Question: Reaction and diffusion in a planar catalyst layer. In class, we solved the problem on the diffusion of reactant A into a porous spherical catalyst
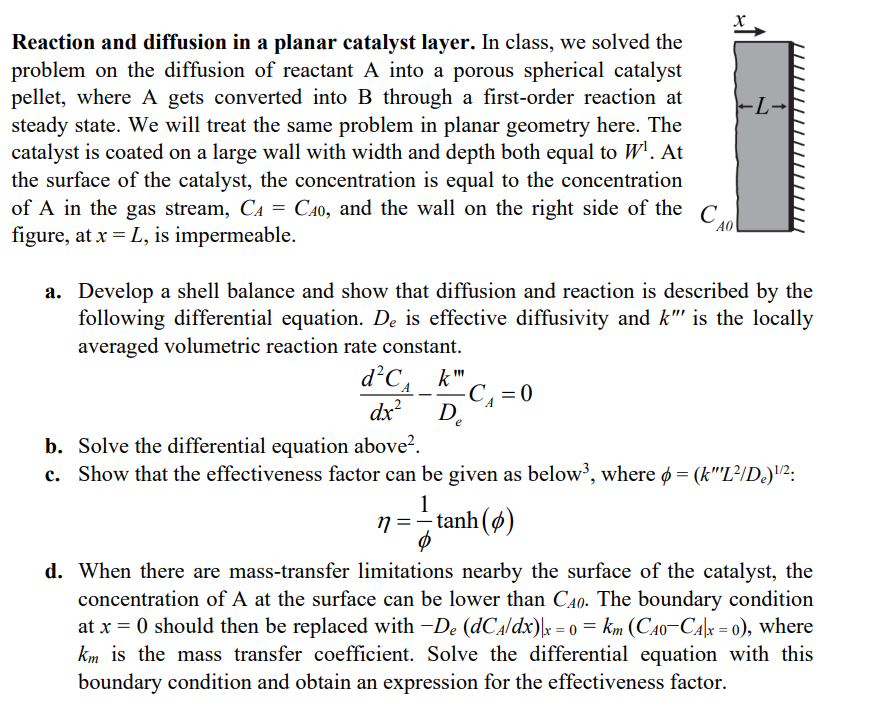
Reaction and diffusion in a planar catalyst layer. In class, we solved the problem on the diffusion of reactant A into a porous spherical catalyst pellet, where A gets converted into B through a first-order reaction at steady state. We will treat the same problem in planar geometry here. The catalyst is coated on a large wall with width and depth both equal to W1. At the surface of the catalyst, the concentration is equal to the concentration of A in the gas stream, CA=CA0, and the wall on the right side of the figure, at x=L, is impermeable. a. Develop a shell balance and show that diffusion and reaction is described by the following differential equation. De is effective diffusivity and k is the locally averaged volumetric reaction rate constant. dx2d2CADekCA=0 b. Solve the differential equation above 2. c. Show that the effectiveness factor can be given as below 3, where =(kL2/De)1/2 : =1tanh() d. When there are mass-transfer limitations nearby the surface of the catalyst, the concentration of A at the surface can be lower than CA0. The boundary condition at x=0 should then be replaced with De(dCA/dx)x=0=km(CA0CAx=0), where km is the mass transfer coefficient. Solve the differential equation with this boundary condition and obtain an expression for the effectiveness factor
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


