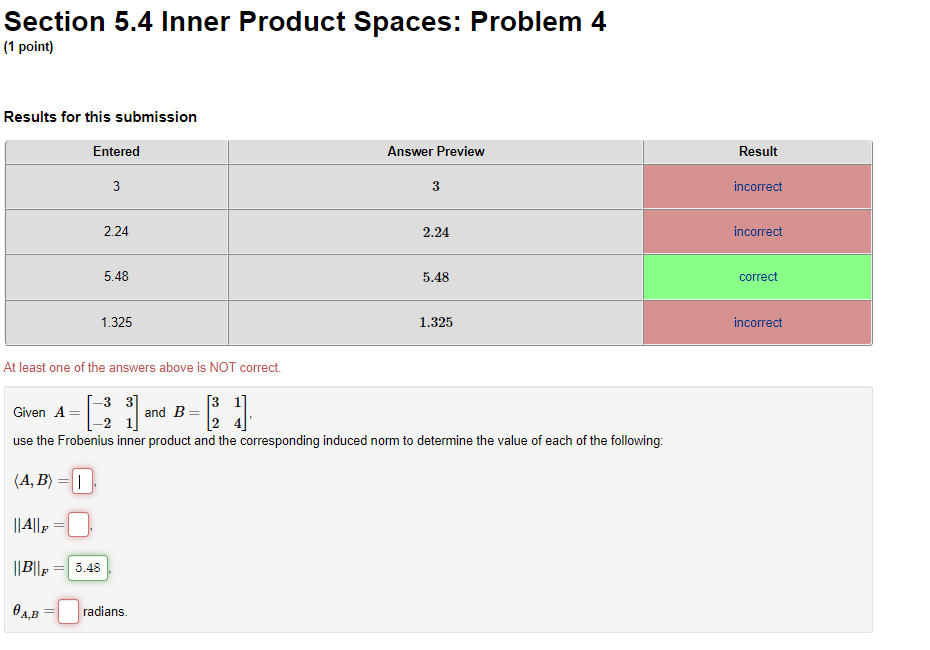
Question: Section 5.4 Inner Product Spaces: Problem 3 (1 point) Use the inner product = / f(x)g(x)dx in the vector space C[0, 1] to find ,

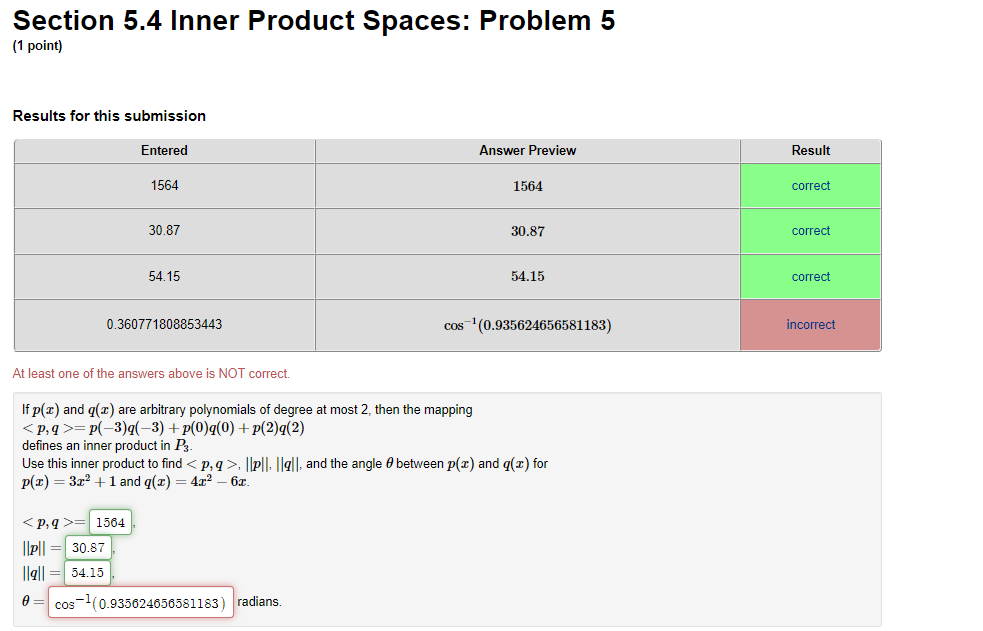

=p(-3)q(-3) + p(0)q(0) + p(2)q(2) defines an inner product in P3. Use this inner product to find , Ilpll, ||gl|, and the angle @ between p(x) and q(I) for p(x) = 3x2 + 1 and q(x) = 4x2 - 61.
= 1564 Ilpll = 30.87 llall = 54.15 cos ( 0.935624656581183 ) radians.Section 5.4 Inner Product Spaces: Problem 6 (1 point) Use the inner product
=p(-1)q(-1) + p(0)q(0) + p(3)q(3) in Pa to find the orthogonal projection of p(x) = 3x2 + 6x + 7 onto the line L spanned by q(r) = 4x2 - 5x - 1. projL(P) =
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


