Question: Required: (e) variable overhead spending variance (f) variable overhead efficiency variance Video Tech Ltd manufactures video game machines. Market saturation and technological innovations have caused

 Required:
Required:
-
(e) variable overhead spending variance
-
(f) variable overhead efficiency variance
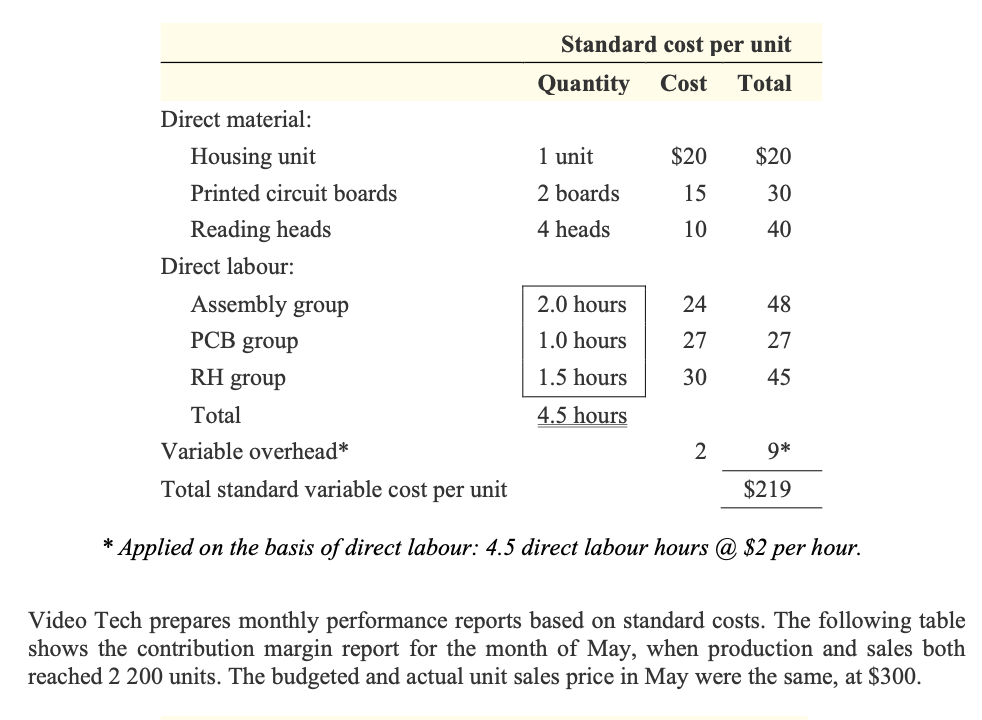
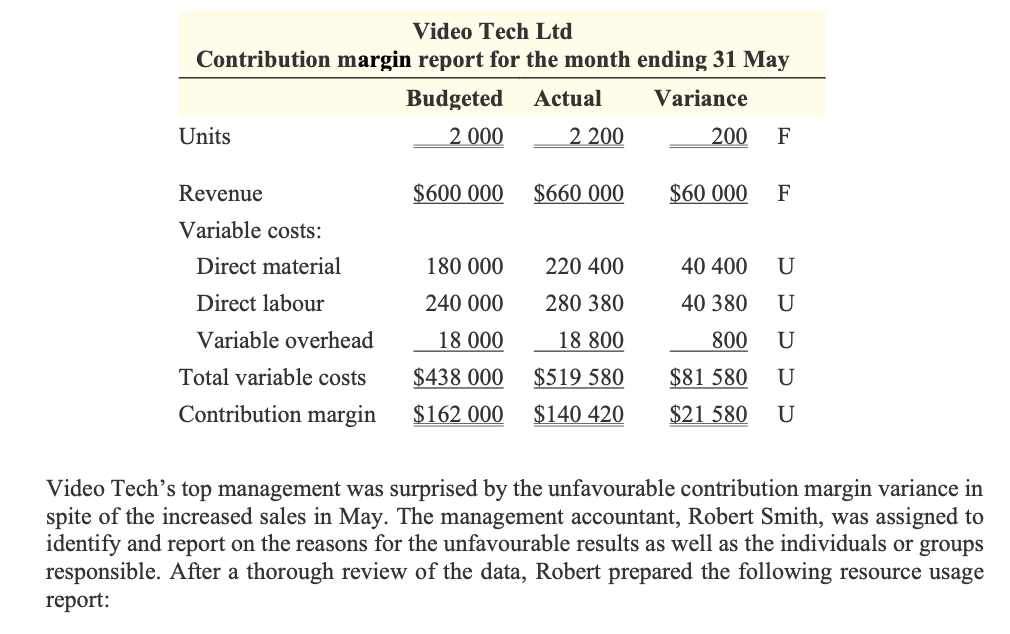
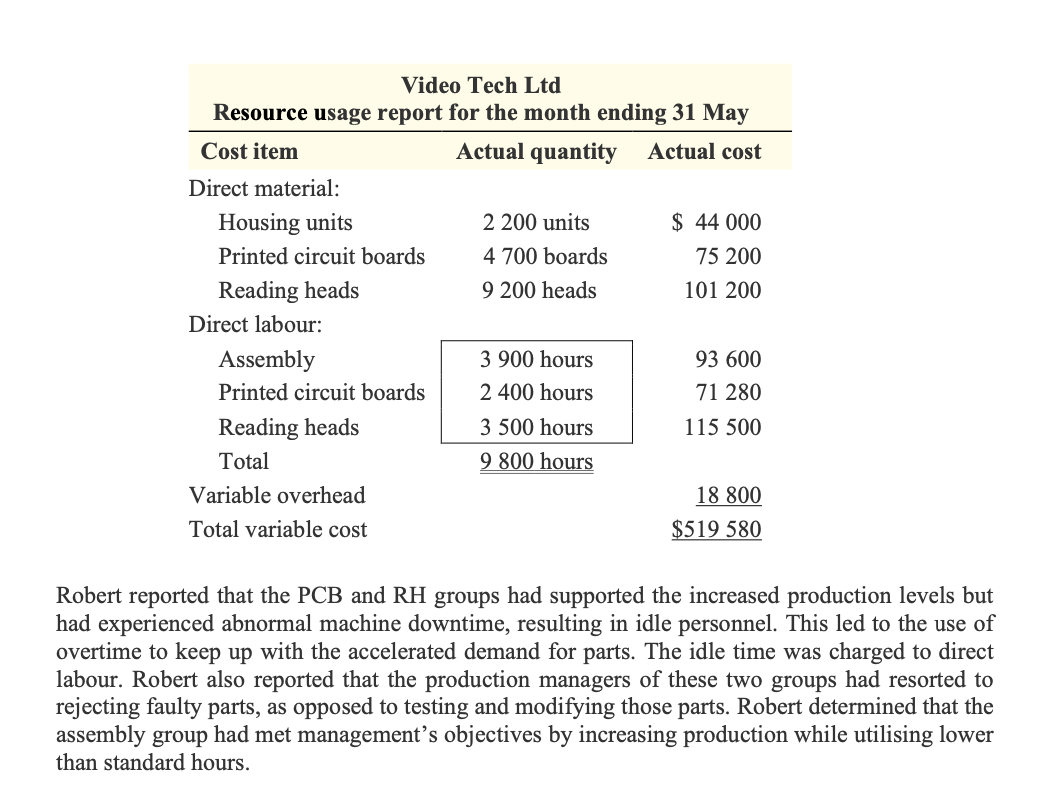
Video Tech Ltd manufactures video game machines. Market saturation and technological innovations have caused pricing pressures that have resulted in declining profits. To stem the slide in profits until new products can be introduced, top management has started to focus on achieving cost savings in manufacturing and increases in sales volume. Sales can be increased only if production volume increases. Therefore, an incentive program has been developed to reward those production managers who contribute to an increase in the number of units produced and achieve cost reductions. In addition, a just-in-time purchasing program has been implemented, and raw materials are purchased on an as-needed basis. The production managers have responded to the pressure to improve manufacturing performance and this has resulted in an increase in the number of completed units over normal production levels. The video game machines are put together by the assembly group, which requires parts from both the printed circuit boards (PCB) and the reading heads (RH) groups. To increase production levels, the PCB and RH groups started to reject parts that previously would have been tested and modified to meet manufacturing standards. Preventative maintenance on machines used in the production of these parts has been postponed, with only emergency repair work being performed to keep production lines moving. The maintenance department is concerned that there will be serious breakdowns and unsafe operating conditions. The more aggressive assembly group production supervisors have pressured maintenance personnel to attend to their machines at the expense of other groups. This has resulted in machine downtime in the PCB and RH groups which, when coupled with demands for accelerated parts delivery by the assembly group, has led to more frequent parts rejections and increased friction between departments. Video Tech uses a standard costing system. The standard costs for video game machines are as follows: Standard cost per unit Quantity Cost Total 1 unit $20 $20 Printed circuit boards 2 boards 15 30 Reading heads 4 heads 10 40 Assembly group 2.0 hours 24 48 PCB group 1.0 hours 27 27 RH group 1.5 hours 30 45 Total 4.5 hours Variable overhead* 2 9* Total standard variable cost per unit $219 * Applied on the basis of direct labour: 4.5 direct labour hours @ $2 per hour. Video Tech prepares monthly performance reports based on standard costs. The following table shows the contribution margin report for the month of May, when production and sales both reached 2 200 units. The budgeted and actual unit sales price in May were the same, at $300. Direct material: Housing unit Direct labour: Video Tech Ltd Contribution margin report for the month ending 31 May Budgeted Actual Variance Units 2 000 2 200 200 F Revenue $600 000 $660 000 $60 000 F Variable costs: Direct material 180 000 220 400 40 400 U Direct labour 240 000 280 380 40 380 U Variable overhead 18 000 18 800 800 U $438 000 $519 580 $81 580 U Total variable costs Contribution margin $162 000 $140 420 $21 580 U Video Tech's top management was surprised by the unfavourable contribution margin variance in spite of the increased sales in May. The management accountant, Robert Smith, was assigned to identify and report on the reasons for the unfavourable results as well as the individuals or groups responsible. After a thorough review of the data, Robert prepared the following resource usage report: Video Tech Ltd Resource usage report for the month ending 31 May Cost item Actual quantity Actual cost Direct material: Housing units 2 200 units $44 000 Printed circuit boards 4 700 boards 75 200 Reading heads 9 200 heads 101 200 Direct labour: Assembly 3 900 hours 93 600 2 400 hours 71 280 Printed circuit boards Reading heads Total 3 500 hours 115 500 9800 hours Variable overhead 18 800 $519 580 Total variable cost Robert reported that the PCB and RH groups had supported the increased production levels but had experienced abnormal machine downtime, resulting in idle personnel. This led to the use of overtime to keep up with the accelerated demand for parts. The idle time was charged to direct labour. Robert also reported that the production managers of these two groups had resorted to rejecting faulty parts, as opposed to testing and modifying those parts. Robert determined that the assembly group had met management's objectives by increasing production while utilising lower than standard hours
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


