Question: Saving and Loading JSON You can convert Python objects to JSON strings (and back again) using dumps and loads methods in the json module: >>json.dumps
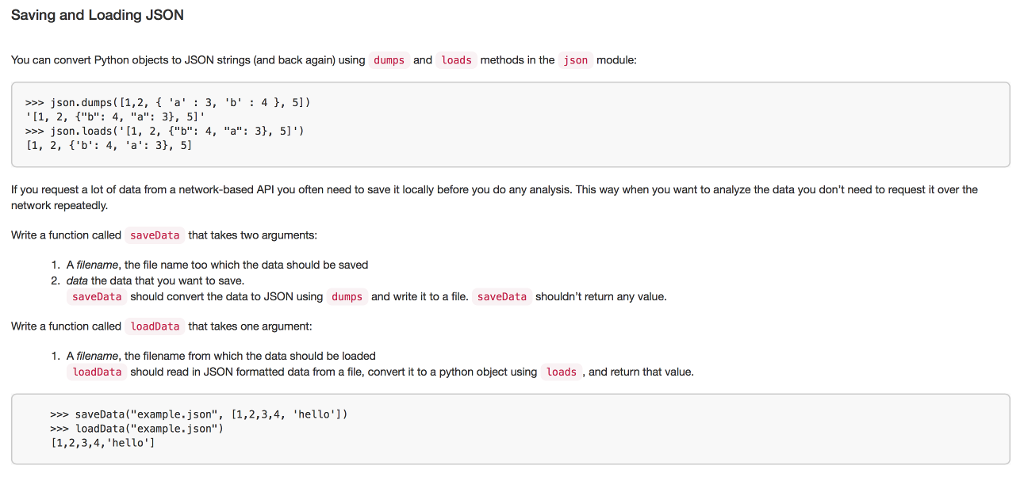
Saving and Loading JSON You can convert Python objects to JSON strings (and back again) using dumps and loads methods in the json module: >>json.dumps ([1,2, 'a'3, 'b' : 4,51) >son. loads ('[1, 2, ["b": 4, "a":3,51) If you request a lot of data from a network-based API you often need to save it locally before you do any analysis. This way when you want to analyze the data you don't need to request it over the network repeatedly. Write a function called saveData that takes two arguments: 1. A filename, the file name too which the data should be saved 2. data the data that you want to save saveData should convert the data to JSON using dumps and write it to a file. saveData shouldn't return any value. Write a function called loadData that takes one argument: . A filename, the filename from which the data should be loaded loadData should read in JSON formatted data from a file, convert it to a python object using loads and return that value. saveData("example.json", [1,2,3,4, 'hello']) loadData("example.json") [1,2,3,4, 'hello'] Saving and Loading JSON You can convert Python objects to JSON strings (and back again) using dumps and loads methods in the json module: >>json.dumps ([1,2, 'a'3, 'b' : 4,51) >son. loads ('[1, 2, ["b": 4, "a":3,51) If you request a lot of data from a network-based API you often need to save it locally before you do any analysis. This way when you want to analyze the data you don't need to request it over the network repeatedly. Write a function called saveData that takes two arguments: 1. A filename, the file name too which the data should be saved 2. data the data that you want to save saveData should convert the data to JSON using dumps and write it to a file. saveData shouldn't return any value. Write a function called loadData that takes one argument: . A filename, the filename from which the data should be loaded loadData should read in JSON formatted data from a file, convert it to a python object using loads and return that value. saveData("example.json", [1,2,3,4, 'hello']) loadData("example.json") [1,2,3,4, 'hello']
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


