Question: Question Instructions: For the operation listed below, determine the time complexity of the operation, and choose from the selections provided. Make sure you choose the
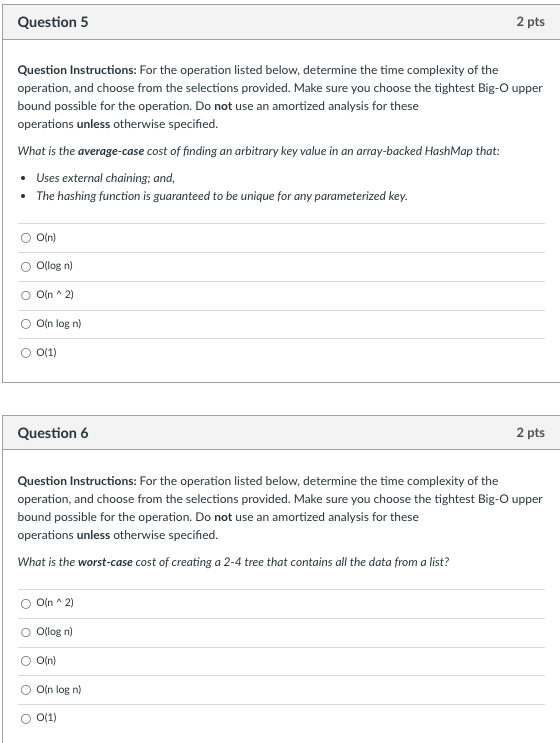
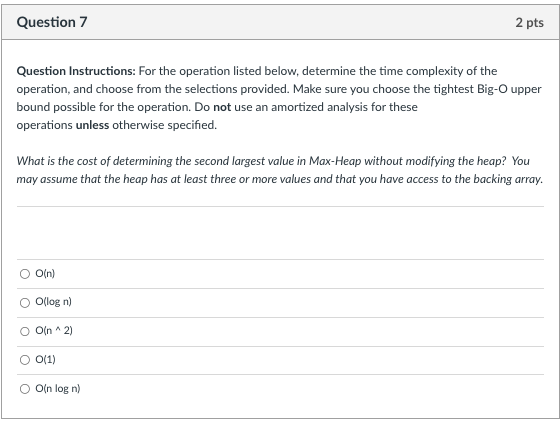
Question Instructions: For the operation listed below, determine the time complexity of the operation, and choose from the selections provided. Make sure you choose the tightest Big-O upper bound possible for the operation. Do not use an amortized analysis for these operations unless otherwise specified. What is the average-case cost of finding an arbitrary key value in an array-backed HashMap that: - Uses external chaining; and, - The hashing function is guaranteed to be unique for any parameterized key. \begin{tabular}{l} O(n) \\ \hlineO(logn) \\ \hlineO(n2) \\ \hlineO(nlogn) \\ O(1) \end{tabular} Question 6 2 pts Question Instructions: For the operation listed below, determine the time complexity of the operation, and choose from the selections provided. Make sure you choose the tightest Big-O upper bound possible for the operation. Do not use an amortized analysis for these operations unless otherwise specified. What is the worst-case cost of creating a 2-4 tree that contains all the data from a list? O(n2) O(logn) O(n) O(nlogn) O(1) Question Instructions: For the operation listed below, determine the time complexity of the operation, and choose from the selections provided. Make sure you choose the tightest Big-O upper bound possible for the operation. Do not use an amortized analysis for these operations unless otherwise specified. What is the cost of determining the second largest value in Max-Heap without modifying the heap? You may assume that the heap has at least three or more values and that you have access to the backing array. \begin{tabular}{l} O(n) \\ \hlineO(logn) \\ \hlineO(n2) \\ \hlineO(1) \\ \hlineO(nlogn) \end{tabular}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


