Question: Question 2 ( 1 4 points ) : You are working on a design of a lower limb ( foot - ankle ) prosthesis for
Question points: You are working on a design of a lower limb footankle prosthesis for individuals who have undergone foot
amputation bone resection at the distal tibia You remember hearing about "osseointegration" in an exciting orthopaedic engineering
class you attended at Clemson, so you plan to attach the foot prosthesis using a solid titanium alloy rod inserted into the distal tibia.
You decide to tackle this problem by identifying typical tibial bone anatomy and mechanical behavior. You assume the tibial bone
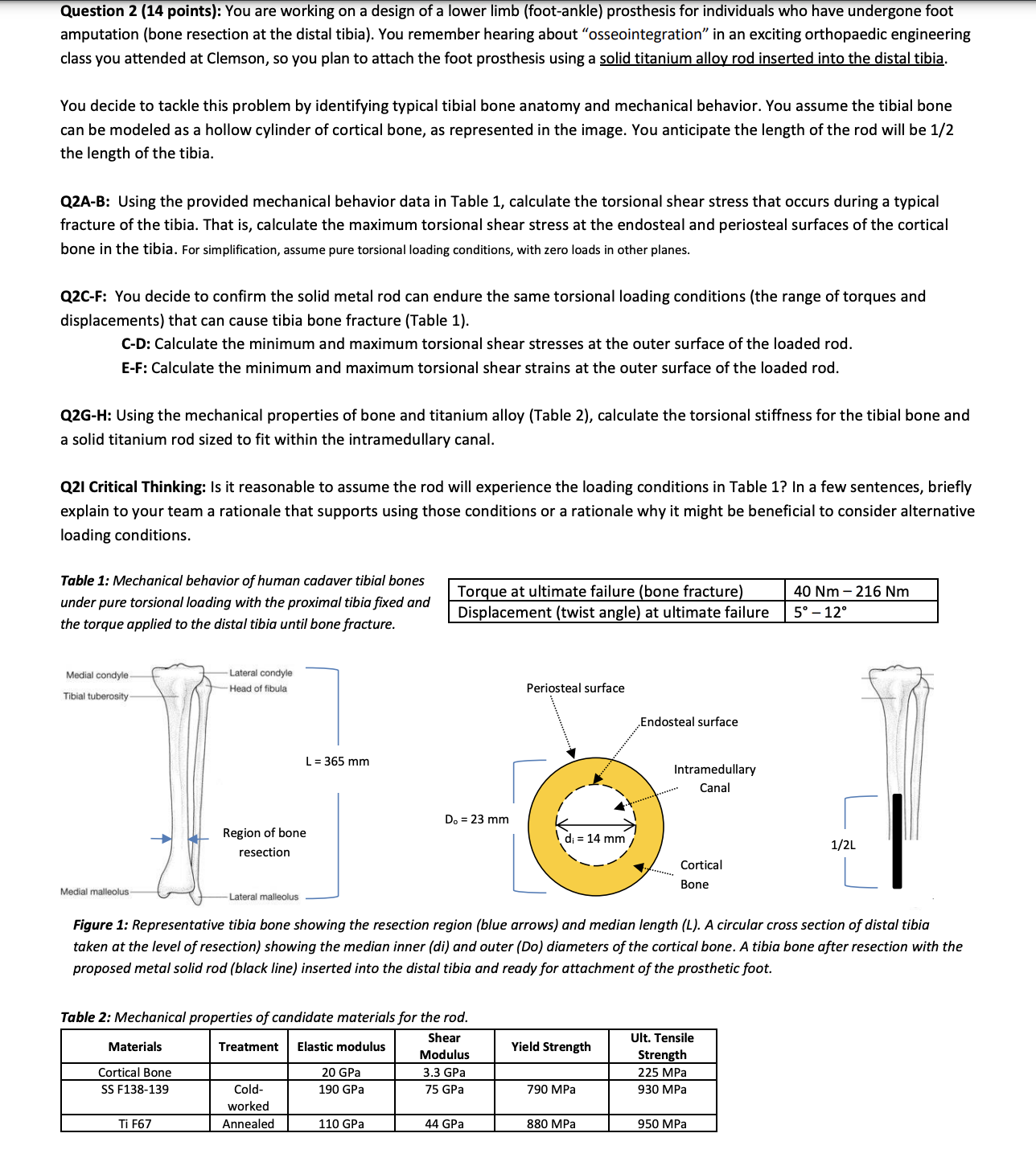
can be modeled as a hollow cylinder of cortical bone, as represented in the image. You anticipate the length of the rod will be
the length of the tibia.
QAB: Using the provided mechanical behavior data in Table calculate the torsional shear stress that occurs during a typical
fracture of the tibia. That is calculate the maximum torsional shear stress at the endosteal and periosteal surfaces of the cortical
bone in the tibia. For simplification, assume pure torsional loading conditions, with zero loads in other planes.
QCF: You decide to confirm the solid metal rod can endure the same torsional loading conditions the range of torques and
displacements that can cause tibia bone fracture Table
CD: Calculate the minimum and maximum torsional shear stresses at the outer surface of the loaded rod.
EF: Calculate the minimum and maximum torsional shear strains at the outer surface of the loaded rod.
QGH: Using the mechanical properties of bone and titanium alloy Table calculate the torsional stiffness for the tibial bone and
a solid titanium rod sized to fit within the intramedullary canal.
Q Critical Thinking: Is it reasonable to assume the rod will experience the loading conditions in Table In a few sentences, briefly
explain to your team a rationale that supports using those conditions or a rationale why it might be beneficial to consider alternative
loading conditions.
Table : Mechanical behavior of human cadaver tibial bones
under pure torsional loading with the proximal tibia fixed and
the torque applied to the distal tibia until bone fracture.
Figure : Representative tibia bone showing the resection region blue arrows and median length L A circular cross section of distal tibia
taken at the level of resection showing the median inner di and outer Do diameters of the cortical bone. A tibia bone after resection with the
proposed metal solid rod black line inserted into the distal tibia and ready for attachment of the prosthetic foot.
Table : Mechanical properties of candidate materials for the rod.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


