Question: quick answer Question No 3. (2.5+5 +2.5) Consider the following Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) with ten customers. Note that we assume that distances are symmetric.
quick answer 
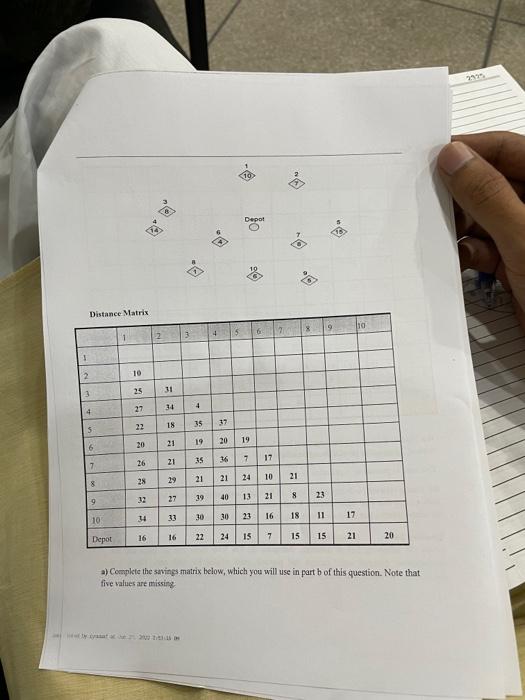
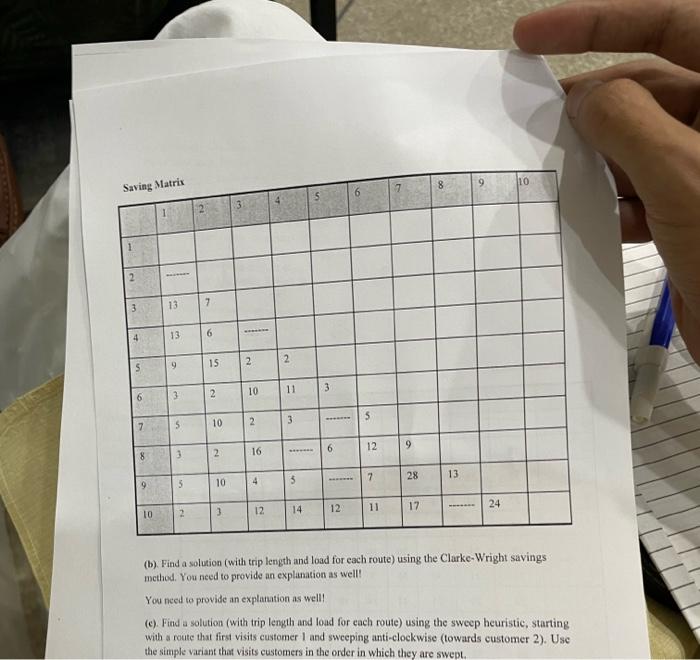
Question No 3. (2.5+5 +2.5) Consider the following Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) with ten customers. Note that we assume that distances are symmetric. That is, the distance from i to j and from j to i are equal for any i and j, which is why only the part of the distance matrix under the diagonal is given. Note that same graphic follows twice, as it may be useful in deriving your answers. Vehicle capacity: 45 by you at Jas 27, 2022 2:53:15 PM To Depot 10 8 5 15 1 2 Distance Matrix 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 105 Depot 10 25 27 22 20 26 2 28 32 34 16 -0 2 31 34 21 4 18 35 21 -A 29 27 33 16 B- 3 19 35 21 39 30 22 4 37 5 Depot 19 6 20 36 7 17 21 24 10 40 13 21 30 23 16 24 15 7 7 21 8 18 8 23 9 11 10 17 15 15 21 20 a) Complete the savings matrix below, which you will use in part b of this question. Note that five values are missing 2925 Saving Matrix 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ***** 13 13 9 3 5 3 5 2 7 6 15 2 10 2 10 3 2 10 2 16 4 12 T 2 11 3 ******* 5 14 3 6 12 6 5 12 7 11 9 28 17 8 13 9 24 10 (b). Find a solution (with trip length and load for each route) using the Clarke-Wright savings method. You need to provide an explanation as well! You need to provide an explanation as well! (e). Find a solution (with trip length and load for each route) using the sweep heuristic, starting with a route that first visits customer 1 and sweeping anti-clockwise (towards customer 2). Use the simple variant that visits customers in the order in which they are swept. Question No 3. (2.5+5 +2.5) Consider the following Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) with ten customers. Note that we assume that distances are symmetric. That is, the distance from i to j and from j to i are equal for any i and j, which is why only the part of the distance matrix under the diagonal is given. Note that same graphic follows twice, as it may be useful in deriving your answers. Vehicle capacity: 45 by you at Jas 27, 2022 2:53:15 PM To Depot 10 8 5 15 1 2 Distance Matrix 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 105 Depot 10 25 27 22 20 26 2 28 32 34 16 -0 2 31 34 21 4 18 35 21 -A 29 27 33 16 B- 3 19 35 21 39 30 22 4 37 5 Depot 19 6 20 36 7 17 21 24 10 40 13 21 30 23 16 24 15 7 7 21 8 18 8 23 9 11 10 17 15 15 21 20 a) Complete the savings matrix below, which you will use in part b of this question. Note that five values are missing 2925 Saving Matrix 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ***** 13 13 9 3 5 3 5 2 7 6 15 2 10 2 10 3 2 10 2 16 4 12 T 2 11 3 ******* 5 14 3 6 12 6 5 12 7 11 9 28 17 8 13 9 24 10 (b). Find a solution (with trip length and load for each route) using the Clarke-Wright savings method. You need to provide an explanation as well! You need to provide an explanation as well! (e). Find a solution (with trip length and load for each route) using the sweep heuristic, starting with a route that first visits customer 1 and sweeping anti-clockwise (towards customer 2). Use the simple variant that visits customers in the order in which they are swept 


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


