Question: Required Skills Inventory - Write concrete classes that implement Java Interfaces according to specifications given in UML. - Implement the major functionality of an array
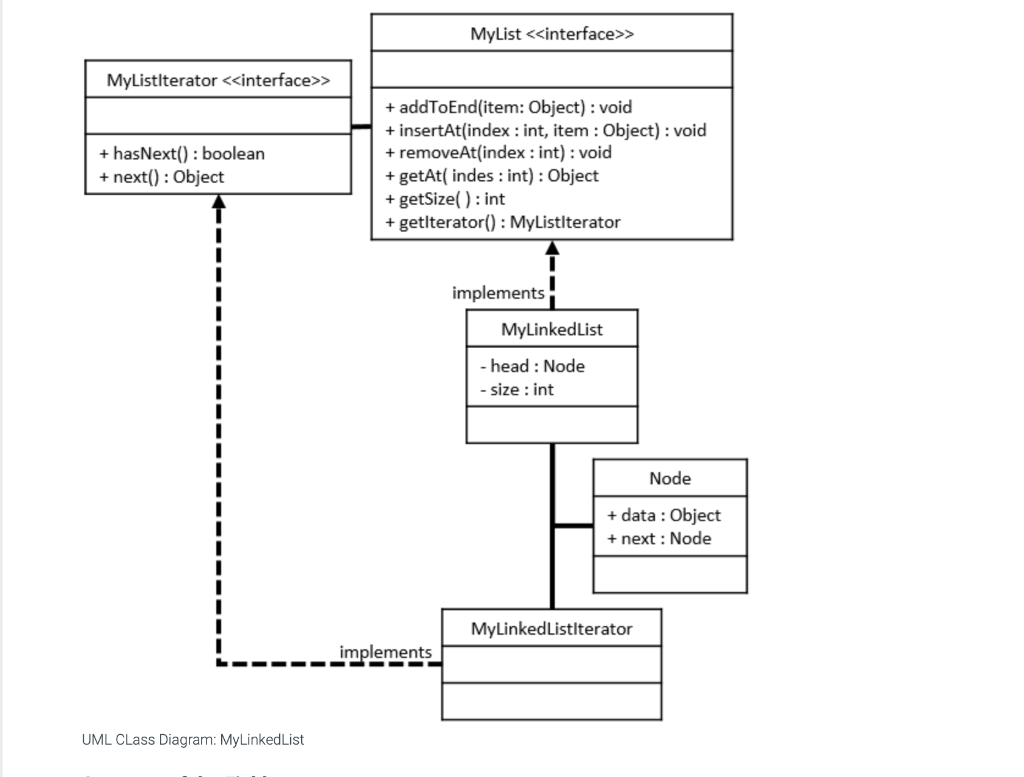
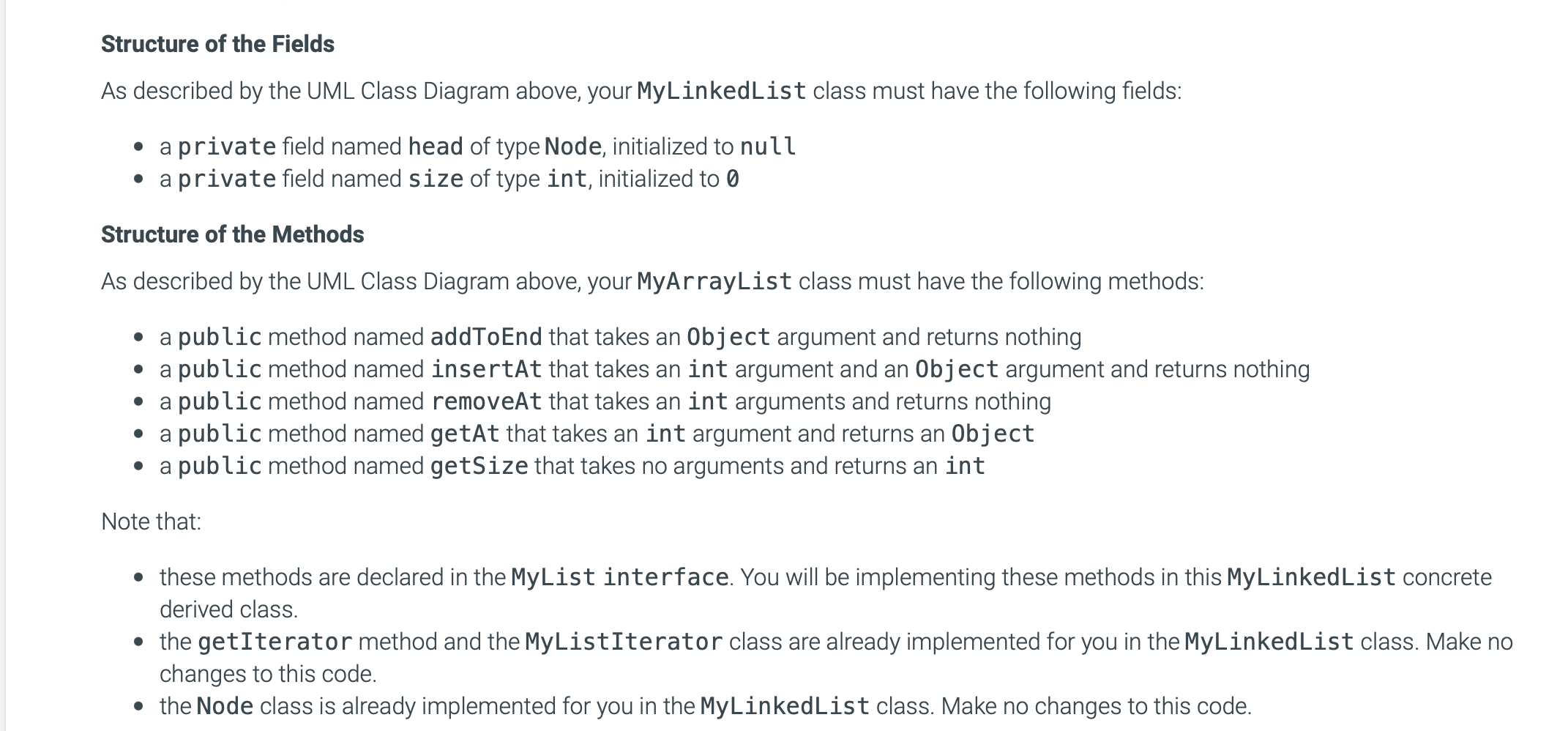

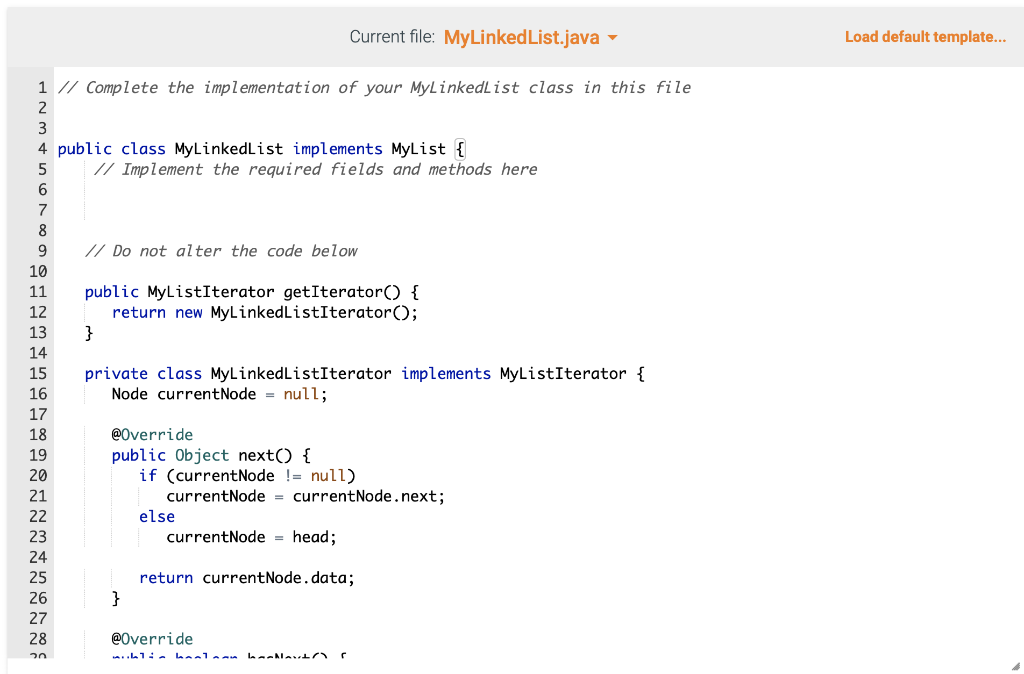
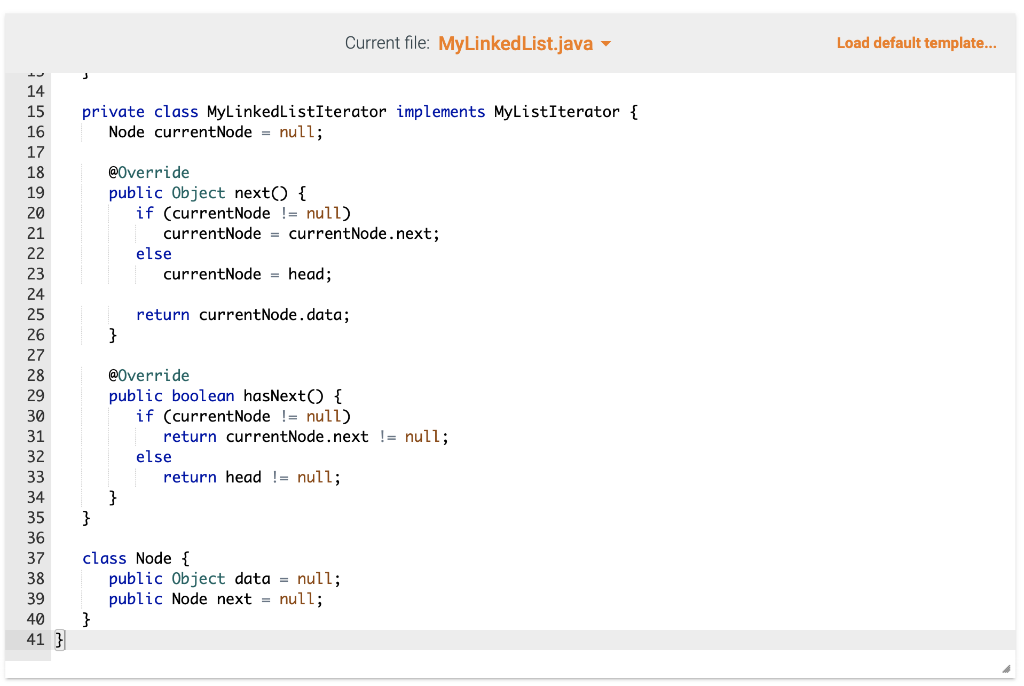

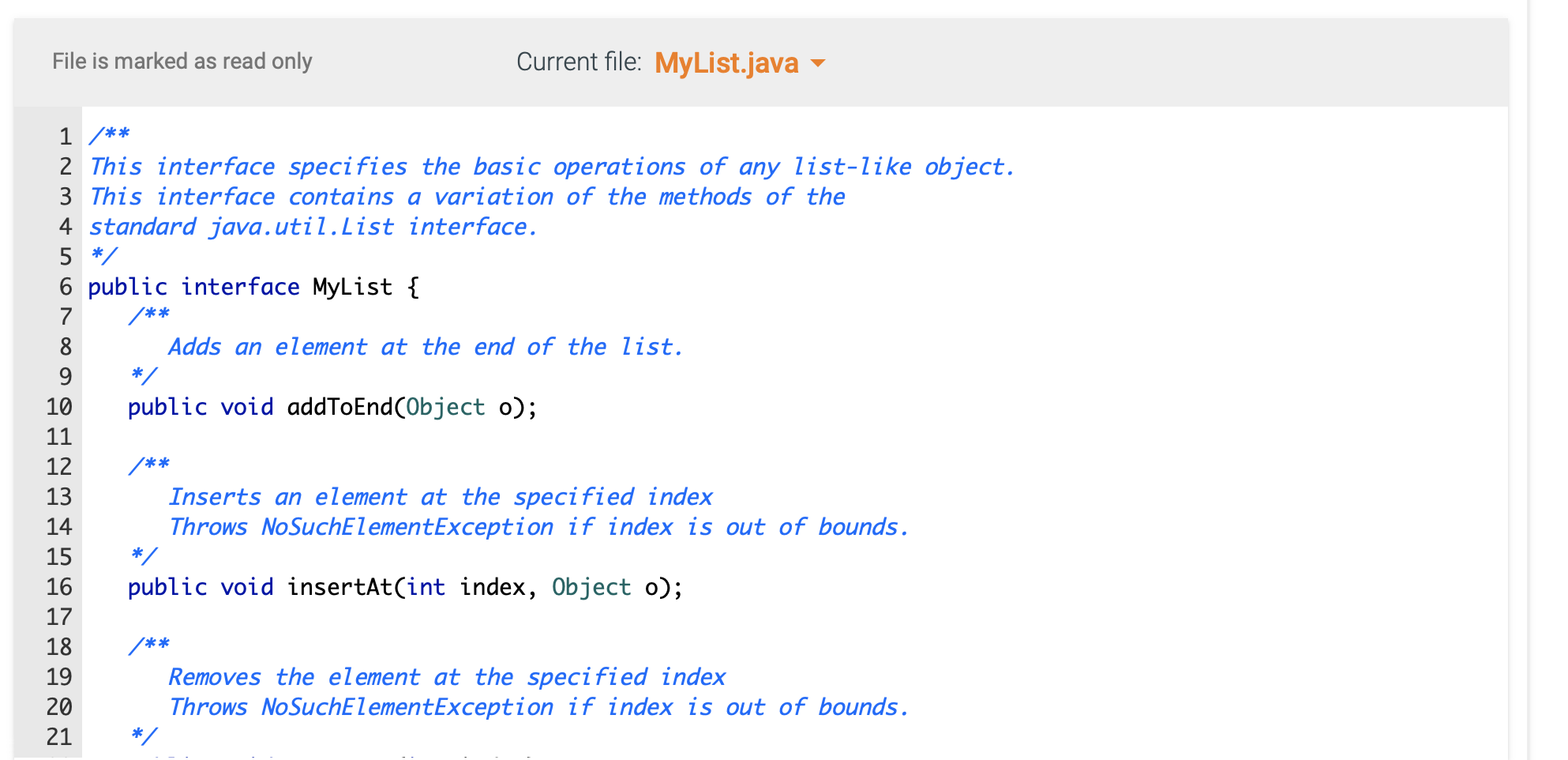
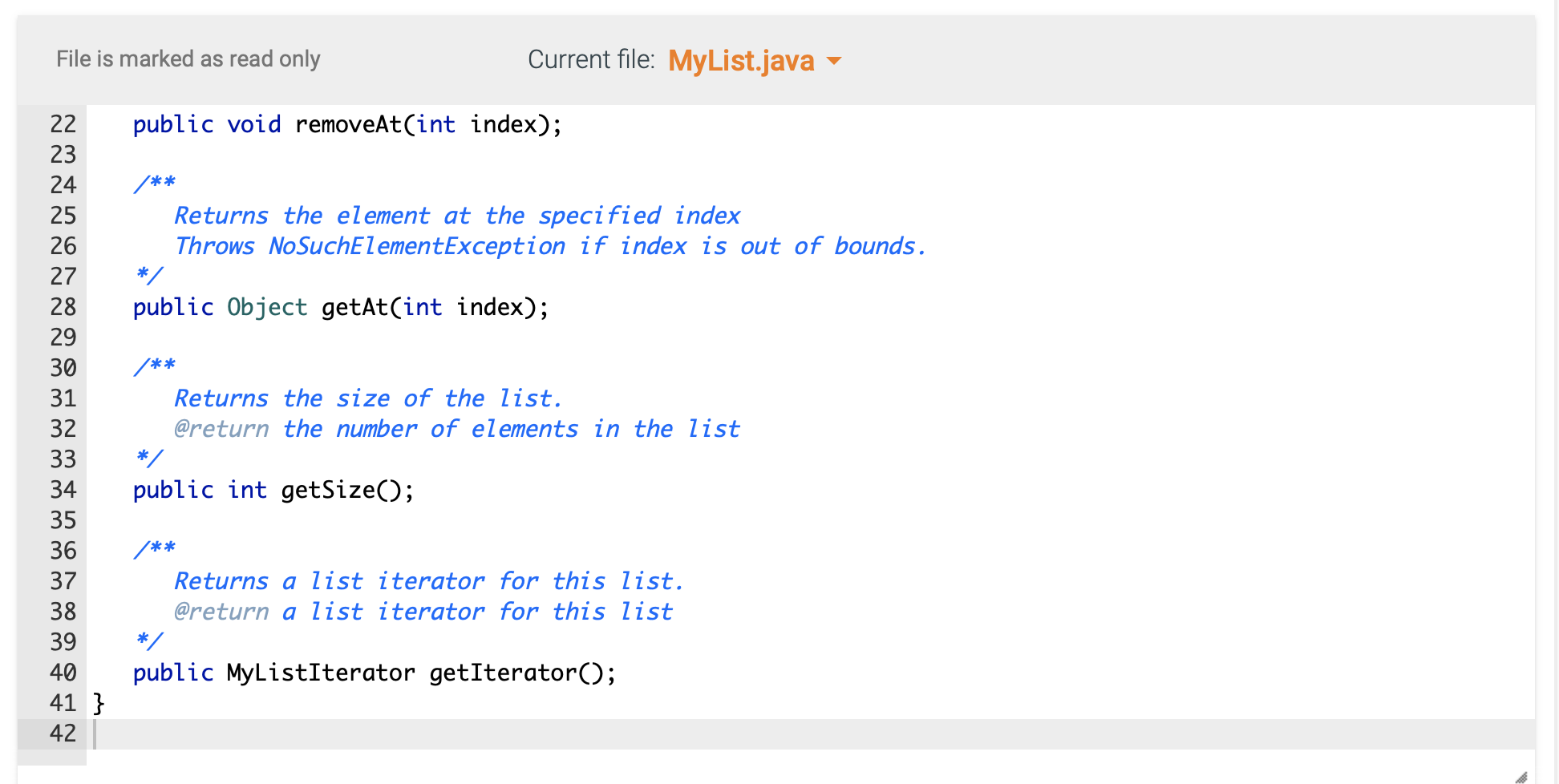
Required Skills Inventory - Write concrete classes that implement Java Interfaces according to specifications given in UML. - Implement the major functionality of an array list. - Implement the major functionality of a linked list. You are not allowed to use any of the standard Java collection types (like ArrayList) for this assignment. You are also not allowed to use arrays for this assignment. Problem Description and Given Info For this assignment you are given the following Java source code files: - MyListiterator.java (This file is complete - make no changes to this file) - MyList.java (This file is complete - make no changes to this file) - MyLinkedlist.java (You must complete this file) - Main. java (You may use this file to write code to test your MyLinkedList) You must complete the public class named MyLinkedList with fields and methods as defined below. Your MyLinkedList will implement the MyList interface that is provided in the myList. j ava file. \begin{tabular}{|l|} \hline MyListlterator > \\ \hline \\ \hline +hasNext():boolean+next():Object \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{|l|} \hline \multicolumn{1}{|c|}{ MyList > } \\ \hline \\ + addToEnd(item: Object) : void \\ + insertAt(index : int, item : Object) : void \\ + removeAt(index : int) : void \\ + getAt( indes : int) : Object \\ + getSize( ) : int \\ + getlterator() : MyListlterator \\ \hline \end{tabular} UML CLass Diagram: MyLinkedList Structure of the Fields As described by the UML Class Diagram above, your MyLinkedList class must have the following fields: - a private field named head of type Node, initialized to null - a private field named size of type int, initialized to Structure of the Methods As described by the UML Class Diagram above, your MyArrayList class must have the following methods: - a public method named addToEnd that takes an Object argument and returns nothing - a public method named insertAt that takes an int argument and an 0bj ect argument and returns nothing - a public method named removeAt that takes an int arguments and returns nothing - a public method named getAt that takes an int argument and returns an 0bject - a public method named getSize that takes no arguments and returns an int Note that: - these methods are declared in the MyList interface. You will be implementing these methods in this MyLinkedList concrete derived class. - the getIterator method and the MyListIterator class are already implemented for you in the MyLinkedList class. Make no changes to this code. - the Node class is already implemented for you in the MyLinkedList class. Make no changes to this code. MyLinkedList 1. This concrete class will store its elements in Node objects. Each Node object has a data variable that stores the element and a next variable that stores a reference to the next Node object in the list. Each instance of MyLinkedList has a Node variable called head. When size is then head is null. When size is not then head is a reference to the first Node object. For each Node object in the list, if this Node's next is null then this is the last Node in the list. 2. addToEnd method - Appends new item to end of list. For example: given the list {1,2,3} and an instruction to addToEnd (99), the result would be this {1,2,3,99} - this method will construct a new Node object who's data is the element to be added, and place this Node appropriately into the list. 3. insertat method - Inserts a new Node at the specified index in the list. Given the list {1,2,3} and an instruction to insertAt (1, 99) , the result would be this {1,99,2,3}. - Throws a NoSuchElementException if the specified index is less than or greater than size. - this method will construct a new Node object who's data is the element to be added, and place this Node appropriately into the list. 4. removeAt method - Removes the element at the specified index. For example: given the list {1,2,3} and an instruction to removeAt (1), the result would be this {1,3}. - Throws a NoSuchElementException if the specified index is less than or greater than or equal to size. 5. getAt method - Returns the item at the specified index. For example: given the list {1,2,3} and an instruction to getAt (1), the return value would be 2 . - Throws a NoSuchElementException if the specified index is less than or greater than or equal to size. 6. getSize method - Returns the number of elements currently stored in the list. Current file: Main.java Load default template... Current file: MyLinkedList.java - Load default template... I/ Complete the implementation of your MyLinkedList class in this file public class MyLinkedList implements MyList \{ I/ Implement the required fields and methods here I/ Do not alter the code below public MyListIterator getIterator() \{ return new MyLinkedListiterator(); \} private class MyLinkedListIterator implements MyListIterator \{ Node currentNode = null; @0verride public Object next() \{ if (currentNode != null) currentNode = currentNode. next; else currentNode = head; return currentNode. data; \} @0verride Current file: MyLinkedList.java - Load default template... File is marked as read only Current tile: MyListiterator.java le is marked as read only Current file: MyList.java / This interface specifies the basic operations of any list-like object. This interface contains a variation of the methods of the standard java.util. List interface. */ public interface MyList \{ /** Adds an element at the end of the list. / public void addToEnd(Object o); / Inserts an element at the specified index Throws NoSuchElementException if index is out of bounds. / public void insertAt(int index, Object o); / Removes the element at the specified index Throws NoSuchElementException if index is out of bounds. public void removeAt(int index); / Returns the element at the specified index Throws NoSuchElementException if index is out of bounds. / public Object getAt(int index); / Returns the size of the list. @return the number of elements in the list */ public int getSize(); / Returns a list iterator for this list. @return a list iterator for this list */ public MyListIterator getIterator(); \}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


