Question: // --------------------------------------------------------------- // RadixSort.java // --------------------------------------------------------------- import java.util.Scanner; /** Class RadixSort **/ public class RadixSort { /** Radix Sort function **/ public static void sort(

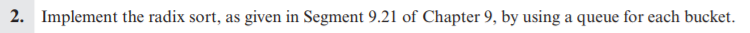
![void sort( int[] a ) { int i, m = a[0], exp](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f50aa877493_08066f50aa8271d6.jpg)
// --------------------------------------------------------------- // RadixSort.java // ---------------------------------------------------------------
import java.util.Scanner;
/** Class RadixSort **/ public class RadixSort { /** Radix Sort function **/ public static void sort( int[] a ) { int i, m = a[0], exp = 1, n = a.length; int[] b = new int[10];
for ( i = 1; i m ) { m = a[i]; } }
while (m / exp > 0) { int[] bucket = new int[10];
for ( i = 0; i
for ( i = 1; i
for ( i = n - 1; i >= 0; i-- ) b[--bucket[(a[i] / exp) % 10]] = a[i];
for ( i = 0; i
exp *= 10; } } /** Main method **/ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner scan = new Scanner( System.in ); System.out.println( "Radix Sort Test " ); int n, i; /** Accept number of elements **/ System.out.println("Enter number of integer elements"); n = scan.nextInt();
/** Create integer array on n elements **/ int arr[] = new int[ n ];
/** Accept elements **/ System.out.println(" Enter "+ n +" integer elements"); for (i = 0; i
/** Call method sort **/ sort(arr);
/** Print sorted Array **/ System.out.println(" Elements after sorting "); for (i = 0; i Pseudocode for Radix Sort 9.21 Our previous description of radix sort assumed that the integers to be sorted each contain the same number of digits. Actually, this requirement is unnecessary as long as you get 0 when you ask for a digit that does not exist. For example, if you ask for the hundreds digit of a two-digit integer, you should get 0. The following algorithm describes a radix sort of an array of positive decimal integers. We number the digits in each integer from the right beginning at 0. Thus, the units digit is digit 0, the tens digit is digit 1, and so on 286 CHAPTER 9 Faster Sorting Methods Algorithm radixSort (a, first, last, maxDigits) // Sorts the array of positive decimal integers a[first..1 ast] nto ascending onder //maxDigits is the number of digits in the longest integer for (i = OtomaxD gits - 1) Clear bucket[0], bucket[1],..., bucket[9] for (index-first to last) digit - digiti of a[index] Place a[index] at end of bucket [digit] Place contents of bucket[0], bucket[1] bucket[9] into the array a This algorithm uses an array of buckets. The nature of a bucket is unspecified, but after you read Chapter 10, you will see that a bucket can be an instance of the ADT queue
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


