Question: Replacement decision Net present value NPV profile Post-audit analysis Internal rate of return Capital budgeting Independent project Payback period Required rate of return Modified integral
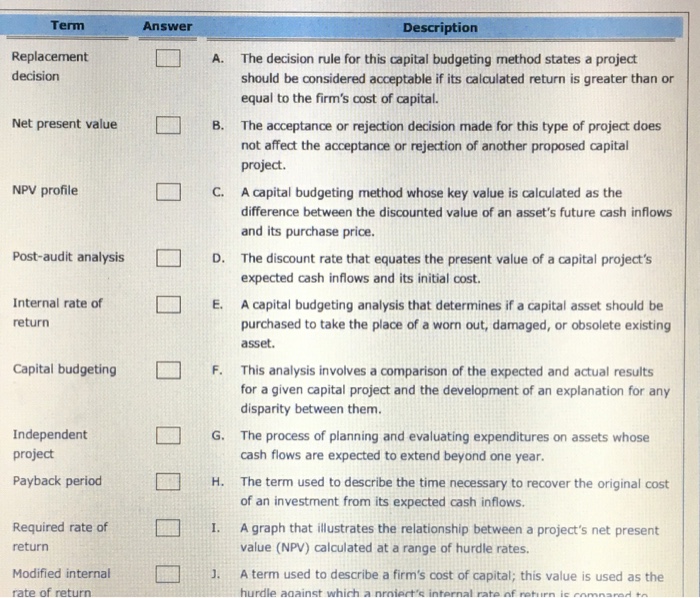
Replacement decision Net present value NPV profile Post-audit analysis Internal rate of return Capital budgeting Independent project Payback period Required rate of return Modified integral rate of return A. The decision rule for this capital budgeting method states a project should be considered acceptable if its calculated return is greater than or equal to the firm's cost of capital. B. The acceptance or rejection decision made for this type of project does not affect the acceptance or rejection of another proposed capital project. C. A capital budgeting method whose key value is calculated as the difference between the discounted value of an asset's future cash inflows and its purchase price. D. The discount rate that equates the present value of a capital project's expected cash inflows and its initial cost. E. A capital budgeting analysis that determines if a capital asset should be return purchased to take the place of a worn out, damaged, or obsolete existing asset. F. This analysis involves a comparison of the expected and actual results for a given capital project and the development of an explanation for any disparity between them. G. The process of planning and evaluating expenditures on assets whose Independent project cash flows are expected to extend beyond one year. H. The term used to describe the time necessary to recover the original cost of an investment from its expected cash inflows. I. A graph that illustrates the relationship between a project's net present value (NPV) calculated at a range of hurdle rates. J. A term used to describe a firm's cost of capital; this value is used as
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


