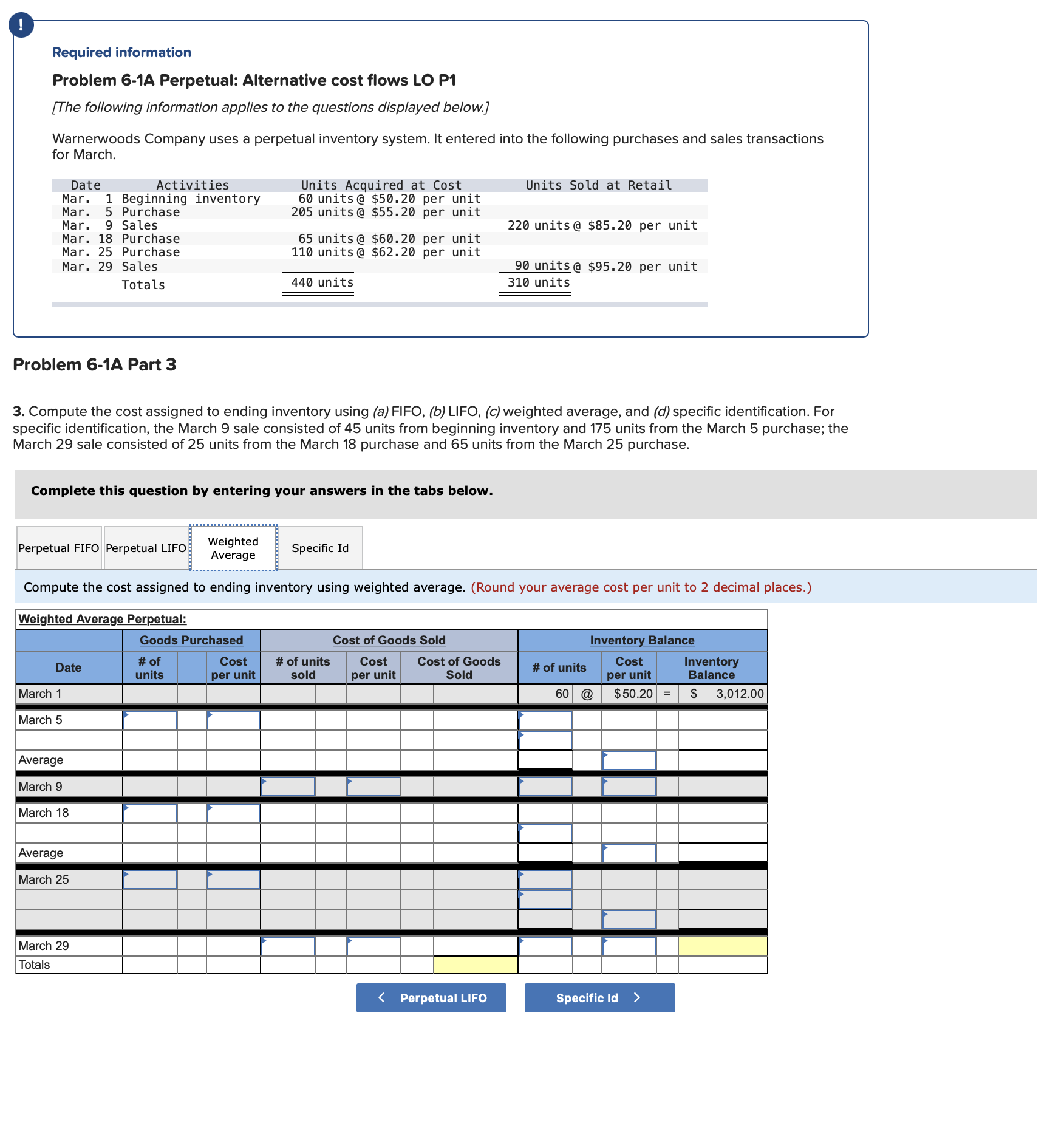
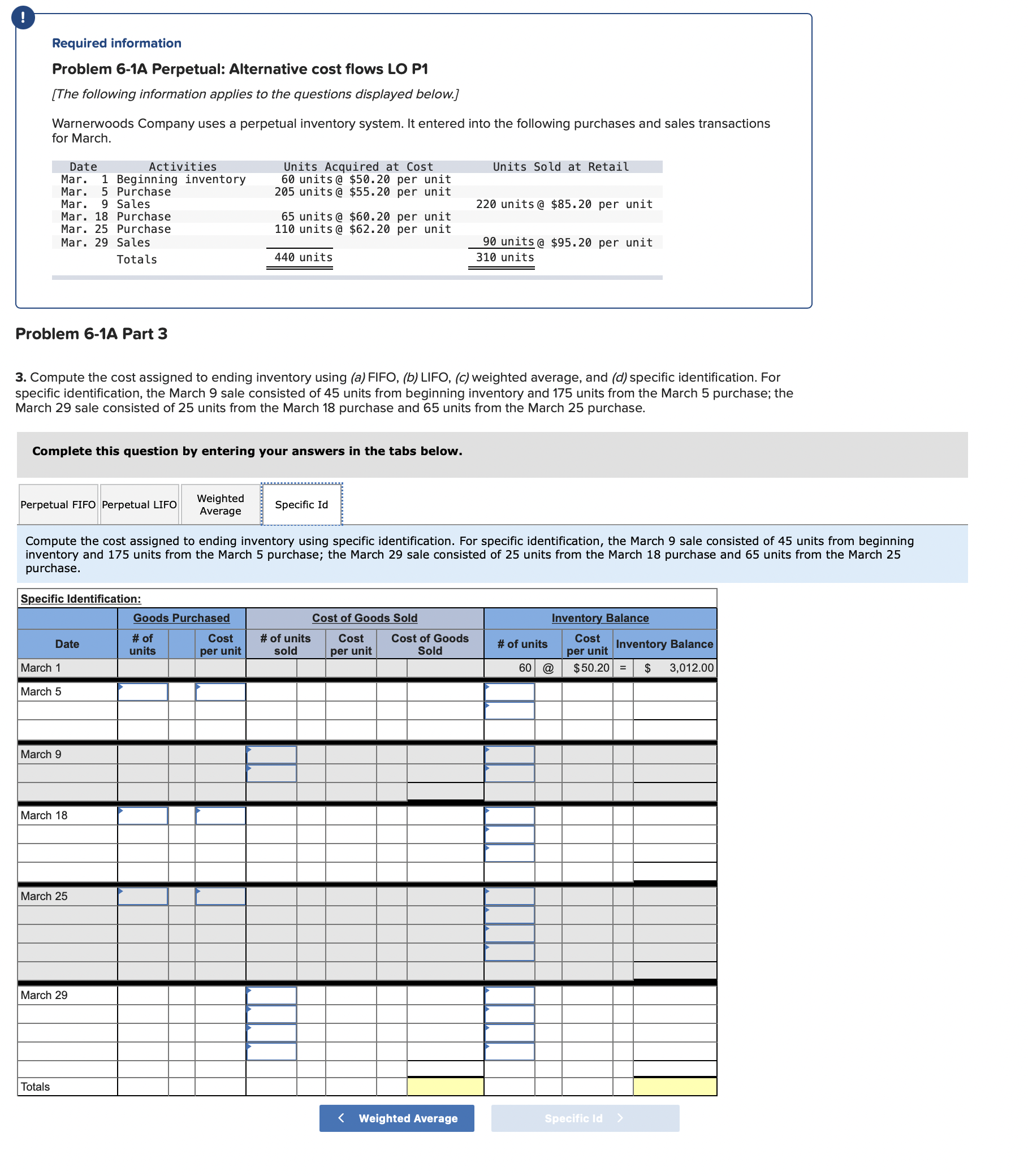
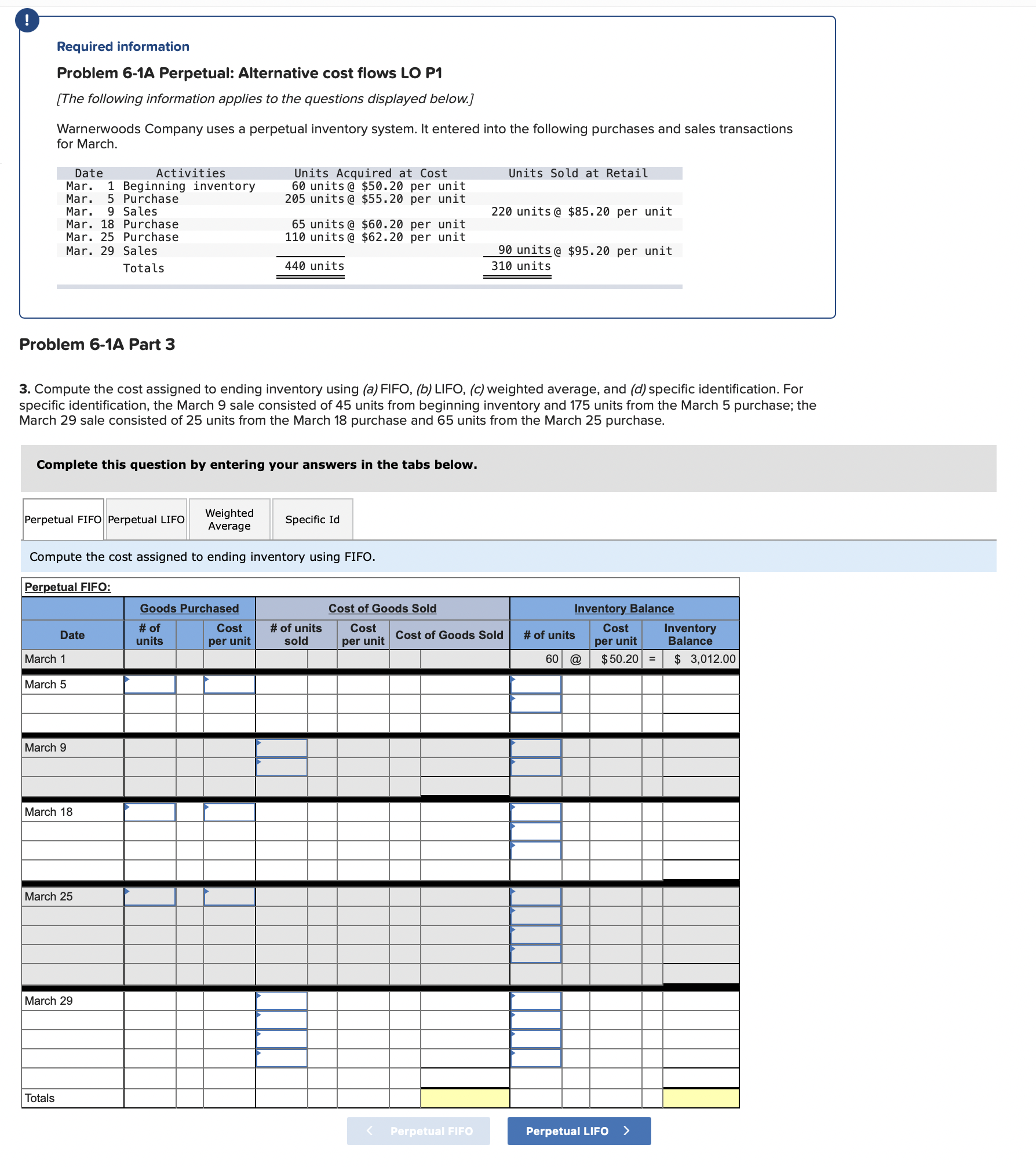
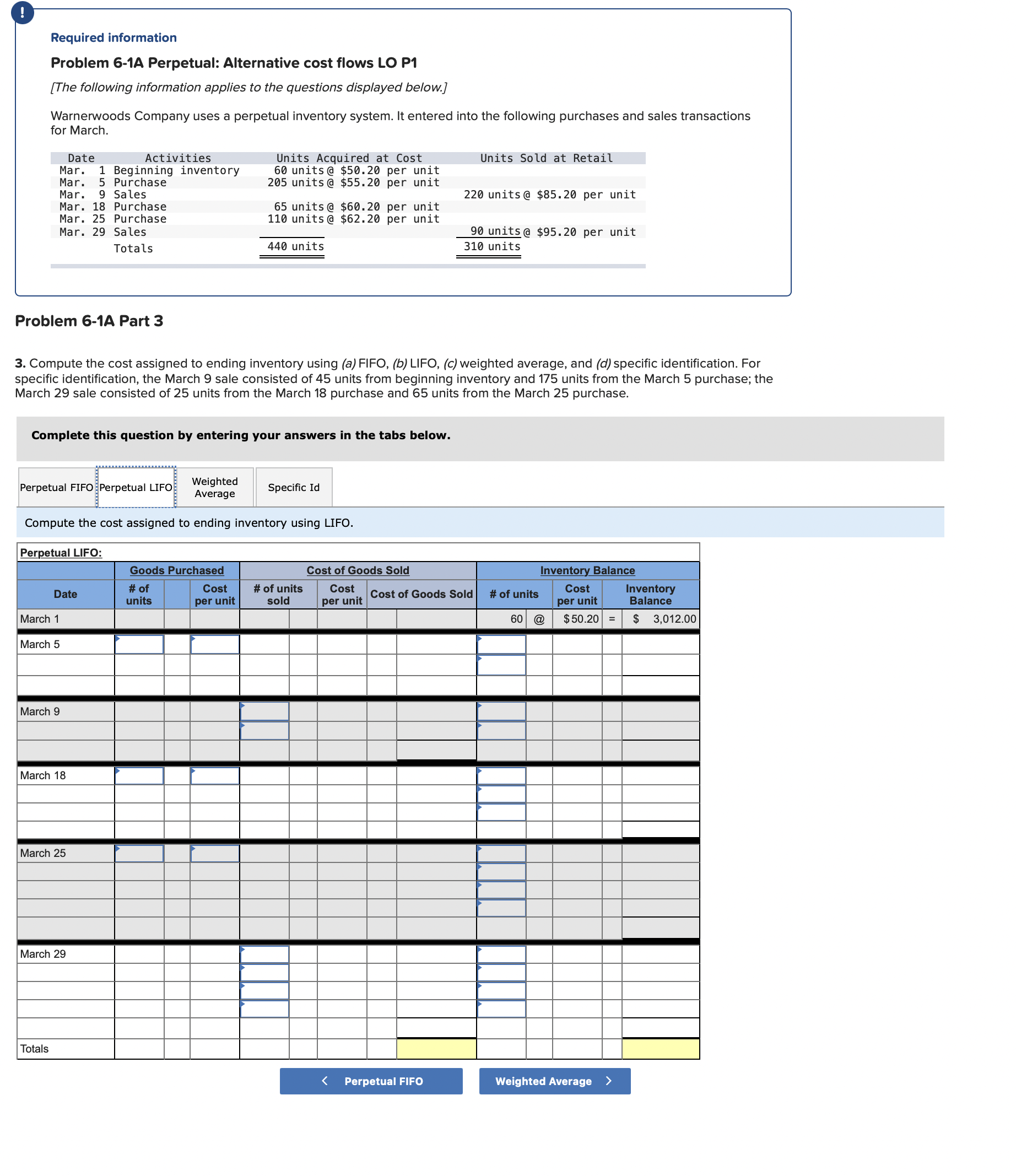
Question: Required information Problem 6-1A Perpetual: Alternative cost flows LO P1 [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Warnerwoods Company uses a perpetual inventory
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


