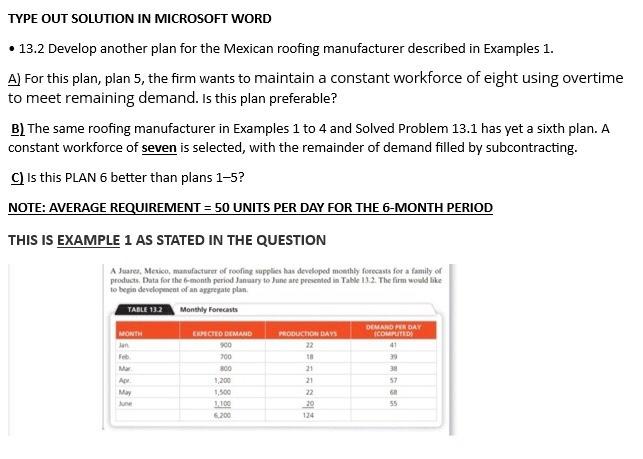
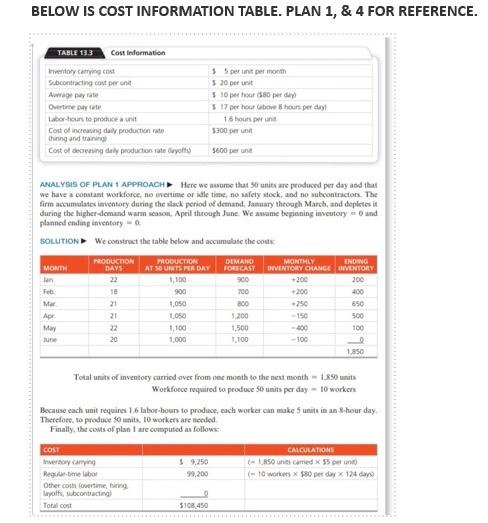
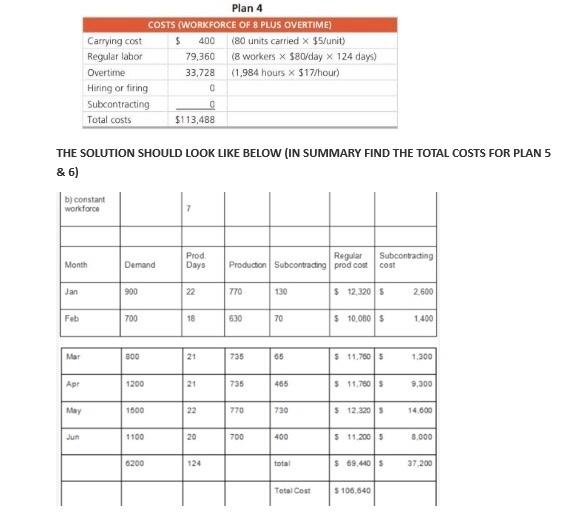
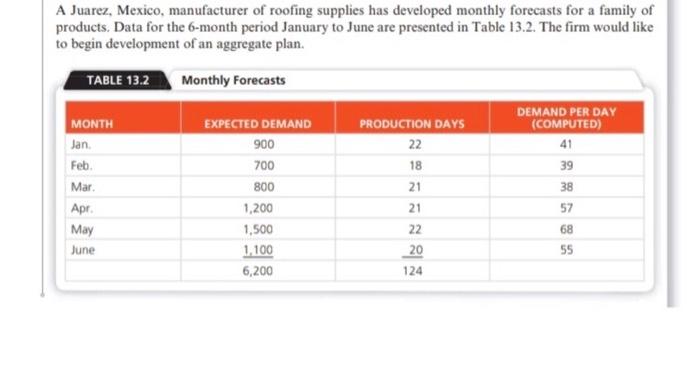
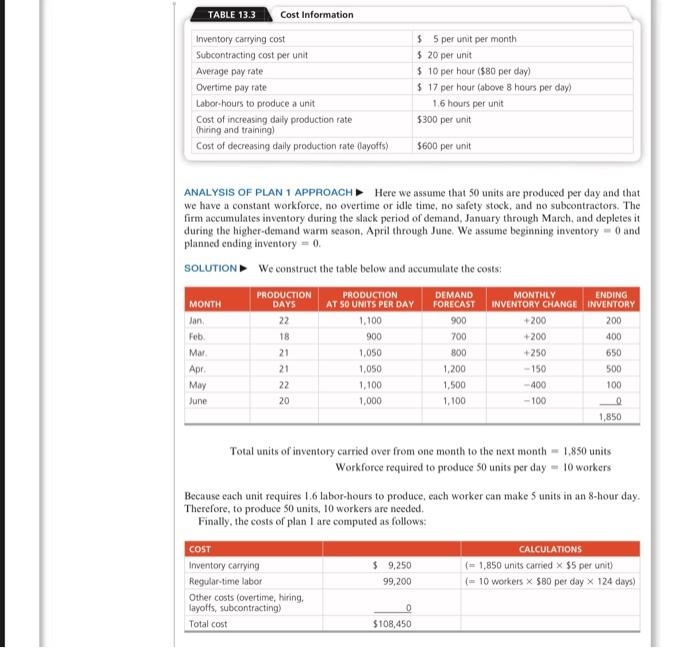
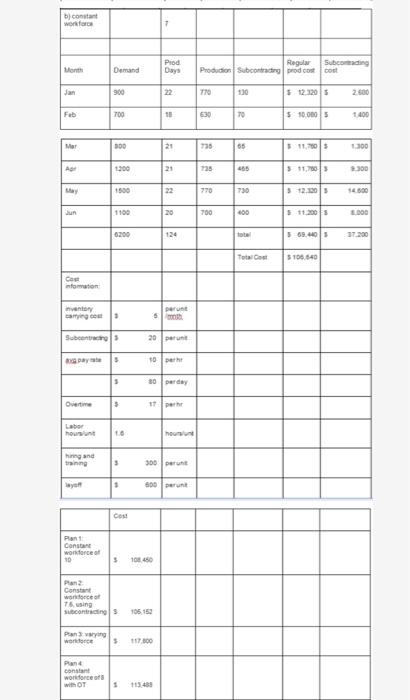
Question: @SHAZEB YOUR SOLUTION IS WRONG STOP ANSWERING MY QUESTIONS THIS HOW THE ANSWER SHOULD BE TYPED Question: TYPE OUT SOLUTION IN MICROSOFT WORD 13.2 Develop
@SHAZEB YOUR SOLUTION IS WRONG STOP ANSWERING MY QUESTIONS
THIS HOW THE ANSWER SHOULD BE TYPED
Question:

TYPE OUT SOLUTION IN MICROSOFT WORD 13.2 Develop another plan for the Mexican roofing manufacturer described in Examples 1. A) For this plan, plan 5, the firm wants to maintain a constant workforce of eight using overtime to meet remaining demand. Is this plan preferable? B) The same roofing manufacturer in Examples 1 to 4 and Solved Problem 13.1 has yet a sixth plan. A constant workforce of seven is selected, with the remainder of demand filled by subcontracting. C) Is this PLAN 6 better than plans 1-5? NOTE: AVERAGE REQUIREMENT = 50 UNITS PER DAY FOR THE 6-MONTH PERIOD THIS IS EXAMPLE 1 AS STATED IN THE QUESTION A Juares, Mexico, manufacturer of roofing supplies has developed monthly forecasts for a family of products. Data for the month period January to June are presented in Table 112. The firm would like to begin development of an aggregate plan TABLE 13.2 Monthly Forecasts MONTH ERECHO DEMAND DEMAND PEN DAY PRODUCTOR DAYS COMPTED lan 900 22 41 700 18 39 Mar 300 21 3 AL 1,200 21 57 May 1,500 22 6 100 20 200 134 55 BELOW IS COST INFORMATION TABLE. PLAN 1, & 4 FOR REFERENCE. TABLE 133 Cost Information Inventory care Subcontracting cost peront Aage pay rate Overtime pay wte bor hours to producent Cost of increasing daily production te thing and trang Cost of decreasing daly production rate Cuyotte 35 per unit per mom 520 per unit $10 per hoor 50 per day 5 17 per hour love hour per day 16 hours per 5300 per unit 5600 per ANALYSIS OF PLAN 1 APPROACH Here we assume that 50 units are produced per day and that we have a constant workforce, no overtime or idle time, no safety stock, and no subcontractors. The firm accumulates inventory during the stack period of demand, January through March, and depletes it during the higher demand warm scan. Apeil through June. We awume beginning inventory and planned ending inventory SOLUTION We construct the table below and accumulate the cost MONTH lan Feb Mar Apr May June PRODUCTION DAYS 22 1e 21 21 22 20 PRODUCTION DIMANO AT SOURIS PER DAY FORECAST 1.100 900 900 700 1,050 800 1,050 1.200 1,100 1,500 1,000 1.100 MONTHLY ENDING INVENTORY CHANGE VENTORY 200 200 +200 400 250 650 - 150 500 -400 100 -100 1.850 Total units of inventory carried over from one month to the next month - 1.850 units Workforce required to produce 56 units per day - 10 worker Because each unit requires 1.6 labor hours to produce, each worker can make 5 units in an 8-hour day Therefore, to produce 50 units. 10 workers are needed Finally, the costs of plantare computed as follows $ 9,250 99,200 COST Inventory canying Regume labor Other coloring Layoffs, subcontracting Total cost CALCULATIONS (-150 units carried x 55 per un (-10 workers $80 per day x 124 days 5108.450 Plan 4 COSTS (WORKFORCE OF 8 PLUS OVERTIME) Carrying cost $ 400 (80 units carried $5/unit) Regular labor 79,360 (8 workers * $80/day x 124 days) Overtime 33,728 (1.984 hours x 517/hour) Hiring or firing 0 Subcontracting 0 Total costs $113,488 THE SOLUTION SHOULD LOOK LIKE BELOW (IN SUMMARY FIND THE TOTAL COSTS FOR PLAN 5 & 6) b) constant workforce Month Demand Prod Days Regular Production Subcontracting prod cost Subcontrading cost Jan 900 22 770 130 $123205 2.500 Fab 700 18 6.30 70 $ 10,000 $ 1.400 Mar 300 21 735 65 $11.7605 1.300 Apr 1200 21 735 465 $ 11,760 9,300 May 1500 22 770 730 $ 12,320 14.000 un 1100 20 700 400 $11.2005 3.000 6200 124 total $69.440s 37 200 Total Cost 5 106,640 - 13.2 Develop another plan for the Mexican roofing manufacturer described in Examples 1 to 4 (pages 538-542) and Solved Problem 13.1 (page 554) a) For this plan, plan 5, the firm wants to maintain a constant workforce of eight using overtime to meet remaining demand. Is this plan preferable? b) The same roofing manufacturer in Examples 1 to 4 and Solved Problem 13.1 has yet a sixth plan. A constant workforce of seven is selected, with the remainder of demand filled by subcontracting. c) is this better than plans 1-5 A Juarez, Mexico, manufacturer of roofing supplies has developed monthly forecasts for a family of products. Data for the 6-month period January to June are presented in Table 13.2. The firm would like to begin development of an aggregate plan. TABLE 13.2 Monthly Forecasts EXPECTED DEMAND 900 DEMAND PER DAY (COMPUTED) 41 39 700 MONTH Jan Feb. Mar Apr May June 38 800 1,200 1,500 1.100 6,200 PRODUCTION DAYS 22 18 21 21 22 20 124 57 68 55 TABLE 13.3 Cost Information Inventory carrying cost Subcontracting cost per unit Average pay rate Overtime pay rate Labor-hours to produce a unit Cost of increasing daily production rate Chiring and training) Cost of decreasing daily production rate (layoffs) $5 per unit per month $ 20 per unit $10 per hour ($80 per clay) $ 17 per hour (above 8 hours per day) 1.6 hours per unit $300 per unit 5600 per unit ANALYSIS OF PLAN 1 APPROACH Here we assume that 50 units are produced per day and that we have a constant workforce, no overtime or idle time, no safety stock, and no subcontractors. The firm accumulates inventory during the slack period of demand, January through March, and depletes it during the higher-cemand warm season. April through June. We assume beginning inventory and planned ending inventory = 0 SOLUTION We construct the table below and accumulate the costs: PRODUCTION PRODUCTION DEMAND MONTHLY ENDING MONTH DAYS AT SO UNITS PER DAY FORECAST INVENTORY CHANGE INVENTORY Jan 22 1.100 900 +200 200 Feb 18 900 700 +200 400 Mar 21 1,050 800 +250 650 Apr. 21 1,050 1,200 - 150 500 May 22 1,100 1,500 -400 100 June 20 1.000 1.100 -100 1,850 Total units of'inventory carried over from one month to the next month - 1,850 units Workforce required to produce 50 units per day - 10 workers Because each unit requires 16 labor-hours to produce, each worker can make 5 units in an 8-hour day. Therefore, to produce 50 units, 10 workers are needed Finally, the costs of plan I are computed as follows: COST CALCULATIONS Inventory carrying $ 9,250 (= 1,850 units carried x $5 per unit) Regular time labor 99,200 (= 10 workers x 580 per day x 124 days) Other costs (overtime, hiring, layoffs, subcontracting 0 Total cost $108,450 b) constant workforce Demand Prod Days Regular Subcoming Production Subcong prod Cocos 900 22 770 130 12.2015 2.600 Fab 700 18 630 70 100005 1400 Mer 300 20 730 65 11.75 300 1200 735 5 11.7603 300 1500 770 730 5 12.1203 500 Jun 1100 20 700 400 S 11.2003 3.000 124 569.03 Totaal $100.540 Ces Information Inventory perunt 3 5 Sober 20 pay 5 to 3 30 per Overtime 5 10 hing and training 3 300 per yo 600D Cost Plant Constant won force 5 168450 Plan Constant wce of Ting subcontings Panwaring word $ 117.800 Pand constant word forces WOT 1 113.40