Question: Required Skills Inventory Write concrete classes that implement Java Interfaces according to specifications given in UML. Implement the major functionality of an array list. Implement
Required Skills Inventory
Write concrete classes that implement Java Interfaces according to specifications given in UML.
Implement the major functionality of an array list.
Implement the major functionality of a linked list.
You are not allowed to use any of the standard Java collection types (like ArrayList) for this assignment. You are also not allowed to use arrays for this assignment.
Problem Description and Given Info
For this assignment you are given the following Java source code files:
MyListIterator.java (This file is complete make no changes to this file)
MyList.java (This file is complete make no changes to this file)
MyLinkedList.java (You must complete this file)
Main.java (You may use this file to write code to test your MyLinkedList)
You must complete the public class named MyLinkedList with fields and methods as defined below. Your MyLinkedList will implement the MyList interface that is provided in the myList.java file.
UML CLass Diagram: MyLinkedList
Structure of the Fields
As described by the UML Class Diagram above, your MyLinkedList class must have the following fields:
a private field named head of type Node, initialized to null
a private field named size of type int, initialized to 0
Structure of the Methods
As described by the UML Class Diagram above, your MyArrayList class must have the following methods:
a public method named addToEnd that takes an Object argument and returns nothing
a public method named insertAt that takes an int argument and an Object argument and returns nothing
a public method named removeAt that takes an int arguments and returns nothing
a public method named getAt that takes an int argument and returns an Object
a public method named getSize that takes no arguments and returns an int
Note that:
these methods are declared in the MyList interface. You will be implementing these methods in this MyLinkedList concrete derived class.
the getIterator method and the MyListIterator class are already implemented for you in the MyLinkedList class. Make no changes to this code.
the Node class is already implemented for you in the MyLinkedList class. Make no changes to this code.
Additional Information
MyLinkedList
This concrete class will store its elements in Node objects. Each Node object has a data variable that stores the element and a next variable that stores a reference to the next Node object in the list. Each instance of MyLinkedList has a Node variable called head. When size is 0 then head is null. When size is not 0 then head is a reference to the first Node object. For each Node object in the list, if this Nodes next is null then this is the last Node in the list.
addToEnd method
Appends new item to end of list. For example: given the list {1, 2, 3} and an instruction to addToEnd(99), the result would be this {1, 2, 3, 99}.
this method will construct a new Node object whos data is the element to be added, and place this Node appropriately into the list.
insertAt method
Inserts a new Node at the specified index in the list. Given the list {1, 2, 3} and an instruction to insertAt(1, 99), the result would be this {1, 99, 2, 3}.
Throws a NoSuchElementException if the specified index is less than 0 or greater than size.
this method will construct a new Node object whos data is the element to be added, and place this Node appropriately into the list.
removeAt method
Removes the element at the specified index. For example: given the list {1, 2, 3} and an instruction to removeAt(1), the result would be this {1, 3}.
Throws a NoSuchElementException if the specified index is less than 0 or greater than or equal to size.
getAt method
Returns the item at the specified index. For example: given the list {1, 2, 3} and an instruction to getAt(1), the return value would be 2.
Throws a NoSuchElementException if the specified index is less than 0 or greater than or equal to size.
getSize method
Returns the number of elements currently stored in the list.
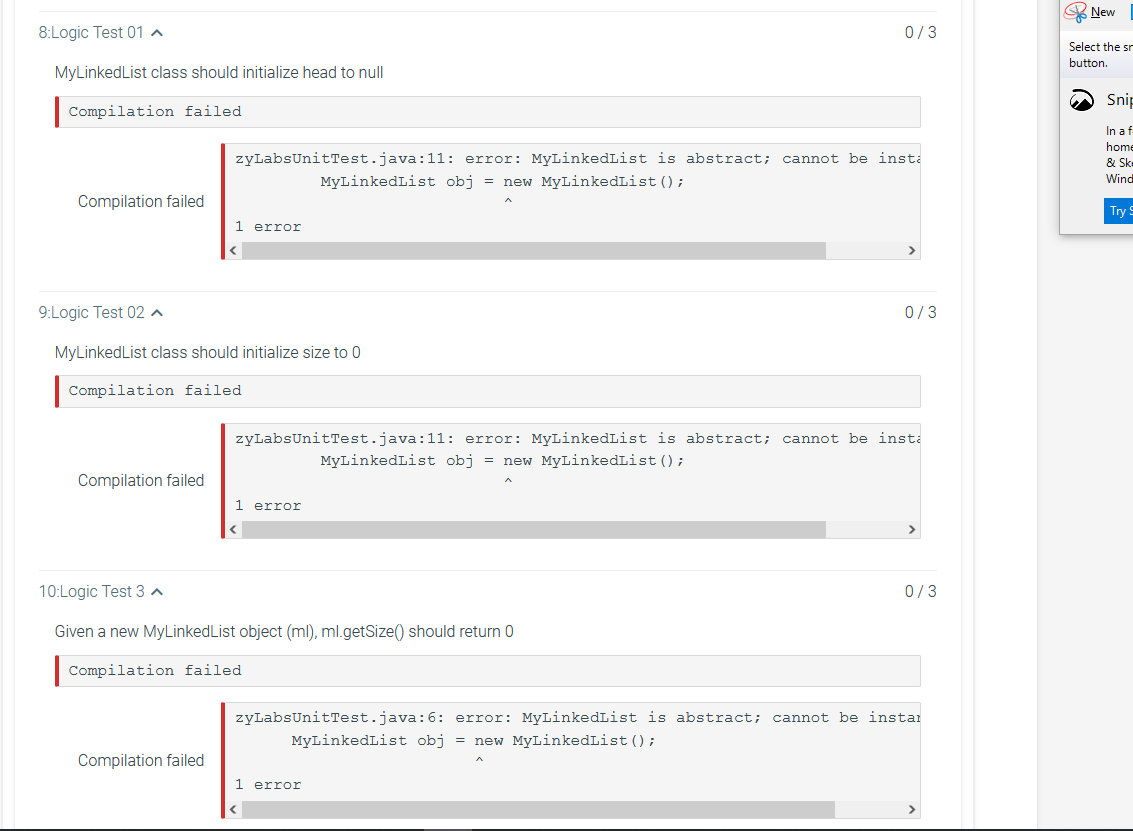
This is what I got so far but the tests are failing
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
abstract class MyLinkedList implements MyList {
// Fields
private Node head = null;
private int size = 0;
// Appends A Node At The End Of The Linked List
//@Override
public void append(Object o) {
// Create A New Node
Node node = new Node();
node.data = o;
node.next = null;
// If List Is Empty, New Node Is Head
if (head == null) {
head = node;
} else {
// Append To The End
// Traverse To Last Node
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null) {
current = current.next;
}
// Append To End
current.next = node;
// Increment The Size
size++;
}
}
// Appends A Node At The Ith Index Of The Linked List
// @Override
public void insertAt(int index, Object o) {
// Check If The Index Is Valid
if (index size + 1) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("Index is out of range.");
} else {
// Create A New Node
Node node = new Node();
node.data = o;
// If I == 0, Insert At Head
if (index == 0) {
node.next = head;
head = node;
} else {
// Get To The (I - 1)th Node
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i
current = current.next;
}
// Append New Node Next To It
node.next = current.next;
current.next = node;
}
// Increment The Size
size++;
}
}
// Removes The Ith Element From The
// @Override
public void removeAt(int index) {
// Check If Index Is Valid
if (index size) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("Index is out of range.");
} else {
// Check If Index == 0, Remove Head
if (index == 0) {
head = head.next;
} else {
// Get To The (I - 1)th Node
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i
current = current.next;
}
// Remove Ith Node
if (current.next != null) {
current.next = current.next.next;
} else {
// Tail Node
current.next = null;
}
}
// Decrement The Size
size--;
}
}
// Returns The Element At Ith Index
// @Override
public Object getAt(int index) {
if (index size) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("Index is out of range.");
} else {
// Get To Ith Index
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i
current = current.next;
}
return current.data;
}
}
// Returns The Size Of The Linked List
// @Override
public int getSize() {
return size + 1;
}
// @Override
public MyListIterator getIterator() {
return new MyLinkedListIterator();
}
private class MyLinkedListIterator implements MyListIterator {
Node currentNode = null;
// @Override
public Object next() {
if (currentNode != null) {
currentNode = currentNode.next;
} else {
currentNode = head;
}
return currentNode.data;
}
// @Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if (currentNode != null) {
return currentNode.next != null;
} else {
return head != null;
}
}
}
class Node {
public Object data;
public Node next = null;
}
}
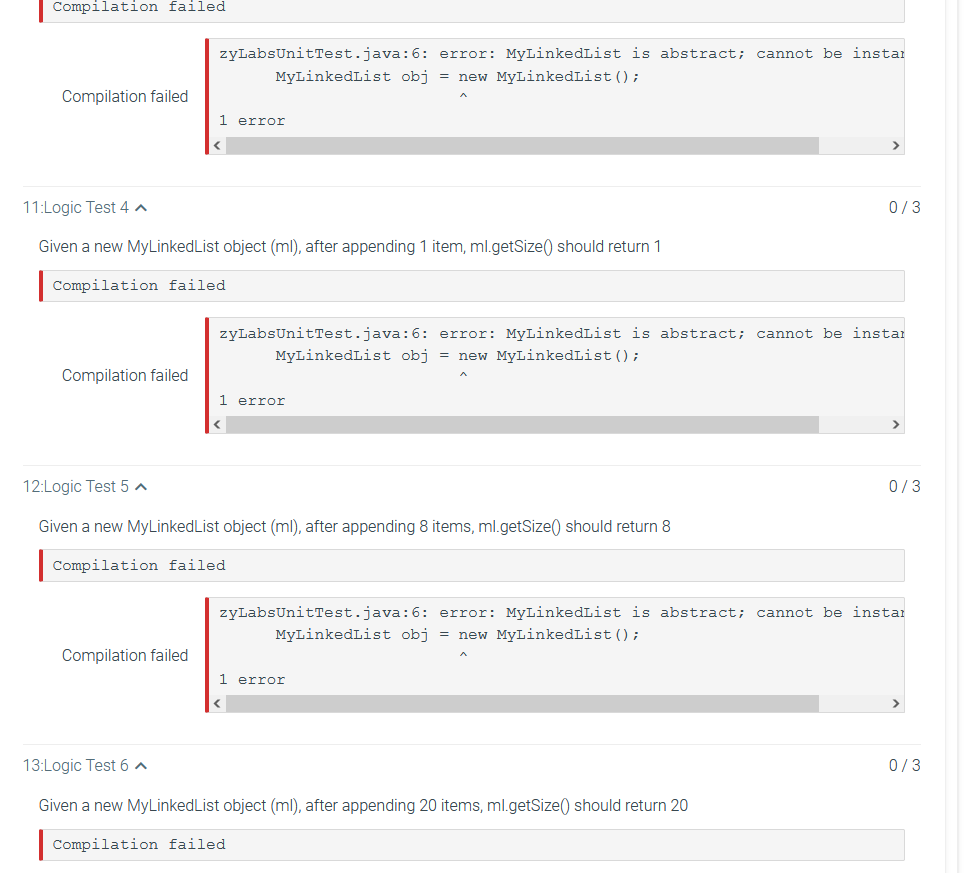
8:Logic Test 01 ^ 0/3 MyLinkedList class should initialize head to null Compilation failed 9:Logic Test 02 0/3 MyLinkedList class should initialize size to 0 10:Logic Test 3 0/3 Given a new MyLinkedList object (ml), ml.getSize() should return 0 Compilation failed 11:Logic Test 4 0/3 Given a new MyLinkedList object (ml), after appending 1 item, ml.getSize(0 should return 1 Compilation failed 12:Logic Test 5 0/3 Given a new MyLinkedList object (ml), after appending 8 items, ml.getSize() should return 8 Compilation failed 13:Logic Test 6 0/3 Given a new MyLinkedList object (ml), after appending 20 items, ml.getSize() should return 20 Compilation failed
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


