Question: (b) Consider the distance matrix in Table 1 for the following Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP). Where City 1 is the depot and rest of the

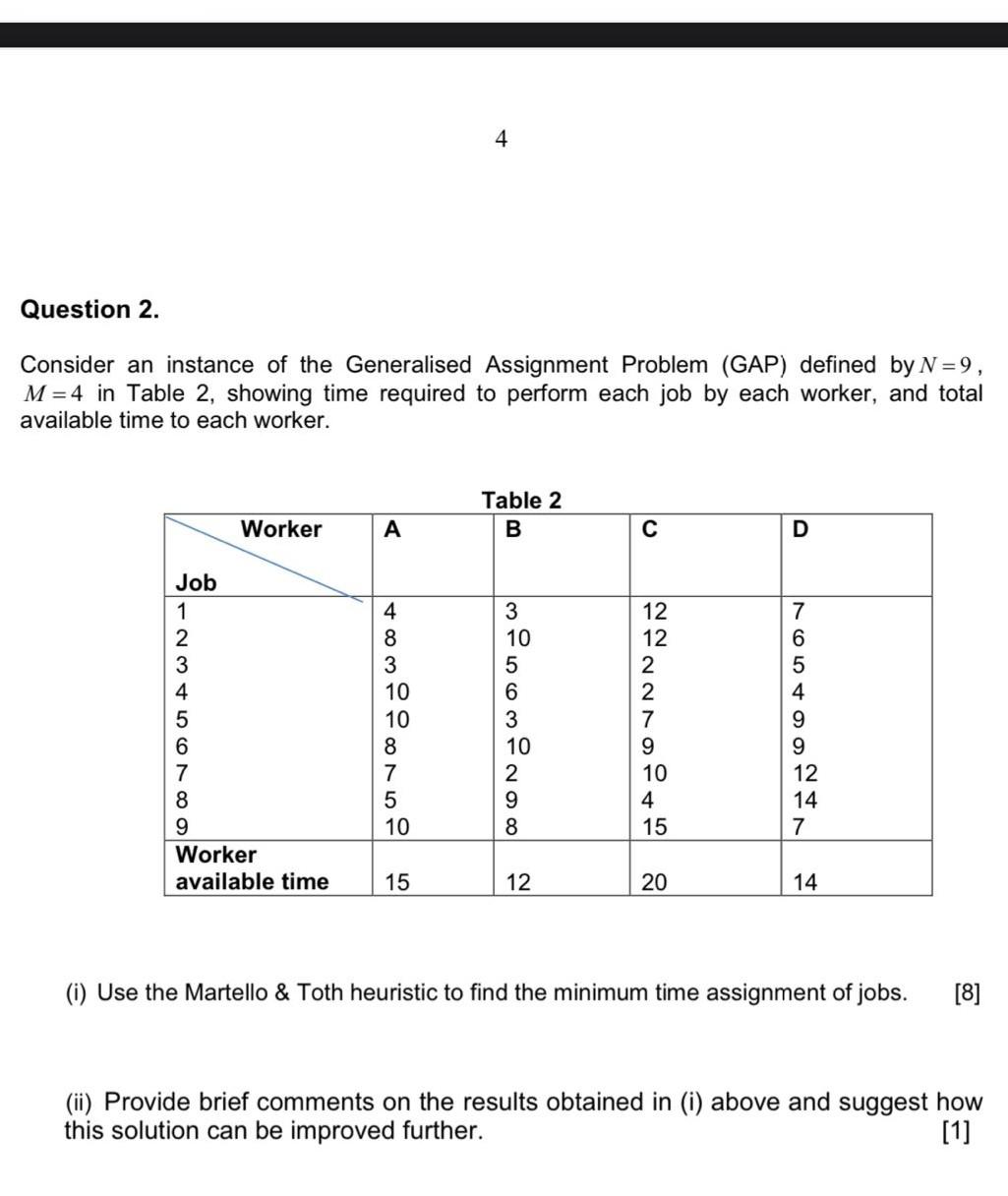
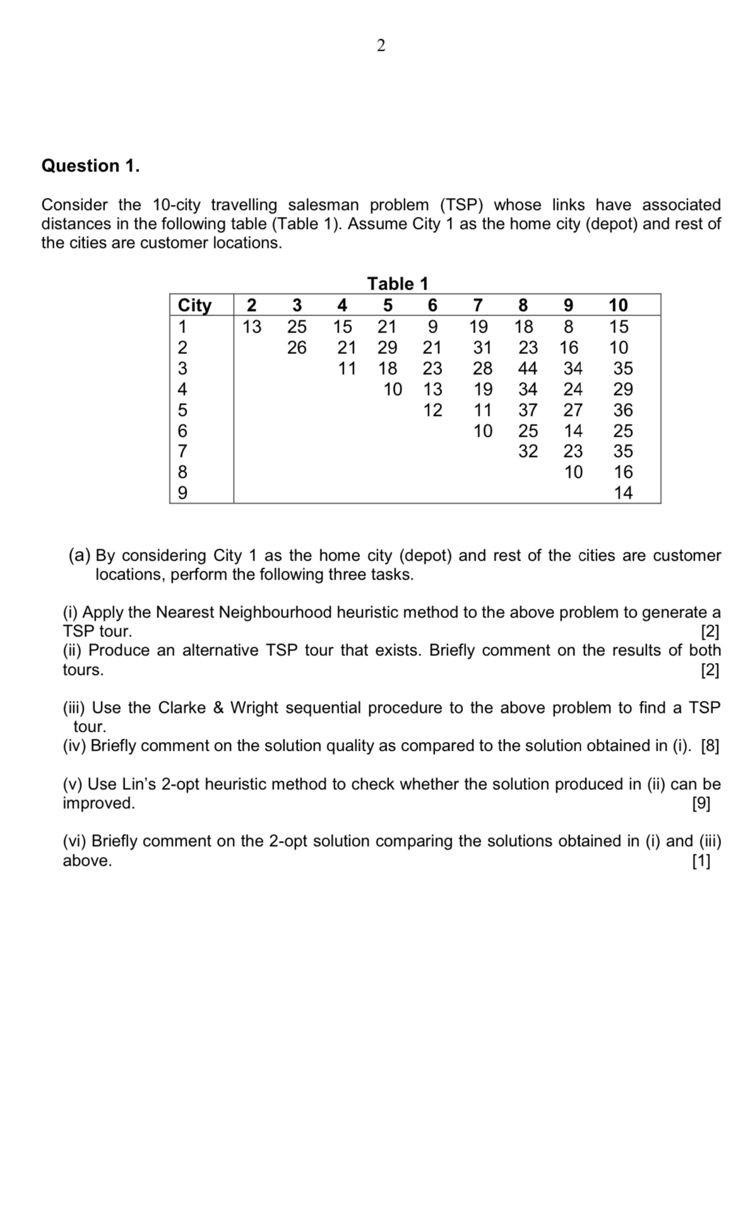
(b) Consider the distance matrix in Table 1 for the following Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP). Where City 1 is the depot and rest of the cities are customer locations with known demands. All vehicles leave and terminate at the depot. There are 2 lorries available, each with 50 -ton capacity. (Assume there are no restrictions on driver-time or the distance travelled by each vehicle.) Also consider the following customer demand information. (i) Solve the above VRP using the Clarke \& Write sequential method (you may use the list of savings found in (a)(iii)) to satisfy the customer demand at a minimum total distance travelled the lorries subject to the given constraints. List the sequences of customers in the routes and their distances. Calculate total distance travelled by the lorries. [5] (ii) By looking at the results obtained in (b)(i) briefly describe why the total distance travelled by two lorries is greater than the distance of the TSP tour produced by C\&W method. [1] (iii) Provide an example of a real-life VRP application that fits with the above scenario. Consider an instance of the Generalised Assignment Problem (GAP) defined by N=9, M=4 in Table 2 , showing time required to perform each job by each worker, and total available time to each worker. (i) Use the Martello \& Toth heuristic to find the minimum time assignment of jobs. [8] (ii) Provide brief comments on the results obtained in (i) above and suggest how this solution can be improved further. Question 1. Consider the 10-city travelling salesman problem (TSP) whose links have associated distances in the following table (Table 1). Assume City 1 as the home city (depot) and rest of the cities are customer locations. (a) By considering City 1 as the home city (depot) and rest of the cities are customer locations, perform the following three tasks. (i) Apply the Nearest Neighbourhood heuristic method to the above problem to generate a TSP tour. [2] (ii) Produce an alternative TSP tour that exists. Briefly comment on the results of both tours. [2] (iii) Use the Clarke \& Wright sequential procedure to the above problem to find a TSP tour. (iv) Briefly comment on the solution quality as compared to the solution obtained in (i). [8] (v) Use Lin's 2-opt heuristic method to check whether the solution produced in (ii) can be improved. (vi) Briefly comment on the 2-opt solution comparing the solutions obtained in (i) and (iii) above
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


