Question: Question 6, Text Exercise 4.4 5 HW Score: 71.21%, 7.83 of 11 points Part 4 of 6 [/ ML E R Rl i Each firm
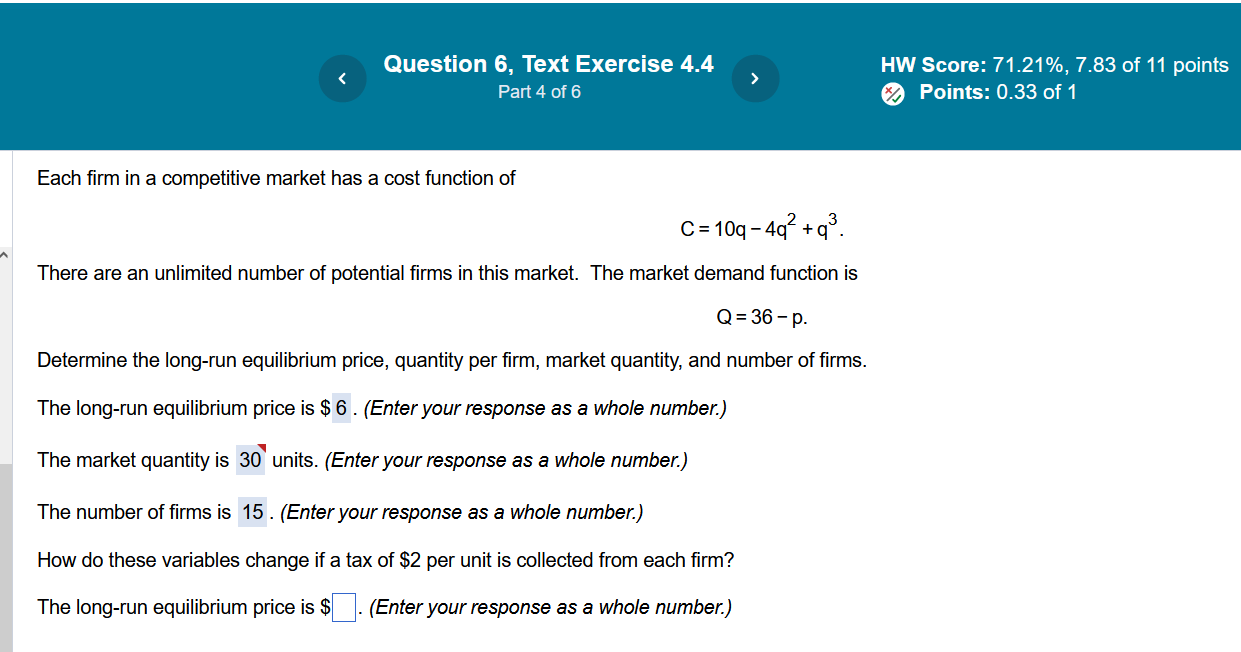
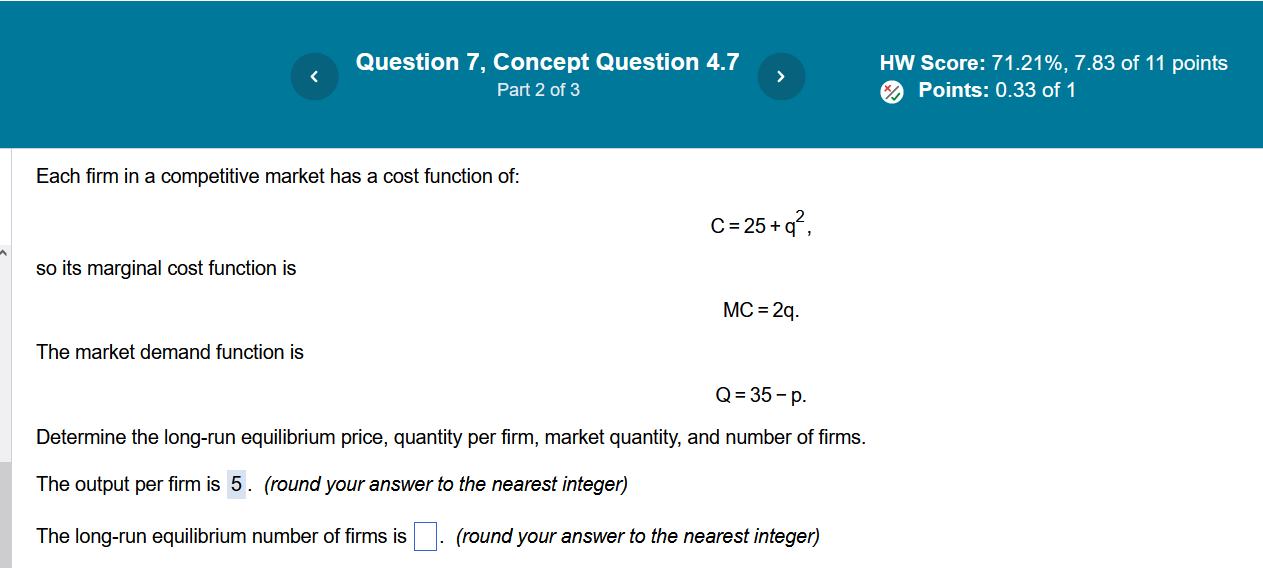
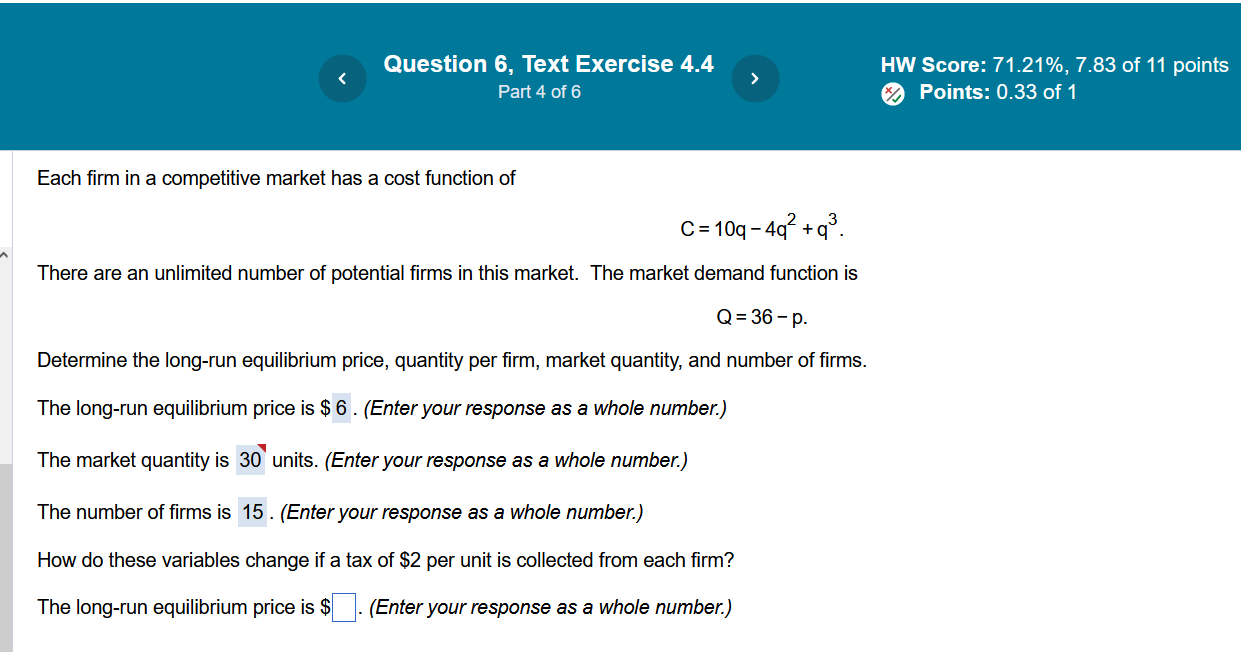
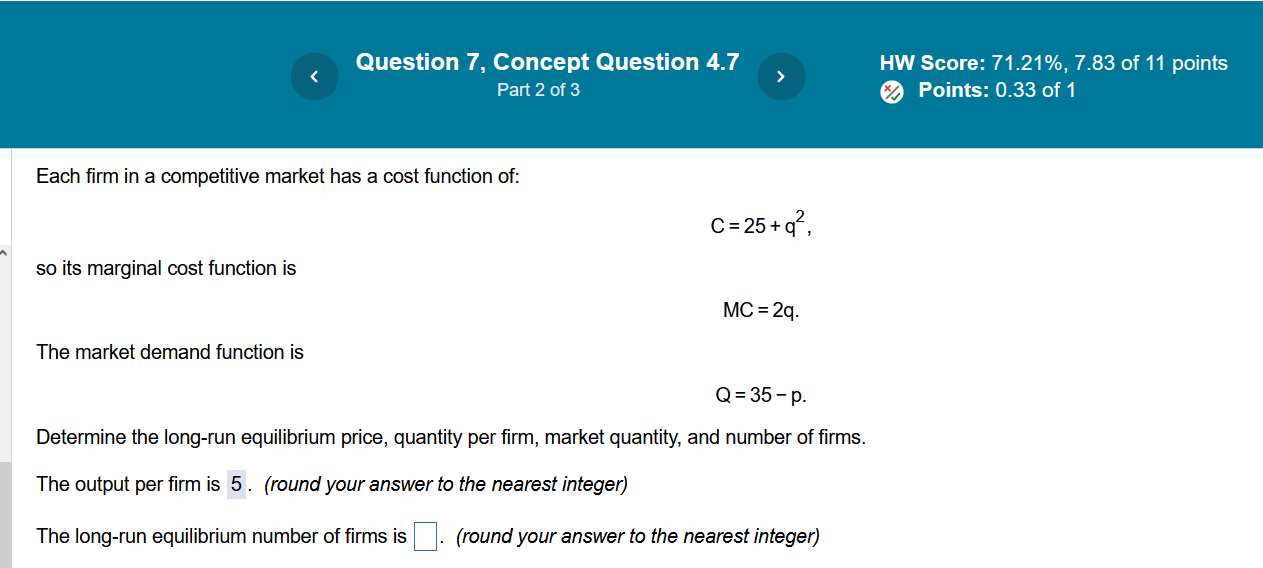
Question 6, Text Exercise 4.4 5 HW Score: 71.21%, 7.83 of 11 points Part 4 of 6 [/ ML E R Rl i Each firm in a competitive market has a cost function of C=10q-4q +q. There are an unlimited number of potential firms in this market. The market demand function is Q=36-p. Determine the long-run equilibrium price, quantity per firm, market quantity, and number of firms. The long-run equilibrium price is $ 6 . (Enter your response as a whole number.) The market quantity is 30' units. (Enter your response as a whole number.) The number of firms is 15 . (Enter your response as a whole number.) How do these variables change if a tax of $2 per unit is collected from each firm? The long-run equilibrium price is $| |. (Enter your response as a whole number.) Question 7, Concept Question 4.7 N HW Score: 71.21%, 7.83 of 11 points Part 2 of 3 Points: 0.33 of 1 Each firm in a competitive market has a cost function of: C=25+, i so its marginal cost function is MC=2q. The market demand function is Q=35-p. Determine the long-run equilibrium price, quantity per firm, market quantity, and number of firms. The output per firmis 5. (round your answer to the nearest integer) The long-run equilibrium number of firms is | |. (round your answer to the nearest integer)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


