Question: Question list Question 15 Question 16 K This question: 6 point(s) possible Suppose the monthly charges for cell phone plans are normally distributed with
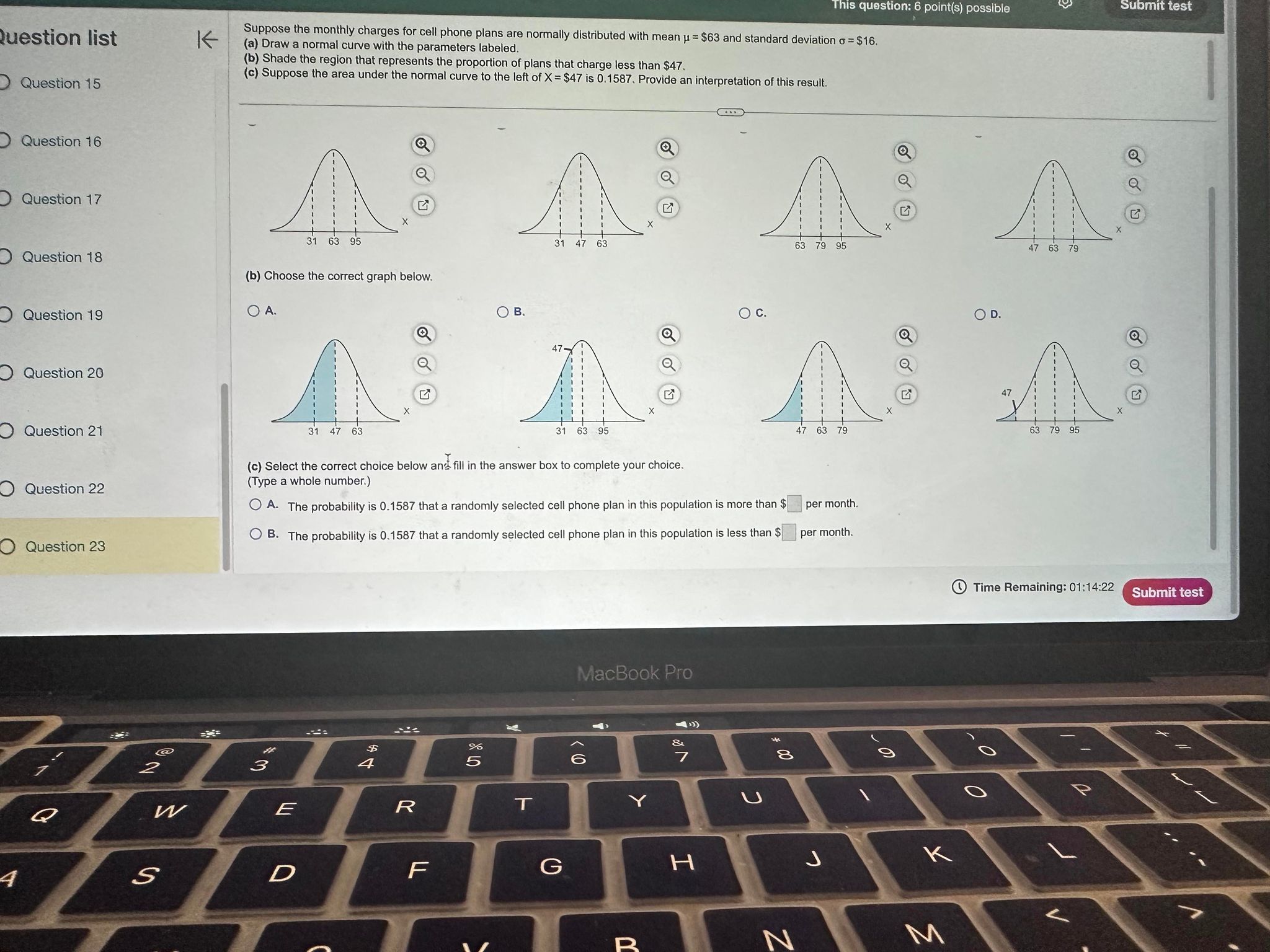
Question list Question 15 Question 16 K This question: 6 point(s) possible Suppose the monthly charges for cell phone plans are normally distributed with mean = $63 and standard deviation = $16. (a) Draw a normal curve with the parameters labeled. (b) Shade the region that represents the proportion of plans that charge less than $47. (c) Suppose the area under the normal curve to the left of X= $47 is 0.1587. Provide an interpretation of this result. C Submit test Question 17 Question 18 31 63 95 (b) Choose the correct graph below. O Question 19 A. Question 20 Question 21 O Question 22 O B. 31 47 63 Q C. 63 79 95 X { A D. 47 63 79 X Q N N N A 31 47 63 (c) Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box to complete your choice. (Type a whole number.) OA. The probability is 0.1587 that a randomly selected cell phone plan in this population is more than $ 47 63 79 per month. 47 63 79 95 Question 23 02 Q W B. The probability is 0.1587 that a randomly selected cell phone plan in this population is less than $ per month. #3 3 E $ 4 R % 5 T MacBook Pro Y & 7 4 S D F G H R C 8 00% J K N M Time Remaining: 01:14:22 Submit test a e 3 Test K Question 18 of 23 > This test: 100 point(s) possible This question: 6 point(s) possible Submit test According to an almanac, 60% of adult smokers started smoking before turning 18 years old. (a) If 300 adult smokers are randomly selected, how many would we expect to have started smoking before turning 18 years old? (b) Would it be unusual to observe 255 smokers who started smoking before turning 18 years old in a random sample of 300 adult smokers? Why? (a) We would expect about (Type a whole number.) adult smokers to have started smoking before turning 18 years old. (b) Would it be unusual to observe 255 smokers who started smoking before turning 18 years old in a random sample of 300 adult smokers? OA. Yes, because 255 is greater than +20. OB. Yes, because 255 is between -20 and + 20. OC. No, because 255 is less than - 20. OD. No, because 255 is between -2 and +20. E. No, because 255 is greater than +20. MacBook Pro Time Remaining: 01:13:41 Next Module 3 Test n list on 11 on 12 on 13 On 14 On 15 on 16 on 17 on 18 on 19 Find the probability P(E) if P(E) = 0.38. The probability P(E) is (Simplify your answer.) This test: 100 point(s) possible < Question 11 of 23 > This question: 2 point(s) possible MacBook Pro cin mung Time Remaining: 01:13:01 Submi 180 213 est: Module 3 Test stion list estion 15 estion 16 estion N 5.4.3 estion 18 estion 19 stion 20 stion 21 stion 22 stion 23 K < Question 17 of 23 > This test: 100 point(s) possible This question: 3 point(s) possible Suppose that E and F are two events and that P(E and F) = 0.1 and P(E) = 0.2. What is P(FIE)? P(FIE)=(Type an integer or a decimal.) MacBook Pro cin mung Submit tes Time Remaining: 01:13:36 Module 3 Test on list Eion 15 K Question 19 of 23 > This test: 100 point(s) possible This question: 8 point(s) possible Submit test A university conducted a survey of 382 undergraduate students regarding satisfaction with student government. Results of the survey are shown in the table by class rank. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. Click the icon to view the table. tion 16 tion 17 tion 18 tion 19 2.42 tion 20 stion 21 (a) If a survey participant is selected at random, what is the probability that he or she is satisfied with student government? P(satisfied) = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (b) If a survey participant is selected at random, what is the probability that he or she is a junior? P(junior) = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (c) If a survey participant is selected at random, what is the probability that he or she is satisfied and a junior? P(satisfied and junior) = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (d) If a survey participant is selected at random, what is the probability that he or she is satisfied or a junior? P(satisfied or junior) = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) stion 22 stion 23 2 #3 % 205 $ 4 MacBook Pro 66 87 & * 00 8 Time Remaining: 01:13:47 Next 0 Test K cin mung Question 20 of 23 > This test: 100 point(s) possible This question: 8 point(s) possible Submit test About 18% of the population of a large country is math phobic. If two people are randomly selected, what is the probability both are math phobic? What is the probability at least one is math phobic? Assume the events are independent. (a) The probability that both will be math phobic is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) (b) The probability that at least one person is math phobic is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) MacBook Pro Time Remaining: 01:13:55 Next
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


