Question: Review Lexical Analysis and Example Source Code given , and then implement a lexical analyzer that reads its input from a file and recognizes only
Review Lexical Analysis and Example Source Code given and then
implement a lexical analyzer that reads its input from a file and recognizes only arithmetic
expressions, including variable names and bit integer literals as operands. Write your
program in Python.
a Simple library function is acceptable; however, you should not use any library function
that significantly reduces workload eg java.util.regex
Variable names
o consist of strings of uppercase letters, lowercase letters, and digits but must begin
with a letter.
o have no length limitation
Arithmetic Expression may have the following operators:
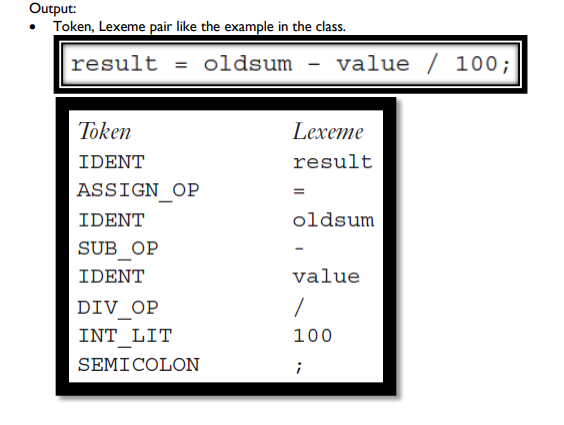
Output:
Token, Lexeme pair like the example in the class.
front.c a lexical analyzer system for simple
arithmetic expressions
#include
#include
Global declarations
Variables
int charClass;
char lexeme ;
char nextChar;
int lexLen;
int token;
int nextToken;
FILE infp;
Function declarations
void addChar;
void getChar;
void getNonBlank;
int lex;
Character classes
#define LETTER
#define DIGIT
#define UNKNOWN
Token codes
#define INTLIT
#define IDENT
#define ASSIGNOP
#define ADDOP
#define SUBOP
#define MULTOP
#define DIVOP
#define LEFTPAREN
#define RIGHTPAREN
main driver
main
Open the input data file and process its contents
errnot err;
err fopens&infpD:AcademicResearchCourse TeachingMarshallCS lecture slidescslecturefrontinr; If you face problem here, move the front.in file to a directory where the path does not have any space.
if err
printfERROR cannot open front.in
;
else
getChar;
do
lex;
while nextToken EOF;
lookup a function to lookup operators and parentheses
and return the token
int lookupchar ch
switch ch
case :
addChar;
nextToken LEFTPAREN;
break;
case :
addChar;
nextToken RIGHTPAREN;
break;
case :
addChar;
nextToken ADDOP;
break;
case :
addChar;
nextToken SUBOP;
break;
case :
addChar;
nextToken MULTOP;
break;
case :
addChar;
nextToken DIVOP;
break;
default:
addChar;
nextToken EOF;
break;
return nextToken;
addChar a function to add nextChar to lexeme
void addChar
if lexLen
lexemelexLen nextChar;
lexemelexLen;
else
printfError lexeme is too long
;
getChar a function to get the next character of
input and determine its character class
void getChar
if nextChar getcinfp EOF
if isalphanextChar
charClass LETTER;
else if isdigitnextChar
charClass DIGIT;
else charClass UNKNOWN;
else
charClass EOF;
getNonBlank a function to call getChar until it
returns a nonwhitespace character
void getNonBlank
while isspacenextChar
getChar;
lex a simple lexical analyzer for arithmetic
expressions
int lex
lexLen ;
getNonBlank;
switch charClass
Parse identifiers
case LETTER:
addChar;
getChar;
while charClass LETTER charClass DIGIT
addChar;
getChar;
nextToken IDENT;
break;
Parse integer literals
case DIGIT:
addChar;
getChar;
while charClass DIGIT
addChar;
getChar;
nextToken INTLIT;
break;
Parentheses and operators
case UNKNOWN:
lookupnextChar;
getChar;
break;
EOF
case EOF:
nextToken EOF;
lexemeE;
lexemeO;
lexemeF;
lexeme;
break;
End of switch
printfNext token is: d Next lexeme is s
nextToken, lexeme;
return nextToken;
End of function lex
sum total
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


