Question: Recall that self clocking is the process by which a TCP sender uses acknowledgments from the receiver to trigger transmissions. Why is self-clocking important? Check
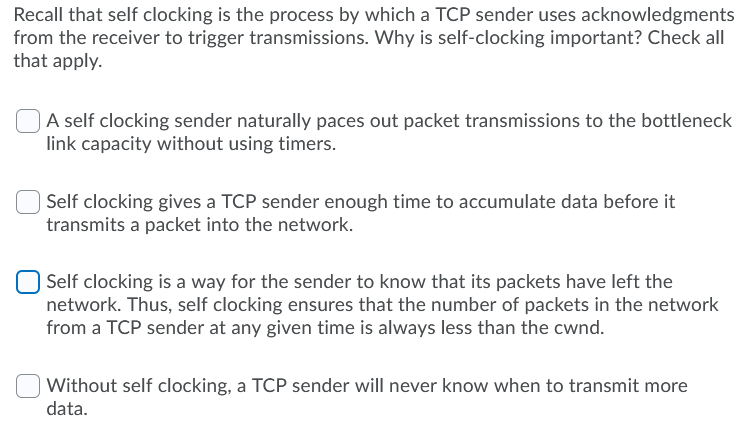
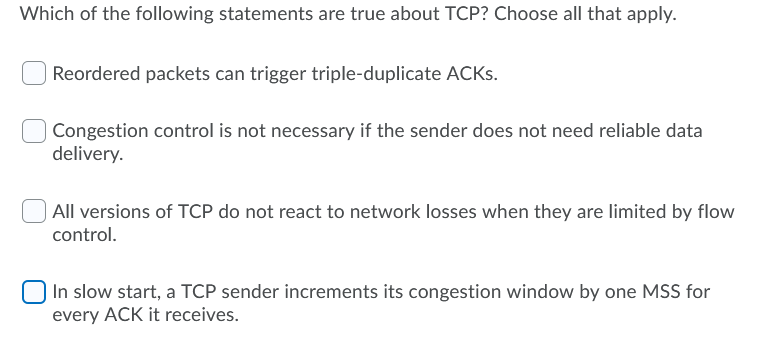


Recall that self clocking is the process by which a TCP sender uses acknowledgments from the receiver to trigger transmissions. Why is self-clocking important? Check all that apply. A self clocking sender naturally paces out packet transmissions to the bottleneck link capacity without using timers. Self clocking gives a TCP sender enough time to accumulate data before it transmits a packet into the network. Self clocking is a way for the sender to know that its packets have left the network. Thus, self clocking ensures that the number of packets in the network from a TCP sender at any given time is always less than the cwnd. Without self clocking, a TCP sender will never know when to transmit more data. Which of the following statements are true about TCP? Choose all that apply. Reordered packets can trigger triple-duplicate ACKs. Congestion control is not necessary if the sender does not need reliable data delivery. All versions of TCP do not react to network losses when they are limited by flow control. In slow start, a TCP sender increments its congestion window by one MSS for every ACK it receives. Which of the following statements are true about AIMD and sliding windows? Choose all that apply. TCP already used the sliding window protocol to manage retransmissions and flow control, and provided a convenient way to add AIMD-based congestion control. In the congestion avoidance phase, every time a complete window of packets is successfully acknowledged, the congestion window is increased by one. AIMD avoids congestion collapse by never varying the window size. In the congestion avoidance phase, every time a packet is successfully acknowledged, the congestion window is increased by one. Assume the network supports a sender up to a window of 25 packets, after which it starts dropping packets. If congestion window is updated in integer increments every round, how many rounds does a new TCP Tahoe flow remain in slow start before its congestion window reaches 25 packets, starting from an initial window of 1 packet? A
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


