Question: Series and Parallel Circuits PHYSICS NAME: OBJECTIVE: In this activity you will be building and testing series and parallel circuits using a computer simulation. Carefully


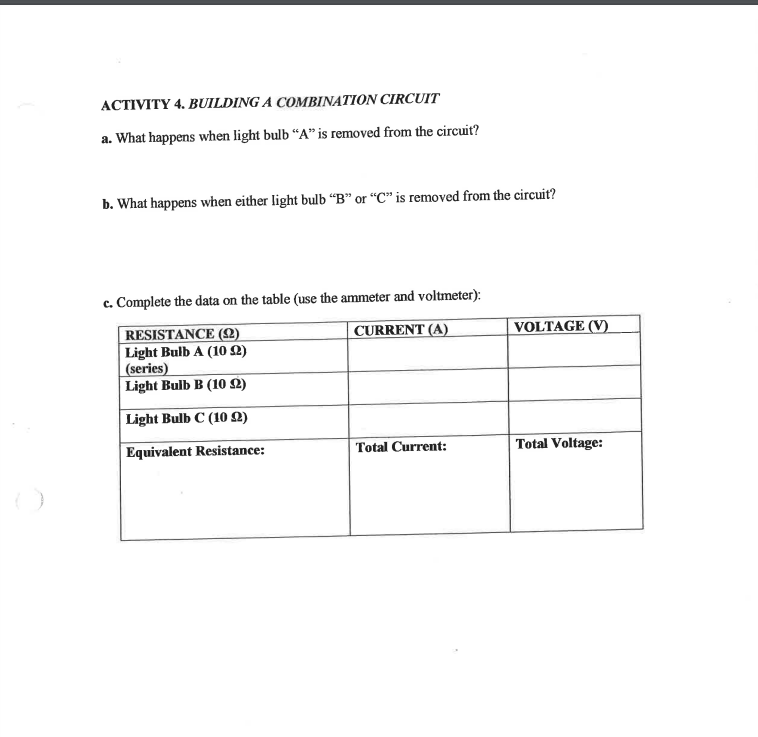
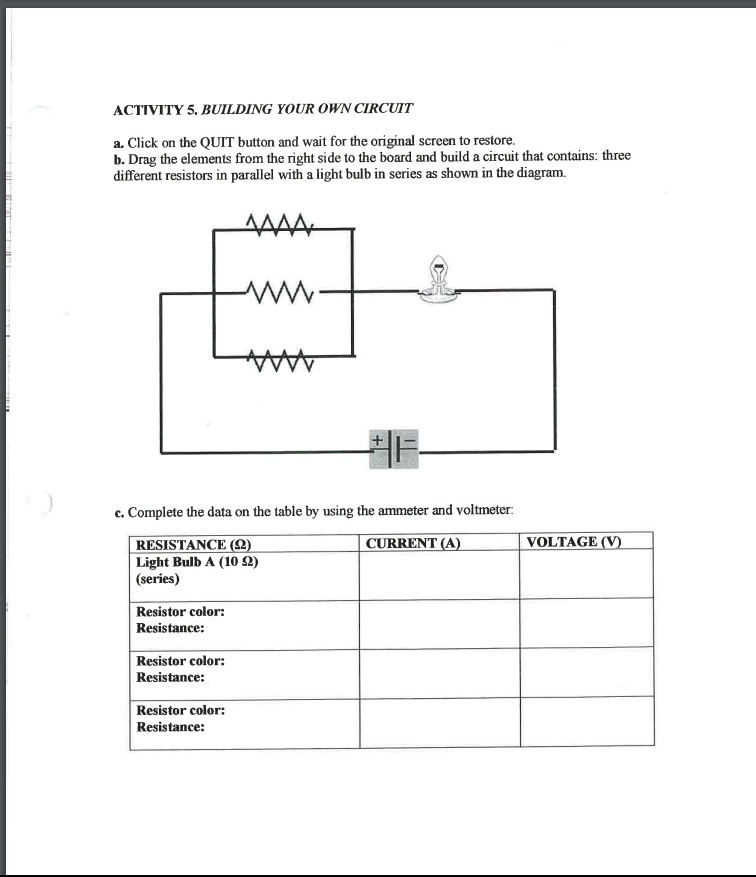
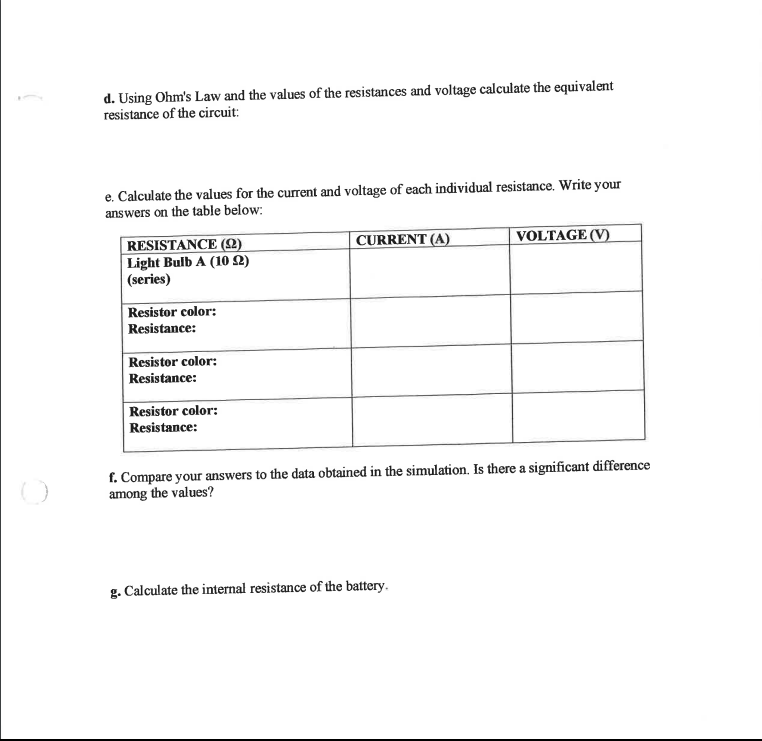
Series and Parallel Circuits PHYSICS NAME: OBJECTIVE: In this activity you will be building and testing series and parallel circuits using a computer simulation. Carefully read and follow the instructions. PROCEDURE: http://phet. colorado. edu/en/simulation/circuit- construction.kit.de 1. Go to the simulation.Ohm-Zone: http://www.article19.com/shockwave/oz.htm- 2. On the right side of the screen you will find assorted items such as resistors, ammeter, voltmeter, circuit board, wires, a battery, bulbs and switches. 3. Click on the hand on the lower left side of the screen and a menu appears. 4. You will complete the first four activities. Just click on each activity and answer the questions. NOTE: The values for voltages are NOT exactly the same as the value given for the battery. This is due to the existence of an internal resistance in the battery. ACTIVITY 1. BUILDING A SIMPLE CIRCUIT. a. What is the voltage of the battery? I ) b. What is another name for voltage? c. In which direction does the electricity flow from the battery? d. Complete the data on the table by replacing the resistors and using the ammeter and voltmeter. RESISTANCE (2) CURRENT (A) VOLTAGE (V) Blue (100 $2) Green (10 2) Purple (200 2) Yellow (20 92)ACTIVITY 2. BUILDING A SERIES CIRCUIT a. How many different paths can the electricity take through the circuit? b. After you remove one of the light bulbs, what happened to the second bulb? c. Complete the data on the table (remember to use the ammeter and voltmeter): RESISTANCE (2) CURRENT (A) VOLTAGE (V) Light Bulb A (10 9) Light Bulb B (10 $2) Equivalent Resistance: Total Current: Total Voltage: ACTIVITY 3. BUILDING A PARALLEL CIRCUIT a. What happens to the electricity at point "A" in the circuit? b. What happens to the electricity at point "B" in the circuit? c. After you remove one of the light bulbs, what happened to the second bulb? d. Complete the data on the table (use the ammeter and voltmeter): RESISTANCE (2) CURRENT (A) VOLTAGE (V) Bulb A (10 92) Light Bulb B (10 2) Equivalent Resistance: Total Current: Total Voltage:ACTIVITY 4. BUILDING A COMBINATION CIRCUIT a. What happens when light bulb "A" is removed from the circuit? b. What happens when either light bulb "B" or "C" is removed from the circuit? c. Complete the data on the table (use the ammeter and voltmeter): RESISTANCE (2) CURRENT (A) VOLTAGE (V) Light Bulb A (10 92) (series) Light Bulb B (10 92) Light Bulb C (10 2) Equivalent Resistance: Total Current: Total Voltage:ACTIVITY 5. BUILDING YOUR OWN CIRCUIT a. Click on the QUIT button and wait for the original screen to restore. b. Drag the elements from the right side to the board and build a circuit that contains: three different resistors in parallel with a light bulb in series as shown in the diagram. c. Complete the data on the table by using the ammeter and voltmeter. RESISTANCE (2) CURRENT (A) VOLTAGE (V) Light Bulb A (10 92) (series) Resistor color: Resistance: Resistor color: Resistance: Resistor color: Resistance:d. Using Ohm's Law and the values of the resistances and voltage calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit: e. Calculate the values for the current and voltage of each individual resistance, Write your answers on the table below: RESISTANCE (2) CURRENT (A) VOLTAGE (V) Light Bulb A (10 92) (series) Resistor color: Resistance: Resistor color: Resistance: Resistor color: Resistance: f. Compare your answers to the data obtained in the simulation. Is there a significant difference ( ) among the values? g. Calculate the internal resistance of the battery
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


