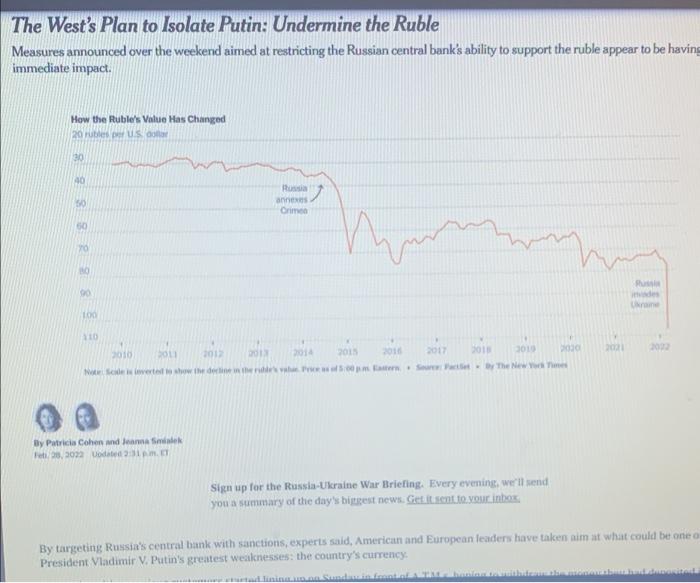
Question: - Read the quotes from to the article: At the heart of the move to restrict the Bank of Russia are its foreign exchange reserves.
- Read the quotes from to the article: "At the heart of the move to restrict the Bank of Russia are its foreign exchange reserves. These are the vast haul of convertible assets other nations' currencies and gold that Russia has built up, financed in large part through the money it earns selling oil and gas to Europe and other energy importers." "As Mr. Bernstam explained, the Bank of Russia has roughly $640 billion in foreign exchange reserves on paper or rather as electronic entries. But a big chunk of that money is not in Russian vaults or financial institutions. Rather, it is held by central and commercial banks in New York, London, Berlin, Paris, Tokyo and elsewhere around the world." - - "Yet the central bank has just about $12 billion of cash in hand an astonishingly small amount, he said. As for the rest of Russia's foreign exchange reserves, roughly $400 billion is invested in assets held outside the country. Another $84 billion is invested in Chinese bonds, and $139 billion is in gold. Question: Why the central bank of Russia has held currencies of other countries (foreign exchanges) and gold, instead of rubles, their own currency? Justify your answer by providing principles, theories and concepts from our lecture slides and the textbook (chapter 1). 2. (50 points) Read the quotes from to the article: * The Bank of Russia took steps on Monday to restore confidence, and more than doubled interest rates to 20 percent from 9.5 percent in order to offset the rapid depreciation of the ruble! ***If the ruble collapses, it could usher in severe inflation and exacerbate a brewing recession, Robert Person, an associate professor of international relations at the United States Military Academy, said, noting that his views were his own and not those of the government or military Question: Does the rapid depreciation of the ruble can cause severe inflation in Russia? Why or why not? Justify your answer by providing principles, theories and concepts from our lecture slides and the textbook (chapter 1). a The West's Plan to Isolate Putin: Undermine the Ruble Measures announced over the weekend aimed at restricting the Russian central bank's ability to support the ruble appear to be having immediate impact. How the Ruble's Value Has Changed 20 ruble USB 20 40 50 RO ann Crime 50 num TO 10 2012 202 2002 2010 2011 2012 2013 2011 2011 3010 Na de werel show the declinedThe New By Patricia Cohen und dann mit Heti 25,3022 Dodate : LT Sign up for the Russia-Ukraine War Briefing. Every evening, we'll send you a summary of the day's biggest news. Get itsent to your inbox By targeting Russia's central bank with sanctions, experts said, American and European leaders have taken aim at what could be one o President Vladimir V. Putin's greatest weaknesses: the country's currency The headquarters of the Bank of Russia, the country's central bank, in Moscow, Andrey Radakow/Bombers The crux of why the Western allies have such leverage comes down to a reality of the modern financial system: Although Russia's central bank owns the assets, it doesn't control them. As Mr. Bernstam explained, the Bank of Russia has roughly $640 billion in foreign exchange reserves on paper - or rather as electronic entries. But a big chunk of that money is not in Russian vaults or financial institutions. Rather, it is held by central and commercial banks in New York, London, Berlin, Paris, Tokyo and elsewhere around the world. In countries like Russia, where the currency is not so stable, the ability to convert to a strong and trusted one like the collar or the euro is crucial. It is evidence that the home currency - in this ease the Russian ruble -- has value Russia's vast store of foreign exchange backs up that value. It assures households and businesses that they can convert their rubles whenever they want, and makes sure that the nation can protect its exchange rate with other currencies. The reserves also lubricate the day-to-day transactions of Russian businesses that export and import But once workers, managers, owners and financiers worry that they can't trade their rubles for dollars or euros ---because banks don't have access to their foreign exchange reserves - they lose confidence It is a point that Lenin himself reportedly made more than a century ago, which was repeated by the economist John Maynard Keynes: "There is no subtler, no surer means of overturning the existing basis of society than to debouch the currency." The Bank of Russia can try to prop up the value of the ruble by using its reserves to buy up rubles that people are selline. But it can do that only as long as it has access to foreign reserves. A natural gas compressor station in Ust-Luka, Russia. Much of Russia's financial reserves are from the money it earns selling oil and gas to Europe and other enery importers, Andrey Radallioomberg The question is how long it can make those transactions. According to Mr. Bernstam's calculations, Russian individuals and companies have deposited $268 billion in foreign denominations in Russian banks. Russia's Attack on Ukraine and the Global Economy A rising concern. Russia's attack on Ukraine could cause dizzying spikes in prices for energy and food and could spook investors. The economic damage trom supply disruptions and economic sanctions would be severe in some countries and industries and unnoticed in others. Yet the central bank has just about $12 billion of cash in hand - an nstonishingly small amount, he said. As for the rest of Russia's foreign exchange reserves, rouphly $400 billion is invested in assets held outside the country. Another $84 billion is invested in Chinese bonds, and $139 billion is in gold. The central bank could trade in some of those bonds for renminbi, which would enable it to buy goods from China but not from other countries. It could also sell gold, although Mr. Bernstam argues that there will be few buyers for the tons that Russia has on hand, Other estimates put the amount of assets held outside Russia at closer to $300 billion. The potentially dire consequences for the economy are the same -If the ruble collapses, it could usher in severe inflation and exacerbate a brewing recession," Robert Person, an associate professor of international relations at the United States Military Academy, said, noting that his views were his own and not those of the government or military "The economic consequences of these measures could turn out to be far more severe than other measures that have gotten more attention in the media" he added. "This gets at the Russian government's basic tools to manage its macroeconomy." www.mes.com/2003/6/2cwrw accel-brunnbichim 11 Themed Sesund and its alles previously imposed similar sanctions on Venezuela, Iran and Syria, but they all have much smaller The mass on Monday to restore confidence, and more than doubled interest rates to 20 percent from 9.5 percent in er det the depreciation of the rule. The bank also released an additional S7 billion worth of reserves that had been set aside conform coed down the Moscow stock exchange for the day. Meanwhile, the foreign ministry moved to order companies percent of the foren currencies in a bid to pin up demand for rules and prevent them from stockpiling dollars and euros Mbwarned that the West attack on the Russian ruble needed to be handled with care. "We don't want to destroy them," he the political system to collapse Arred article mistated how far the value of the ruble had fallen versus the dollar. At point Monday a ruble was worthless in London. Since the 2007 she has written about thestar, books and see the other