Question: Round robin, weighted fair queuing, and priority queuing Let us compare three resource allocation policies. Recall that Round robin simply gives each queue a turn
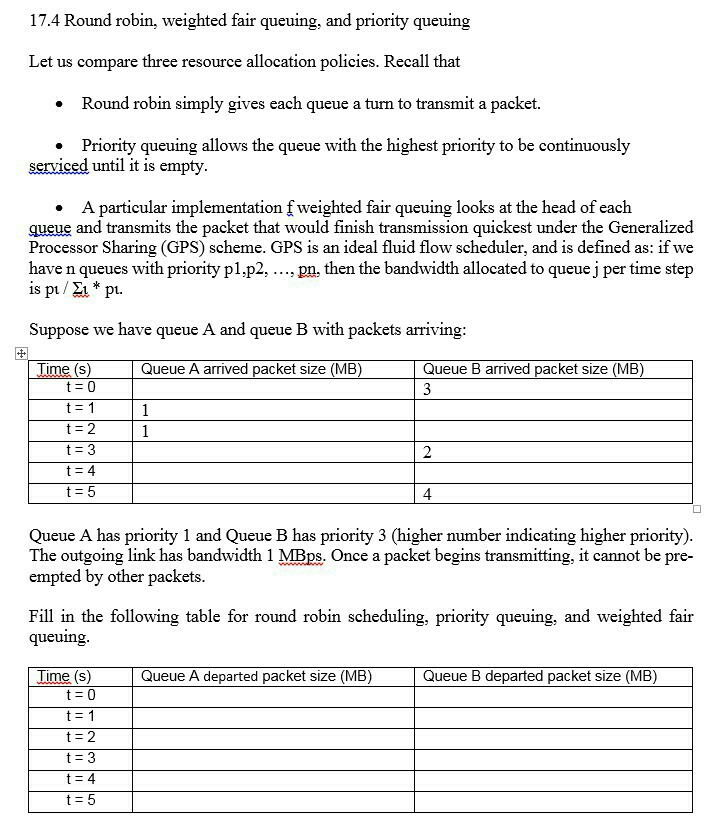
Round robin, weighted fair queuing, and priority queuing Let us compare three resource allocation policies. Recall that Round robin simply gives each queue a turn to transmit a packet. Priority queuing allows the queue with the highest priority to be continuously serviced until it is empty. A particular implementation f weighted fair queuing looks at the head of each queue and transmits the packet that would finish transmission quickest under the Generalized Processor Sharing (GPS) scheme. GPS is an ideal fluid flow scheduler, and is defined as: if we have n queues with priority p_1, p_2, ..., pn, then the bandwidth allocated to queue j per time step is p_t/sigma t* pt. Suppose we have queue A and queue B with packets arriving: Queue A has priority 1 and Queue B has priority 3 (higher number indicating higher priority). The outgoing link has bandwidth 1 MBps. Once a packet begins transmitting, it cannot be preempted by other packets. Fill in the following table for round robin scheduling, priority queuing, and weighted fair queuing
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


