Question: Recommender question: We are given a recommender problem with users{1,...,} anditems{1,...,}. We will use the labels{1,1} to represent the target rating (dislikes,likes). Each user is
Recommender question:
We are given a recommender problem with users{1,...,} anditems{1,...,}. We will use the labels{1,1} to represent the target rating (dislikes,likes). Each user is likely to provide feedback for only a small subset of possible items, and hence we must constrain the models so as not to overfit. Our goal in this problem is to understand how a simple neural network model applies to this problem, and what the constraints of the model are.
Schematic representation of the simple neural network model
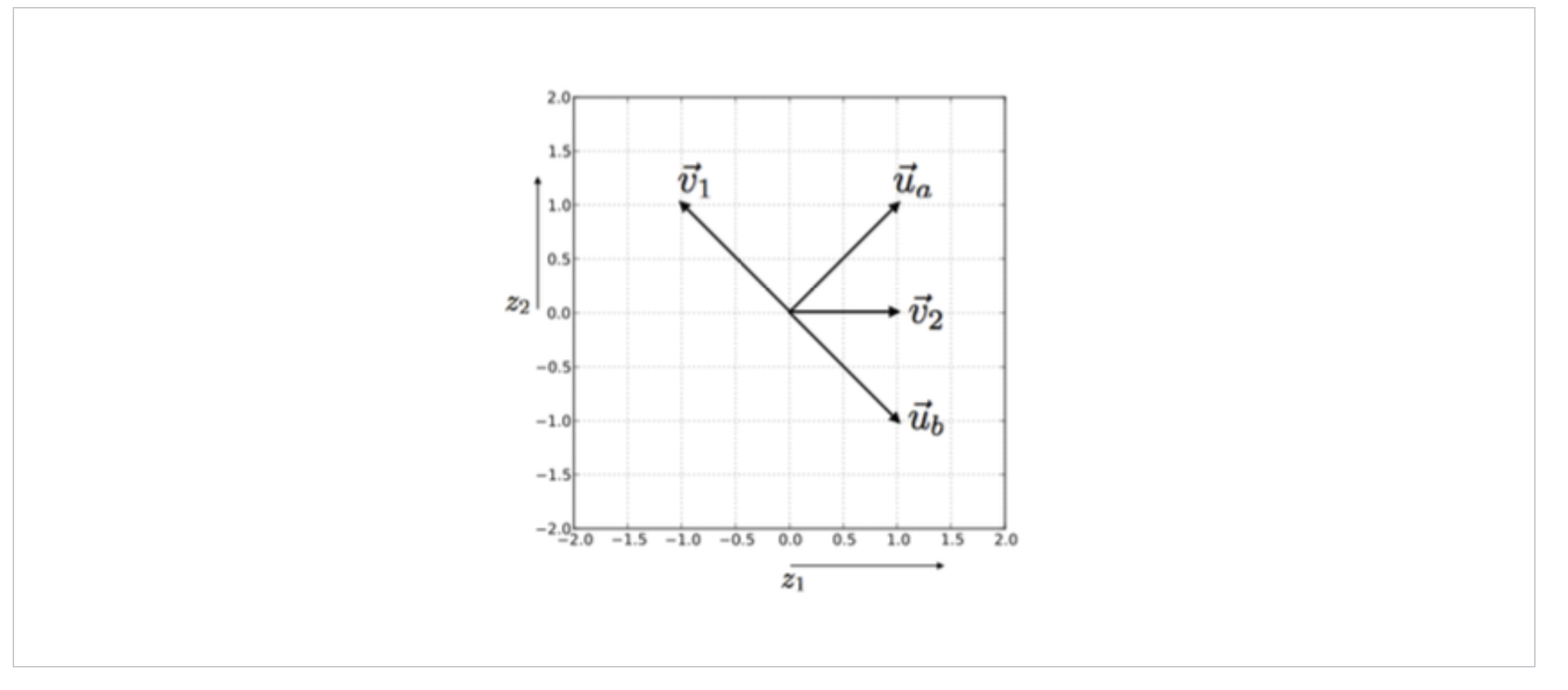
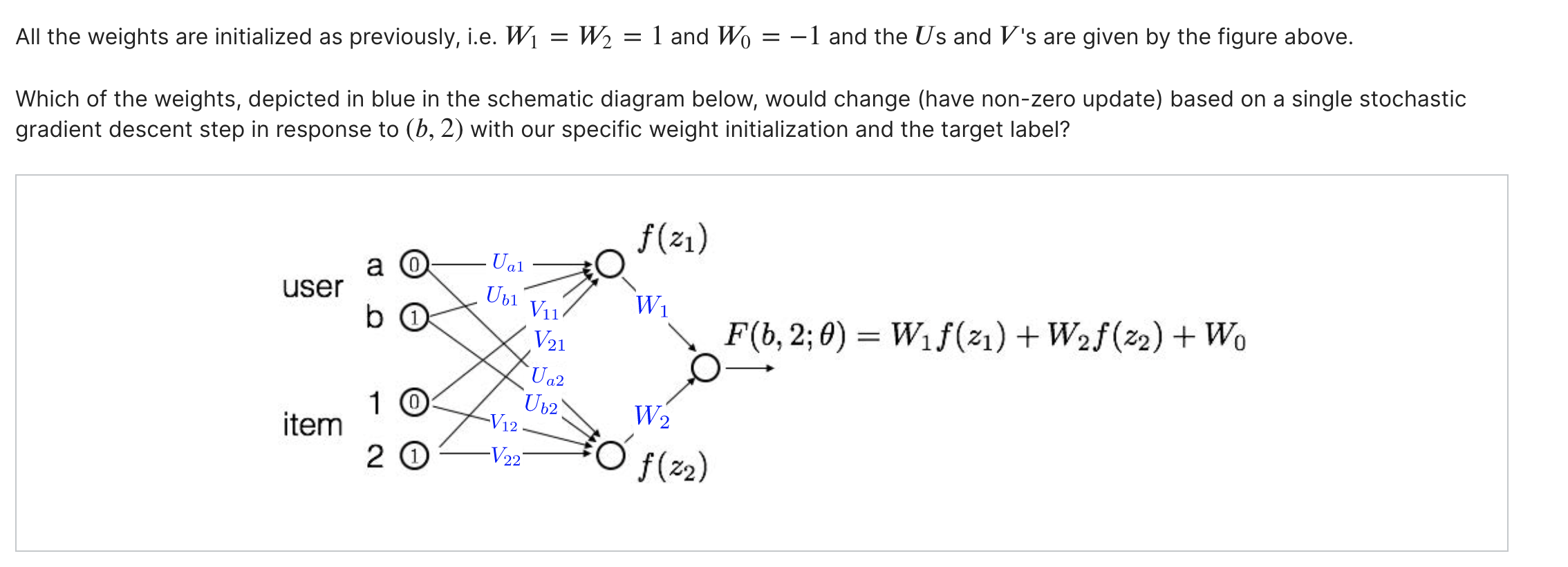
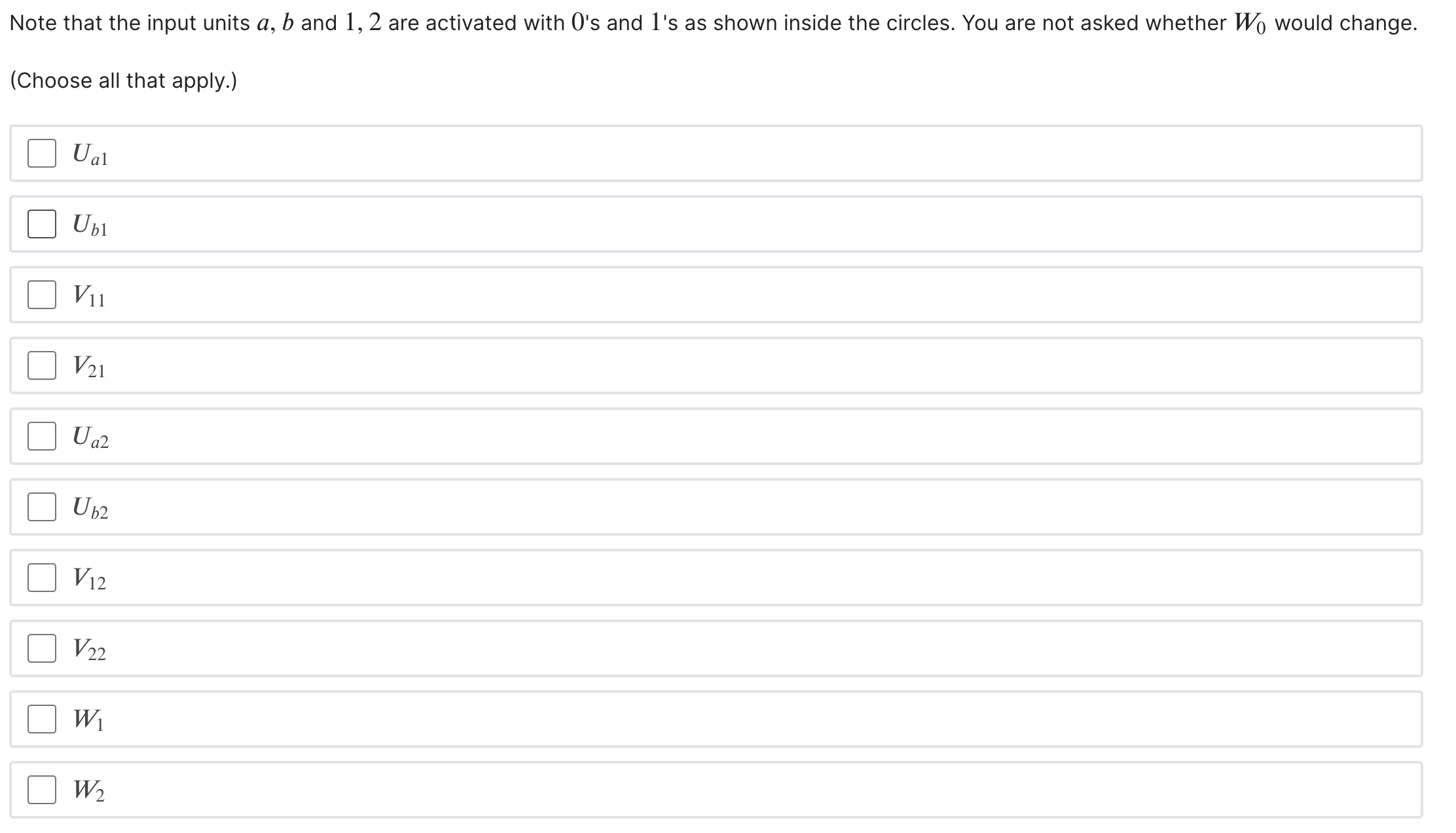
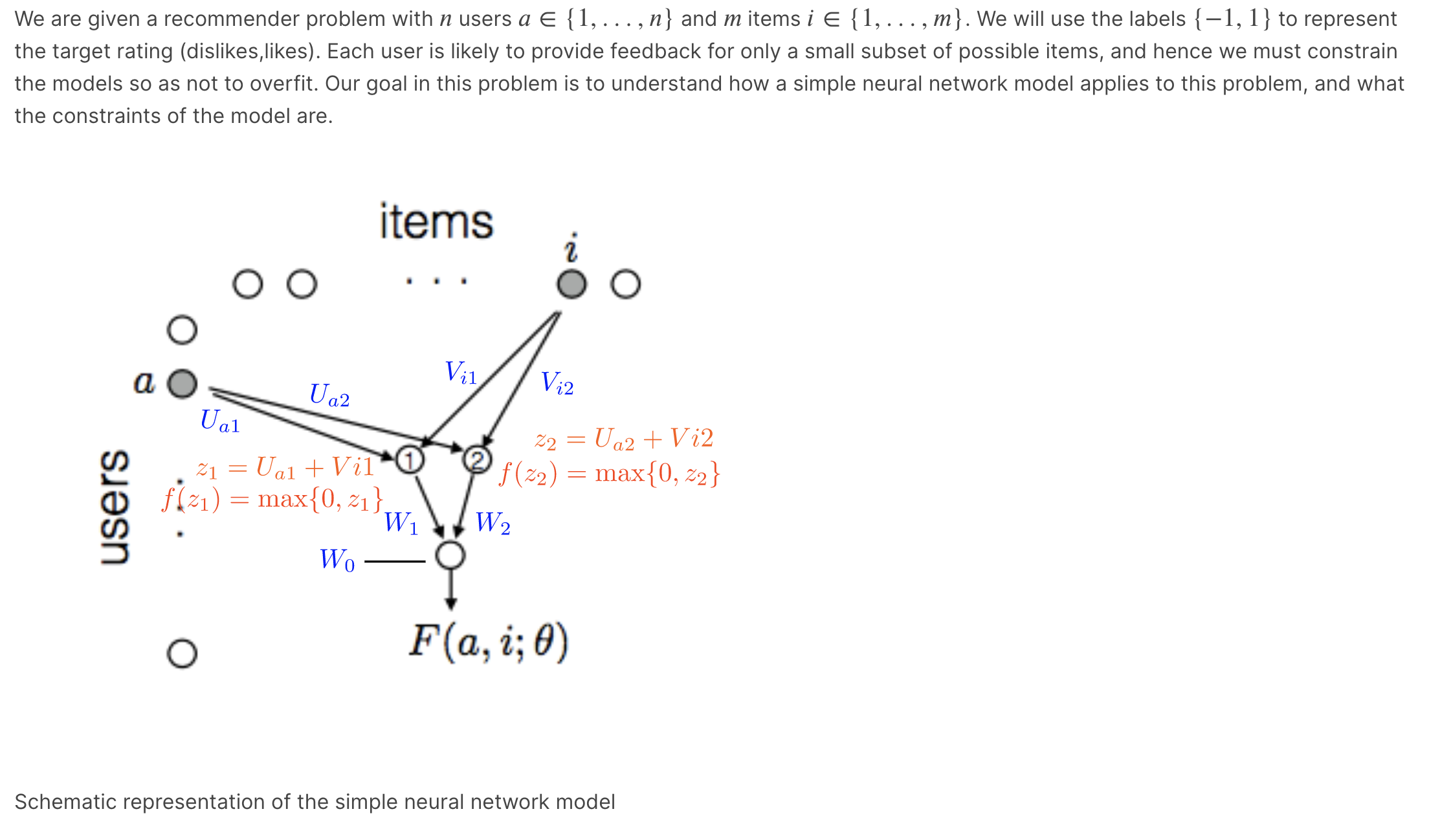

\fAll the weights are initialized as previously, i.e. VVl = IV; = 1 and VVO = 1 and the Us and V's are given by the figure above. Which of the weights, depicted in blue in the schematic diagram below, would change (have non-zero update) based on a single stochastic gradient descent step in response to (b, 2) with our specific weight initialization and the target label? \"21) W1 \\ F(b,2; 9) = W1f(21) + WEI-(22) + W0 Note that the input units a, b and 1, 2 are activated with O's and I's as shown inside the circles. You are not asked whether Wo would change. (Choose all that apply.) Ual Ubl V21 U a2 Ub2 V12 V 22 W1 W2We are given a recommender problem with n users a E {1, . . . , n} and m items 1' E {1, . . . , m}. We will use the labels {1, 1} to represent the target rating (dislikes,likes). Each user is likely to provide feedback for only a small subset of possible items, and hence we must constrain the models so as not to overfit. Our goal in this problem is to understand how a simple neural network model applies to this problem, and what the constraints of the model are. Uaz + V12 max{07 2'2} users Schematic representation of the simple neural network model Input Units Consider the simple neural network with 1 hidden layer depicted in the figure above. We use an input unit for each user (the nodes in the left column) and for each item (the nodes in the top row); so in total, there are n + m input units. When making prediction for a selected entry (a, i), only the ath user input unit and ith item input unit are active (i.e. set to the value 1); all other inputs are set to 0 and will not affect the predictions. In other words, only the outgoing weights from these two units matter for predicting the label (1 or 1) for entry (0, i). Hidden Units User a has two outgoing weights, Ual and U02 , and item i has two outgoing weights, Vil and Viz . These weights are fed as inputs to the two hidden units in the model. The hidden units evaluate z1 = Ua1+Vi1, f(Z1) = maX{0,Zl} z2 = Ua2+Viz, f(Zz) = max{0,zz}. Output Thus, for the (a, i) entry, our network outputs 1701,1119) = W1f(Z1)+VV2f(Zz) +VV0 where 0 denotes all the weights U, V, and W. Finally, a sign function is applied to F (a, i; 0) for the classification. In vector notation, each user a has a twodimensional vector of outgoing weights 3,, = [Ugh Ua2]T, and similarly each item 1' has a two > dimensional vector of outgoing weights U i = [Vib Viz]T . The input received by the hidden units is represented as the vector ) T > ) z = [21,zz] = 140+ 12,-. In the problems below, we will consider a simple version of this problem, which has only two users, {a, b}, and two items {1, 2}. So the recommendation problem can be represented as a 2 x 2 matrix. We will initialize the first layer weights as shown in figure below
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


