Question: Qustion can be found in pic Another way to develop beta for use in the CAPM is to unlever beta from a benchmark (a collection
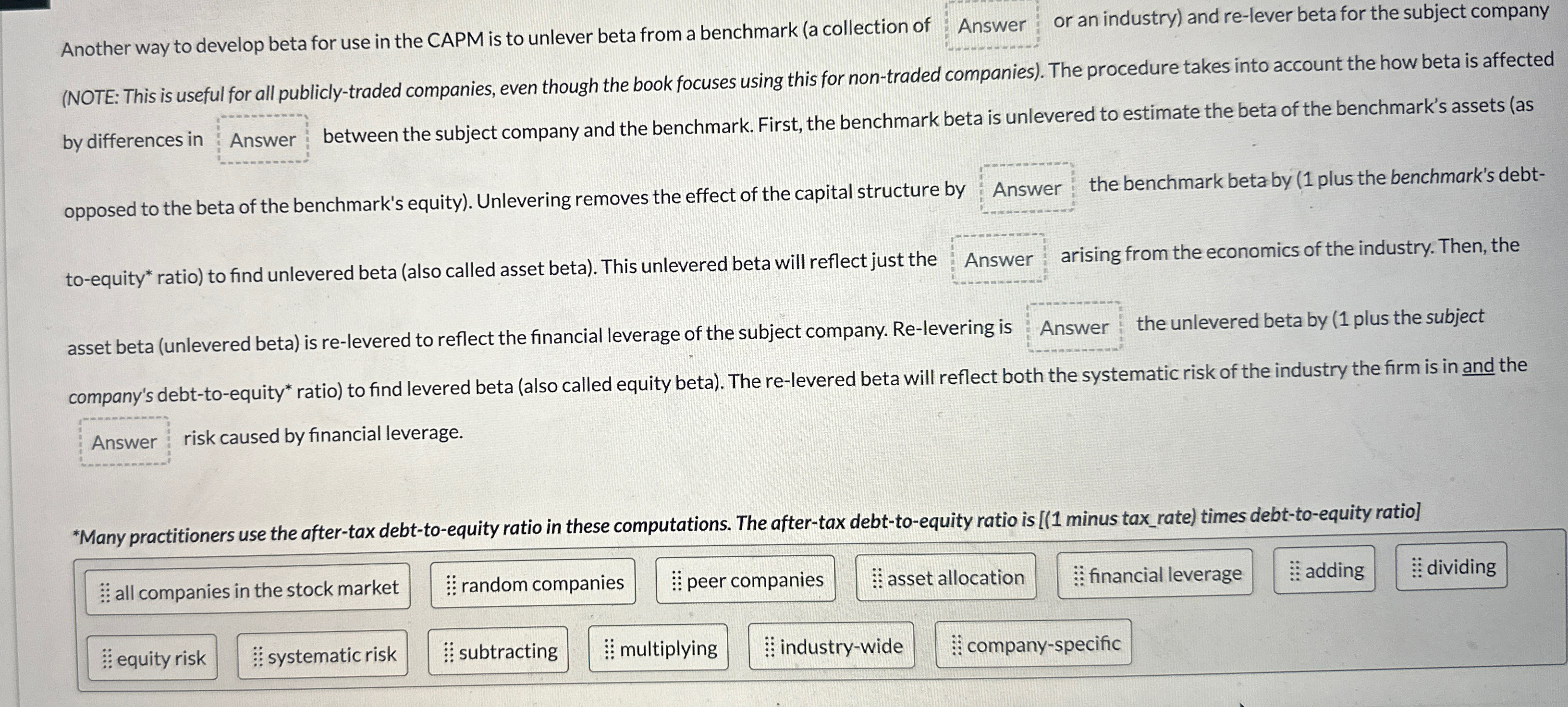
Another way to develop beta for use in the CAPM is to unlever beta from a benchmark (a collection of : Answer : or an industry) and re-lever beta for the subject company (NOTE: This is useful for all publicly-traded companies, even though the book focuses using this for non-traded companies). The procedure takes into account the how beta is affected by differences in : Answer between the subject company and the benchmark. First, the benchmark beta is unlevered to estimate the beta of the benchmark's assets (as opposed to the beta of the benchmark's equity). Unlevering removes the effect of the capital structure by : Answer the benchmark beta by (1 plus the benchmark's debt- to-equity* ratio) to find unlevered beta (also called asset beta). This unlevered beta will reflect just the : Answer : arising from the economics of the industry. Then, the asset beta (unlevered beta) is re-levered to reflect the financial leverage of the subject company. Re-levering is : Answer the unlevered beta by (1 plus the subject company's debt-to-equity* ratio) to find levered beta (also called equity beta). The re-levered beta will reflect both the systematic risk of the industry the firm is in and the risk caused by financial leverage. Answer *Many practitioners use the after-tax debt-to-equity ratio in these computations. The after-tax debt-to-equity ratio is [(1 minus tax_rate) times debt-to-equity ratio] all companies in the stock market random companies peer companies asset allocation financial leverage adding dividing equity risk systematic risk subtracting : multiplying industry-wide company-specific
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


