Question: QUESTION 2 (40 points) Another step in the green methanol production process is wastewater treatment that generates clean water for downstream operations. Specifically, let's take
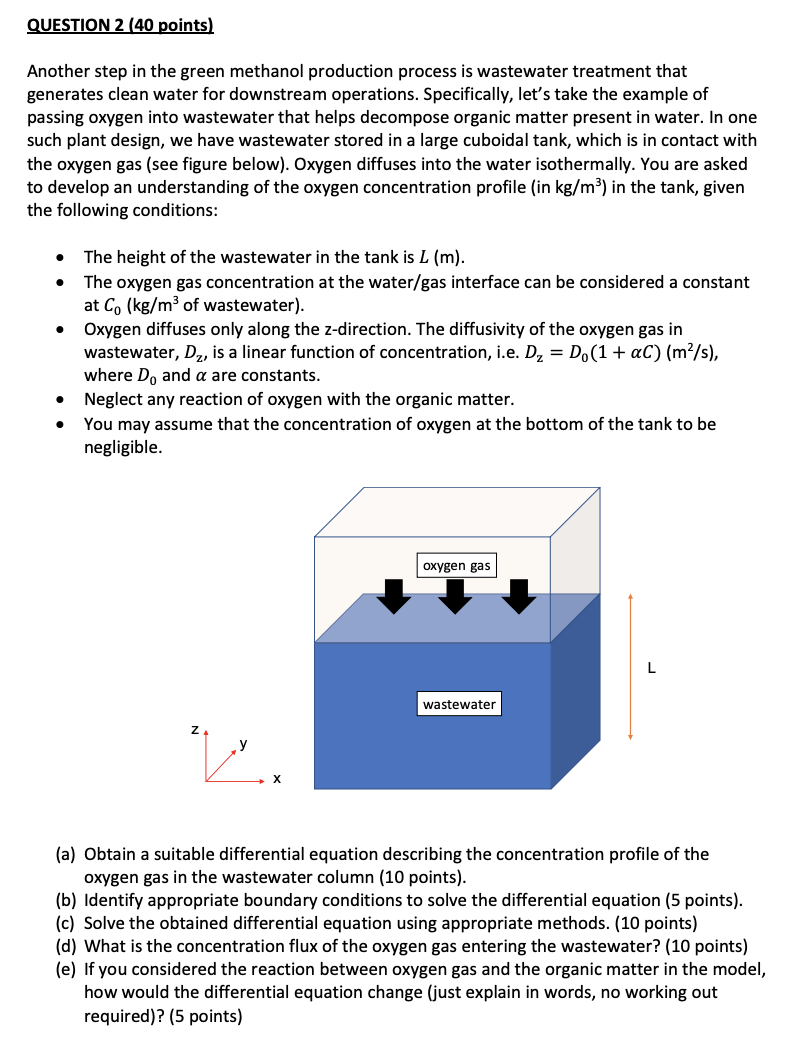
QUESTION 2 (40 points) Another step in the green methanol production process is wastewater treatment that generates clean water for downstream operations. Specifically, let's take the example of passing oxygen into wastewater that helps decompose organic matter present in water. In one such plant design, we have wastewater stored in a large cuboidal tank, which is in contact with the oxygen gas (see figure below). Oxygen diffuses into the water isothermally. You are asked to develop an understanding of the oxygen concentration profile (in kg/m3 ) in the tank, given the following conditions: - The height of the wastewater in the tank is L (m). - The oxygen gas concentration at the water/gas interface can be considered a constant at C0(kg/m3 of wastewater). - Oxygen diffuses only along the z-direction. The diffusivity of the oxygen gas in wastewater, Dz, is a linear function of concentration, i.e. Dz=D0(1+C)(m2/s), where D0 and are constants. - Neglect any reaction of oxygen with the organic matter. - You may assume that the concentration of oxygen at the bottom of the tank to be negligible. (a) Obtain a suitable differential equation describing the concentration profile of the oxygen gas in the wastewater column (10 points). (b) Identify appropriate boundary conditions to solve the differential equation (5 points). (c) Solve the obtained differential equation using appropriate methods. (10 points) (d) What is the concentration flux of the oxygen gas entering the wastewater? ( 10 points) (e) If you considered the reaction between oxygen gas and the organic matter in the model, how would the differential equation change (just explain in words, no working out required)? (5 points) QUESTION 2 (40 points) Another step in the green methanol production process is wastewater treatment that generates clean water for downstream operations. Specifically, let's take the example of passing oxygen into wastewater that helps decompose organic matter present in water. In one such plant design, we have wastewater stored in a large cuboidal tank, which is in contact with the oxygen gas (see figure below). Oxygen diffuses into the water isothermally. You are asked to develop an understanding of the oxygen concentration profile (in kg/m3 ) in the tank, given the following conditions: - The height of the wastewater in the tank is L (m). - The oxygen gas concentration at the water/gas interface can be considered a constant at C0(kg/m3 of wastewater). - Oxygen diffuses only along the z-direction. The diffusivity of the oxygen gas in wastewater, Dz, is a linear function of concentration, i.e. Dz=D0(1+C)(m2/s), where D0 and are constants. - Neglect any reaction of oxygen with the organic matter. - You may assume that the concentration of oxygen at the bottom of the tank to be negligible. (a) Obtain a suitable differential equation describing the concentration profile of the oxygen gas in the wastewater column (10 points). (b) Identify appropriate boundary conditions to solve the differential equation (5 points). (c) Solve the obtained differential equation using appropriate methods. (10 points) (d) What is the concentration flux of the oxygen gas entering the wastewater? ( 10 points) (e) If you considered the reaction between oxygen gas and the organic matter in the model, how would the differential equation change (just explain in words, no working out required)? (5 points)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


