Question: Should all variables other than S remain fixed, sketch C and P . In doing so and as with the sketches of CE(S, t), first
Should all variables other than S remain fixed, sketch C and P . In doing so and as with the sketches of CE(S, t), first compute the asymptotic behavior as S 0 and as S . Then use the sign of as given in Equation 7.13. Also notice from Equation 7.13 how the value of (or the d1 value near the present value of E) allows a more rapid jump near S = E as t T. What does this mean about the graph?
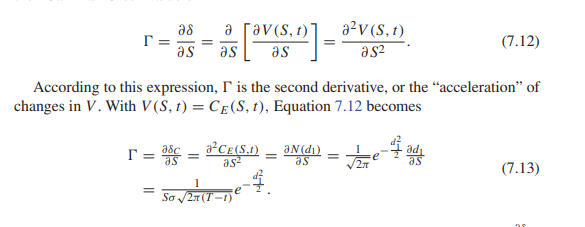
av (S, t) a2 v (S, 1) T = (7.12) as as as a $2 According to this expression, I' is the second derivative, or the "acceleration" of changes in V. With V(S, t) = CE(S, ), Equation 7.12 becomes a-CE(S.D) aN(di) T = asc ad as as- as as (7.13) = So 21 (T-1)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


