Question: Question 2: Consider the following supplydemand framework for the USD/ A. Given that the European nations have flexible exchange rates, can you discuss two examples
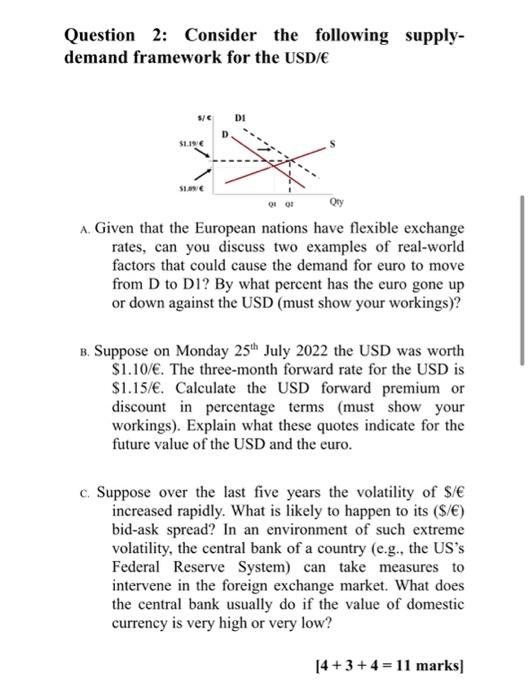
Question 2: Consider the following supplydemand framework for the USD/ A. Given that the European nations have flexible exchange rates, can you discuss two examples of real-world factors that could cause the demand for euro to move from D to D1? By what percent has the euro gone up or down against the USD (must show your workings)? B. Suppose on Monday 25th July 2022 the USD was worth $1.10/. The three-month forward rate for the USD is $1.15/. Calculate the USD forward premium or discount in percentage terms (must show your workings). Explain what these quotes indicate for the future value of the USD and the euro. c. Suppose over the last five years the volatility of $/ increased rapidly. What is likely to happen to its ($/) bid-ask spread? In an environment of such extreme volatility, the central bank of a country (e.g., the US's Federal Reserve System) can take measures to intervene in the foreign exchange market. What does the central bank usually do if the value of domestic currency is very high or very low? [4+3+4=11marks] Question 2: Consider the following supplydemand framework for the USD/ A. Given that the European nations have flexible exchange rates, can you discuss two examples of real-world factors that could cause the demand for euro to move from D to D1? By what percent has the euro gone up or down against the USD (must show your workings)? B. Suppose on Monday 25th July 2022 the USD was worth $1.10/. The three-month forward rate for the USD is $1.15/. Calculate the USD forward premium or discount in percentage terms (must show your workings). Explain what these quotes indicate for the future value of the USD and the euro. c. Suppose over the last five years the volatility of $/ increased rapidly. What is likely to happen to its ($/) bid-ask spread? In an environment of such extreme volatility, the central bank of a country (e.g., the US's Federal Reserve System) can take measures to intervene in the foreign exchange market. What does the central bank usually do if the value of domestic currency is very high or very low? [4+3+4=11marks]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


