Question: What makes implementing a queue with a Linked List potentially easier than implementing a queue with a typical array? No capacity limitation There's no
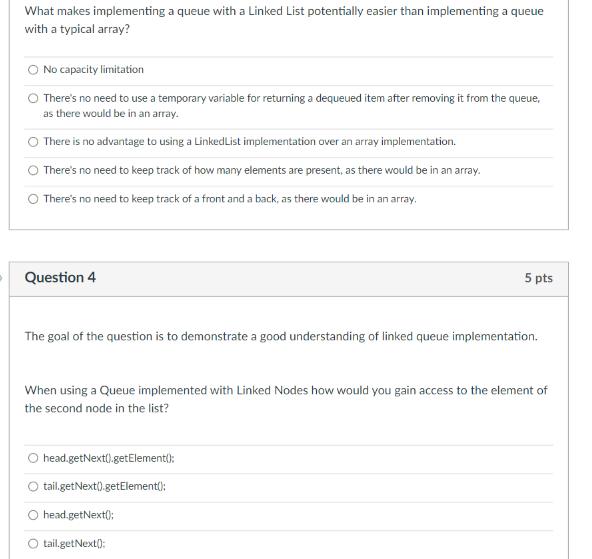
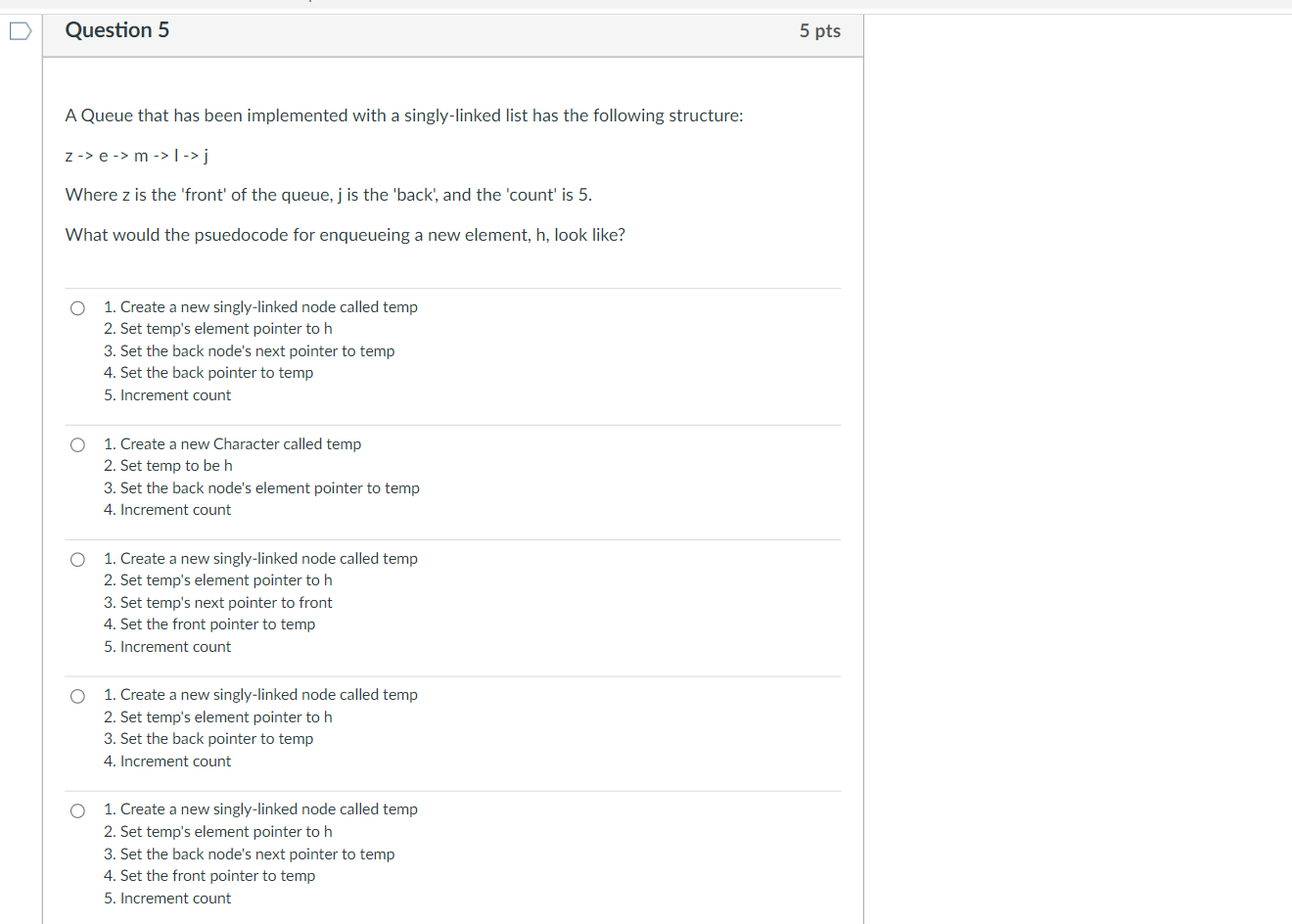
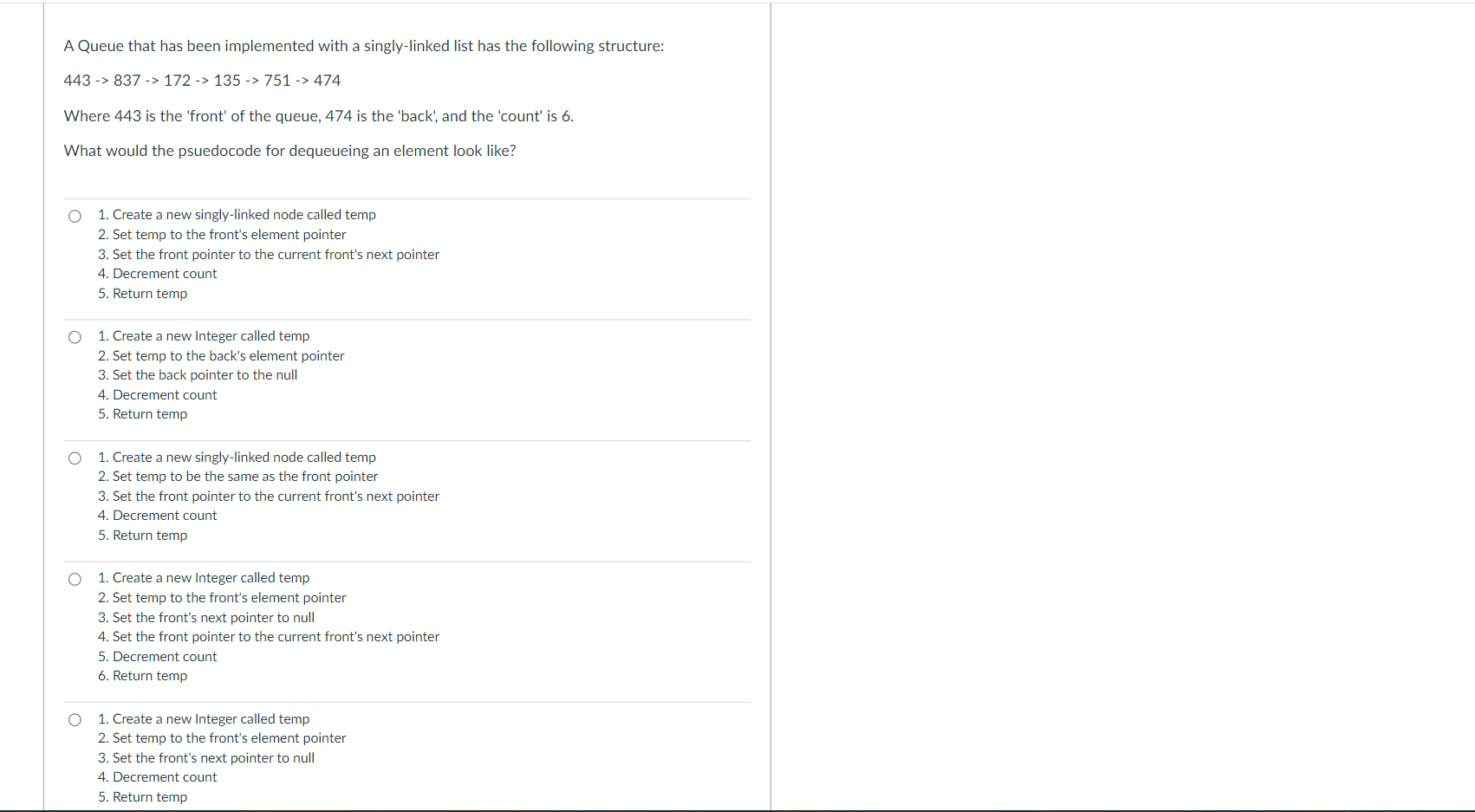
What makes implementing a queue with a Linked List potentially easier than implementing a queue with a typical array? No capacity limitation There's no need to use a temporary variable for returning a dequeued item after removing it from the queue, as there would be in an array. There is no advantage to using a Linked List implementation over an array implementation. There's no need to keep track of how many elements are present, as there would be in an array. There's no need to keep track of a front and a back, as there would be in an array. Question 4 The goal of the question is to demonstrate a good understanding of linked queue implementation. 5 pts When using a Queue implemented with Linked Nodes how would you gain access to the element of the second node in the list? head.getNext().getElement(): tail.getNext().getElement(): head.getNext(): tail.getNext(); Question 5 A Queue that has been implemented with a singly-linked list has the following structure: z -> e-> m-> |->j. Where z is the 'front' of the queue, j is the 'back', and the 'count' is 5. What would the psuedocode for enqueueing a new element, h, look like? O 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp's element pointer to h 3. Set the back node's next pointer to temp 4. Set the back pointer to temp 5. Increment count 1. Create a new Character called temp 2. Set temp to be h 3. Set the back node's element pointer to temp 4. Increment count 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp's element pointer to h 3. Set temp's next pointer to front 4. Set the front pointer to temp 5. Increment count 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp's element pointer to h 3. Set the back pointer to temp 4. Increment count 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp's element pointer to h 3. Set the back node's next pointer to temp 4. Set the front pointer to temp 5. Increment count 5 pts A Queue that has been implemented with a singly-linked list has the following structure: 443->837 -> 172 -> 135 -> 751 -> 474 Where 443 is the 'front' of the queue, 474 is the 'back', and the 'count' is 6. What would the psuedocode for dequeueing an element look like? 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp to the front's element pointer 3. Set the front pointer to the current front's next pointer 4. Decrement count 5. Return temp 1. Create a new Integer called temp 2. Set temp to the back's element pointer 3. Set the back pointer to the null 4. Decrement count 5. Return temp 1. Create a new singly-linked node called temp 2. Set temp to be the same as the front pointer 3. Set the front pointer to the current front's next pointer 4. Decrement count 5. Return temp 1. Create a new Integer called temp 2. Set temp to the front's element pointer 3. Set the front's next pointer to null 4. Set the front pointer to the current front's next pointer 5. Decrement count 6. Return temp 1. Create a new Integer called temp 2. Set temp to the front's element pointer 3. Set front's next pointer to null 4. Decrement count 5. Return temp
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The detailed answer for the above question is provided below Answer Breakdown Question 1 The answer ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


