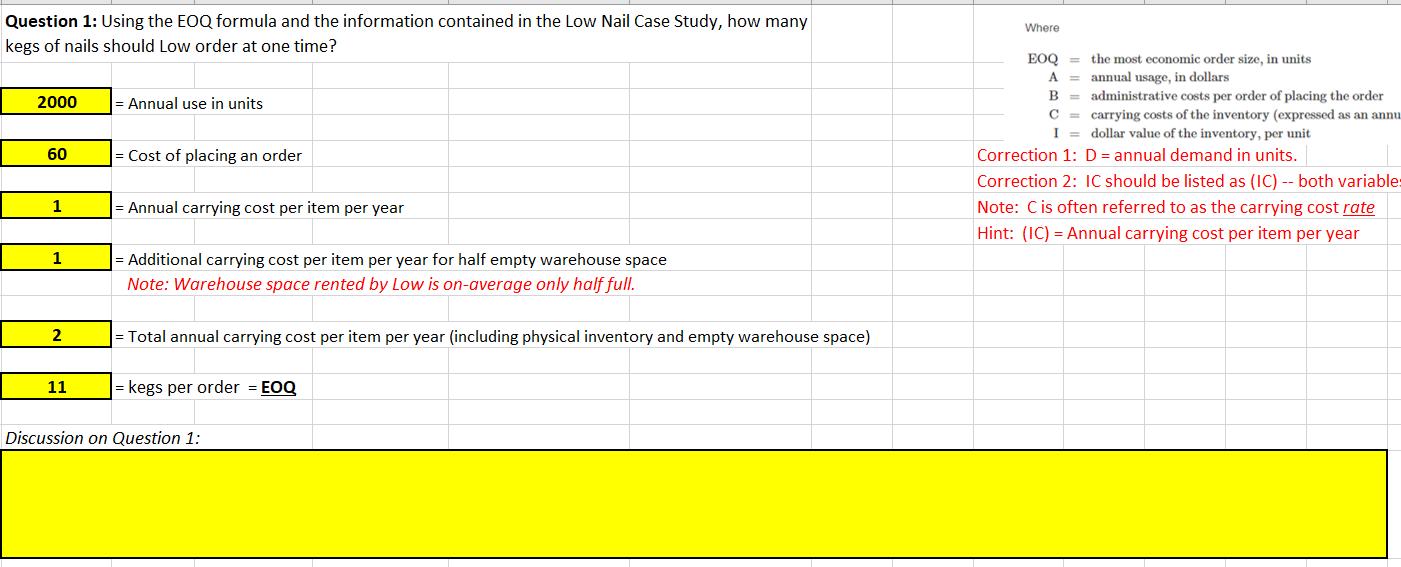
Question 1: Using the EOQ formula and the information contained in the Low Nail Case Study, how many Where kegs of nails should Low order at one time? EOQ = the most economic order size, in units = annual usage, in dollars B = administrative costs per order of placing the order C = carrying costs of the inventory (expressed as an annu I = dollar value of the inventory, per unit Correction 1: D = annual demand in units. Correction 2: 1C should be listed as (IC) -- both variables A. 2000 = Annual use in units 60 = Cost of placing an order Annual carrying cost per item per year Note: Cis often referred to as the carrying cost rate Hint: (IC) = Annual carrying cost per item per year = Additional carrying cost per item per year for half empty warehouse space Note: Warehouse space rented by Low is on-average only half full. = Total annual carrying cost per item per year (including physical inventory and empty warehouse space) 11 |= kegs per order = EOQ Discussion on Question 1:
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (167 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts