Question: SECTION B (40 marks) Answer ALL questions from Section B (there are multiple parts to each question, you must attempt all parts of each selected
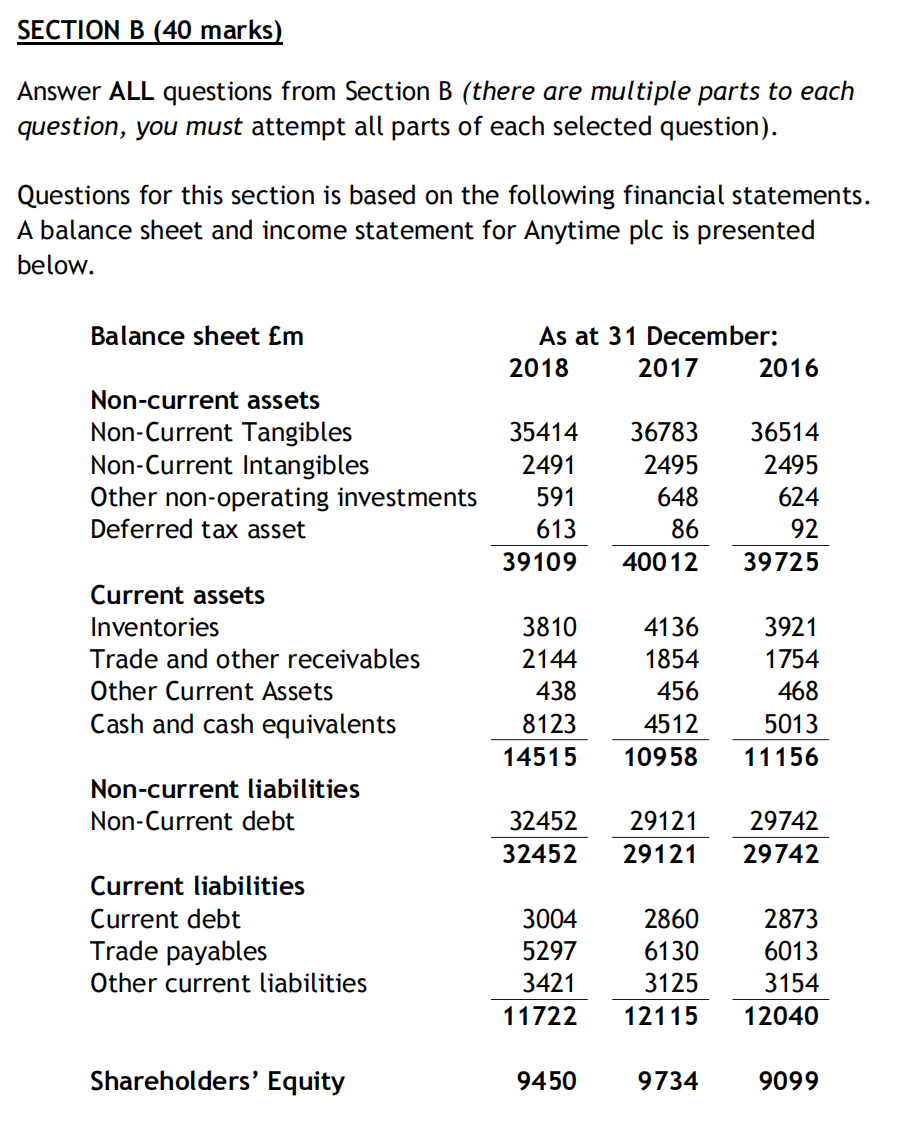
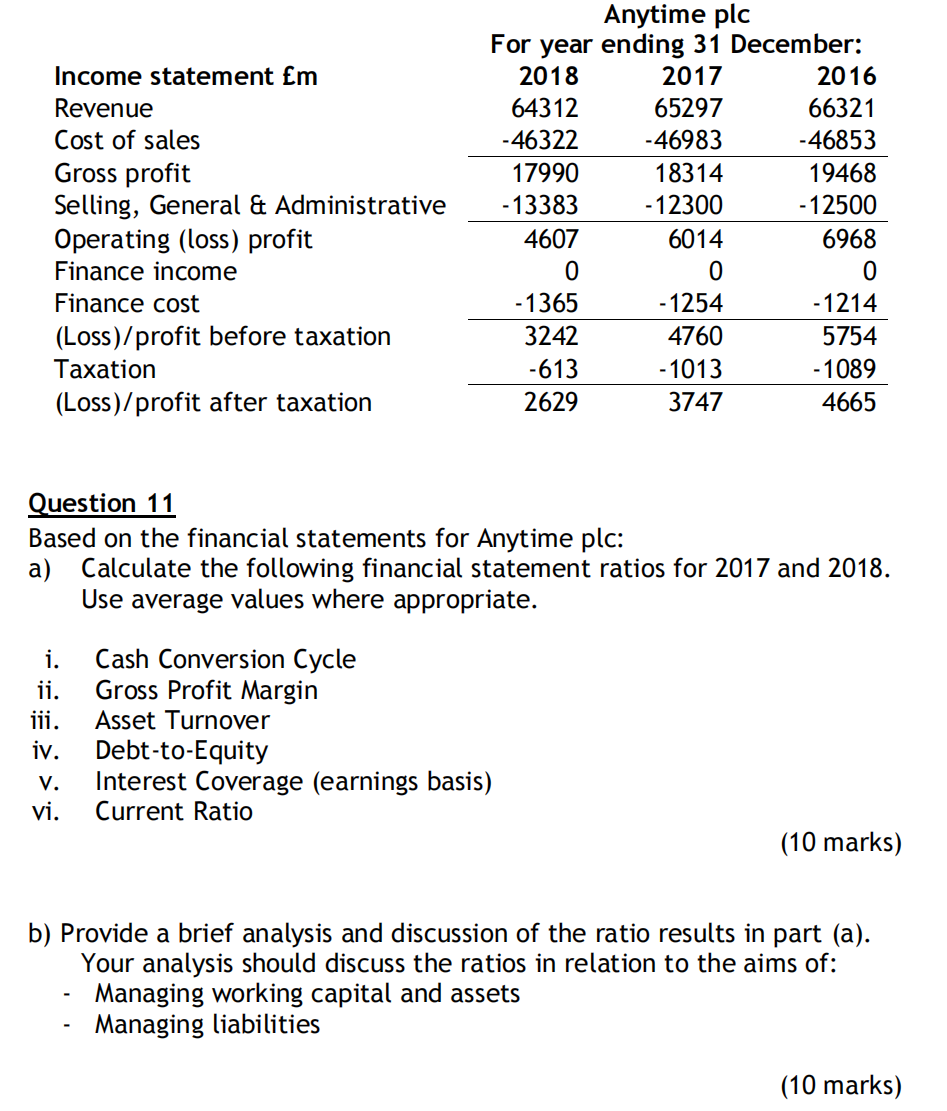

SECTION B (40 marks) Answer ALL questions from Section B (there are multiple parts to each question, you must attempt all parts of each selected question). Questions for this section is based on the following financial statements. A balance sheet and income statement for Anytime plc is presented below. Balance sheet Em As at 31 December: 2018 2017 2016 Non-current assets Non-Current Tangibles Non-Current Intangibles Other non-operating investments Deferred tax asset 35414 2491 591 613 39109 36783 2495 648 86 40012 36514 2495 624 92 39725 Current assets Inventories Trade and other receivables Other Current Assets Cash and cash equivalents 3810 2144 438 8123 14515 4136 1854 456 4512 10958 3921 1754 468 5013 11156 Non-current liabilities Non-Current debt 32452 32452 29121 29121 29742 29742 Current liabilities Current debt Trade payables Other current liabilities 3004 5297 3421 11722 2860 6130 3125 12115 2873 6013 3154 12040 Shareholders' Equity 9450 9734 9099 Income statement Em Revenue Cost of sales Gross profit Selling, General & Administrative Operating (loss) profit Finance income Finance cost (Loss)/profit before taxation Taxation (Loss)/profit after taxation Anytime plc For year ending 31 December: 2018 2017 2016 64312 65297 66321 -46322 -46983 -46853 17990 18314 19468 - 13383 - 12300 - 12500 4607 6014 6968 0 0 0 -1365 - 1254 -1214 3242 4760 5754 -613 -1013 - 1089 2629 3747 4665 Question 11 Based on the financial statements for Anytime plc: a) Calculate the following financial statement ratios for 2017 and 2018. Use average values where appropriate. i. ii. iii. iv. V. vi. Cash Conversion Cycle Gross Profit Margin Asset Turnover Debt-to-Equity Interest Coverage (earnings basis) Current Ratio (10 marks) b) Provide a brief analysis and discussion of the ratio results in part (a). Your analysis should discuss the ratios in relation to the aims of: Managing working capital and assets Managing liabilities (10 marks) Question 12 On January 1st 2017, you had a dream which showed you the above financial statements of Anytime plc for Dec 2017 and Dec 2018. The dream also showed that Anytime plc will be liquidated at the beginning of 2019 with shareholders receiving their money in December 2019. If you believed that dream was true, what was the equity value of Anytime plc on Jan 2017? Use an abnormal profit model and a cost of equity of 10%. (5 marks) Question 13 Suppose that Anytime plc has the following R&D outlay, which are spent at the middle of each year. 2018 3450 R&D Outlay 2017 2016 2015 4290 9300 6200 2014 2013 2500 4300 Anytime plc has been expensing R&D outlay under Selling, General & Administrative in the Income Statement. An analyst decides to capitalise the R&D outlays and amortise them over 4 years using a straight-line approach. After making the corresponding adjustments, recalculate, for year 2018, i. Asset Turnover ii. Interest Coverage (earnings basis) SECTION B (40 marks) Answer ALL questions from Section B (there are multiple parts to each question, you must attempt all parts of each selected question). Questions for this section is based on the following financial statements. A balance sheet and income statement for Anytime plc is presented below. Balance sheet Em As at 31 December: 2018 2017 2016 Non-current assets Non-Current Tangibles Non-Current Intangibles Other non-operating investments Deferred tax asset 35414 2491 591 613 39109 36783 2495 648 86 40012 36514 2495 624 92 39725 Current assets Inventories Trade and other receivables Other Current Assets Cash and cash equivalents 3810 2144 438 8123 14515 4136 1854 456 4512 10958 3921 1754 468 5013 11156 Non-current liabilities Non-Current debt 32452 32452 29121 29121 29742 29742 Current liabilities Current debt Trade payables Other current liabilities 3004 5297 3421 11722 2860 6130 3125 12115 2873 6013 3154 12040 Shareholders' Equity 9450 9734 9099 Income statement Em Revenue Cost of sales Gross profit Selling, General & Administrative Operating (loss) profit Finance income Finance cost (Loss)/profit before taxation Taxation (Loss)/profit after taxation Anytime plc For year ending 31 December: 2018 2017 2016 64312 65297 66321 -46322 -46983 -46853 17990 18314 19468 - 13383 - 12300 - 12500 4607 6014 6968 0 0 0 -1365 - 1254 -1214 3242 4760 5754 -613 -1013 - 1089 2629 3747 4665 Question 11 Based on the financial statements for Anytime plc: a) Calculate the following financial statement ratios for 2017 and 2018. Use average values where appropriate. i. ii. iii. iv. V. vi. Cash Conversion Cycle Gross Profit Margin Asset Turnover Debt-to-Equity Interest Coverage (earnings basis) Current Ratio (10 marks) b) Provide a brief analysis and discussion of the ratio results in part (a). Your analysis should discuss the ratios in relation to the aims of: Managing working capital and assets Managing liabilities (10 marks) Question 12 On January 1st 2017, you had a dream which showed you the above financial statements of Anytime plc for Dec 2017 and Dec 2018. The dream also showed that Anytime plc will be liquidated at the beginning of 2019 with shareholders receiving their money in December 2019. If you believed that dream was true, what was the equity value of Anytime plc on Jan 2017? Use an abnormal profit model and a cost of equity of 10%. (5 marks) Question 13 Suppose that Anytime plc has the following R&D outlay, which are spent at the middle of each year. 2018 3450 R&D Outlay 2017 2016 2015 4290 9300 6200 2014 2013 2500 4300 Anytime plc has been expensing R&D outlay under Selling, General & Administrative in the Income Statement. An analyst decides to capitalise the R&D outlays and amortise them over 4 years using a straight-line approach. After making the corresponding adjustments, recalculate, for year 2018, i. Asset Turnover ii. Interest Coverage (earnings basis)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


