Question: Question about Haskell. All solutions must be in Haskell. Exercise 2. Graphs A simple way to represent a directed graph is through a list of
Question about Haskell. All solutions must be in Haskell.
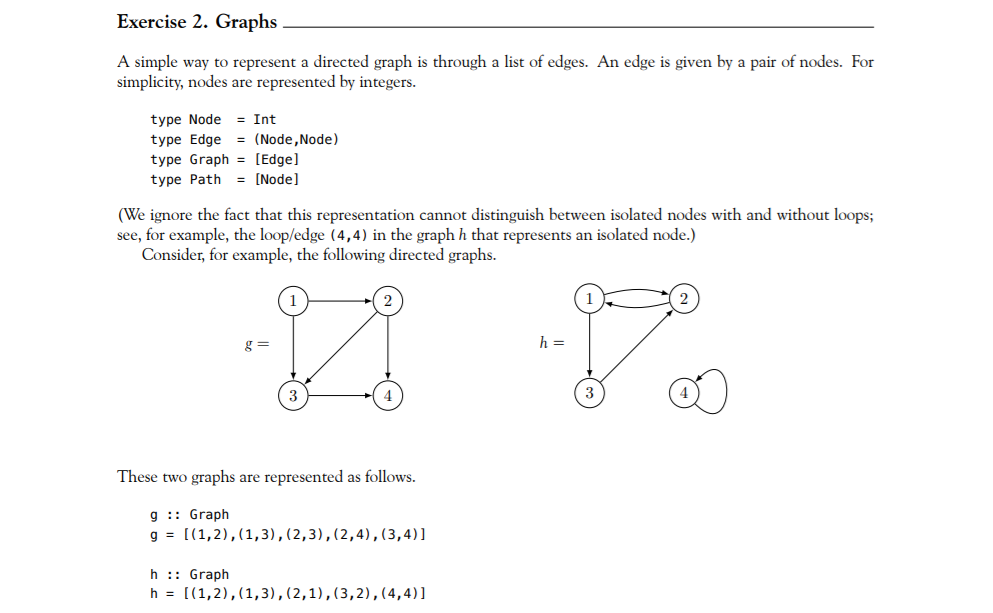
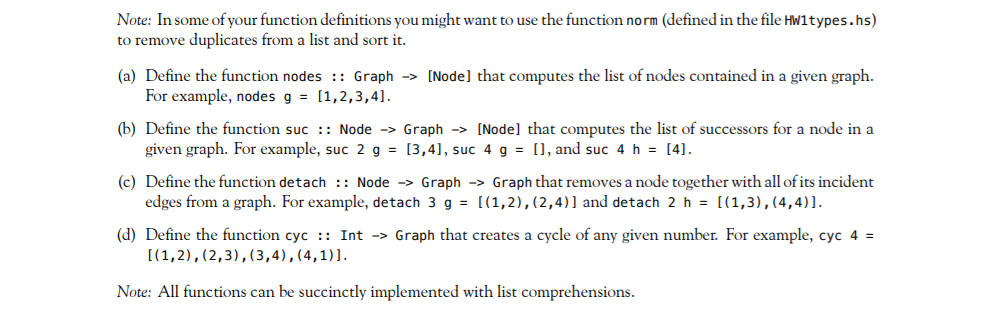
Exercise 2. Graphs A simple way to represent a directed graph is through a list of edges. An edge is given by a pair of nodes. For simplicity, nodes are represented by integers. type Node = Int type Edge = (Node, Node) type Graph = [Edge] type Path = (Node] (We ignore the fact that this representation cannot distinguish between isolated nodes with and without loops; see, for example, the loop/edge (4,4) in the graph h that represents an isolated node.) Consider, for example, the following directed graphs. V h = 3 3 These two graphs are represented as follows. 9 :: Graph g = [(1,2), (1,3), (2,3), (2,4),(3,4)] h :: Graph h = [(1,2),(1,3), (2,1),(3,2), (4,4)] Note: In some of your function definitions you might want to use the function norm (defined in the file HW1types.hs) to remove duplicates from a list and sort it. (a) Define the function nodes :: Graph -> [Node) that computes the list of nodes contained in a given graph. For example, nodes g = [1,2,3,4]. (b) Define the function suc :: Node -> Graph > [Node) that computes the list of successors for a node in a given graph. For example, suc 2 g = [3,4], suc 4 g = [], and suc 4 h = [4]. (c) Define the function detach :: Node -> Graph -> Graph that removes a node together with all of its incident edges from a graph. For example, detach 3 g = [(1,2), (2,4)) and detach 2 h = [(1,3), (4,4)]. (d) Define the function cyc :: Int -> Graph that creates a cycle of any given number. For example, cyc 4 = [(1,2), (2,3), (3,4),(4,1)]. Note: All functions can be succinctly implemented with list comprehensions
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


