Question: Question: So far in this course, we have gone through several examples illustrating the details of how significance testing works. These details included each of
Question:
So far in this course, we have gone through several examples illustrating the details of how significance testing works. These details included each of the following key points. Read through these key points and try to fill in the key terms that are missing. You may use some of the terms from page 345 more than once.
Use these terms:
Type I error?0?Statistical power
Type II error?Power?Central limit theorem
Null?Effect size?Significance test
Critical value?Research
The allows us to predict the center, shape, and spread of the distribution of sample means (or the distribution of sample mean differences) if the null is true.
State the theorem below.
The hypothesis precisely locates the center of the null distribution of sample means (or the null distribution of sample mean differences). This location is at a z value of or at t value of .
The center of the hypothesis distribution of sample means (or mean differences) is estimated from the sample mean (or sample mean difference) and cannot be known before data are collected.
The probability of a is set by researchers when they set the ? value.
By building the null and research hypothesis distributions of sample means (or sample mean differences), we can quantify the probability of failing to reject a false null (i.e., ), as well as the likelihood of rejecting a false null (i.e., ).
The of t or z "cuts" likely values if the null is true from unlikely values if the null is true; if a statistic (e.g., z value, t value) is more extreme than this value, the null hypothesis is unlikely to be true.
If the null is rejected, the hypothesis is considered likely to be true.
After a is performed, researchers know whether or not the null is likely to be true. They do not know how effective the IV was at affecting the DV. To quantify the impact of the IV on the DV, researchers must compute a/an .
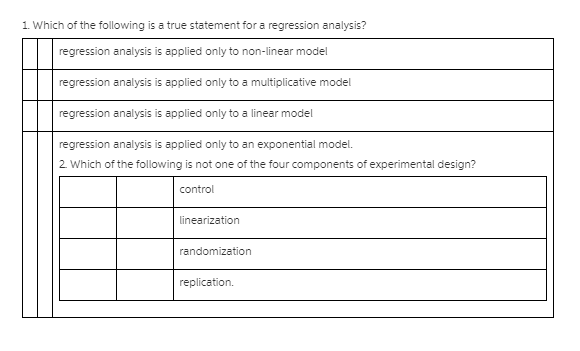
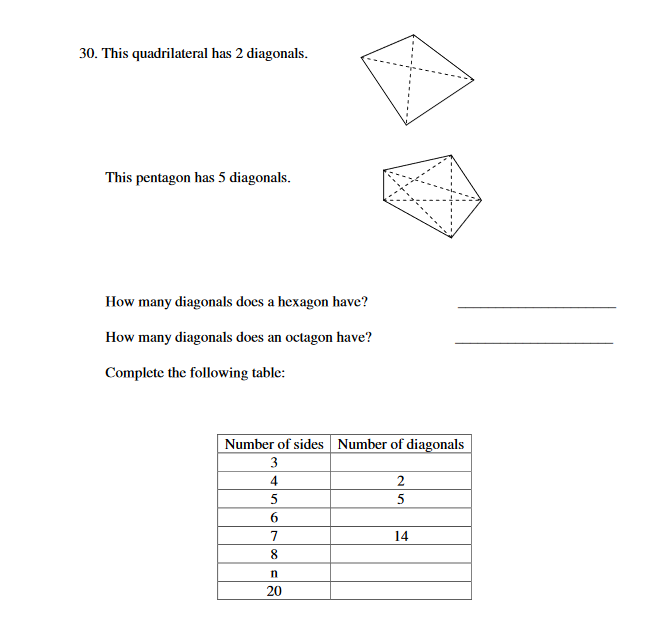
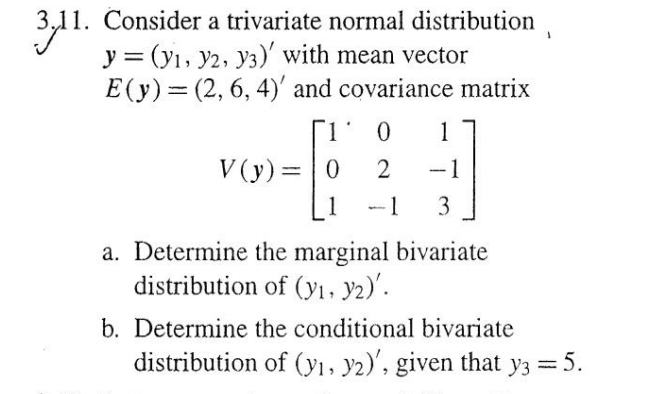

1. IWhich of the following is a true statement for a regression analysis? II regression analysis is applied only to non-linear model II regression analysis is applied only to a multiplicative model II regression analysis is applied only to a linear model -- replical: n. regression analysis is applied only to an exponential model. l Wh it h ofthe following is not one of the four corn ponenls of experimental design? -- 30. This quadrilateral has 2 diagonals. This pentagon has 5 diagonals. How many diagonals does a hexagon have? How many diagonals does an octagon have? Complete the following table: Number of sides |Number of diagonals 3 2 5 5 6 7 14 8 n 203.11. Consider a trivariate normal distribution y = ()1, y2, )3) with mean vector E(y) = (2, 6, 4)' and covariance matrix 1 D - V( y) = 0 2 -1 LI -1 3 a. Determine the marginal bivariate distribution of ()1, y2)'. b. Determine the conditional bivariate distribution of ()1, )2)', given that y3 = 5.Problem 2: Consider the following discrete bivariate distribution: (0.5(x+y) = = 1,2,... Px,Y(x, y) = y = 1, 2, ... otherwise . Calculate the probability of the event P(X - Y = 2). . Calculate the marginal PMF of X
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


