Question: Show more specifically by ignoring overlap integrals between any atoms farther apart than nearest neighbors that where Find the definitions of Show that the energies
- Show more specifically by ignoring overlap integrals between any atoms farther apart than nearest neighbors that
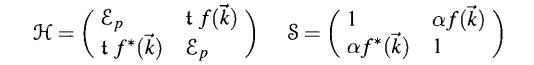
- where
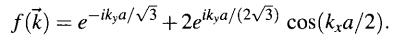
- Find the definitions of
- Show that the energies of the two bands that result are

- where
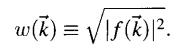
- Setting = 0 because it is just a constant, and taking t = -3.033 eV, a = 0.129, plot Eq. (8.78) between Γ and K (Figures 7.10 and 7.11). Show that in the vicinity of K the two bands are degenerate and have the form of
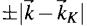
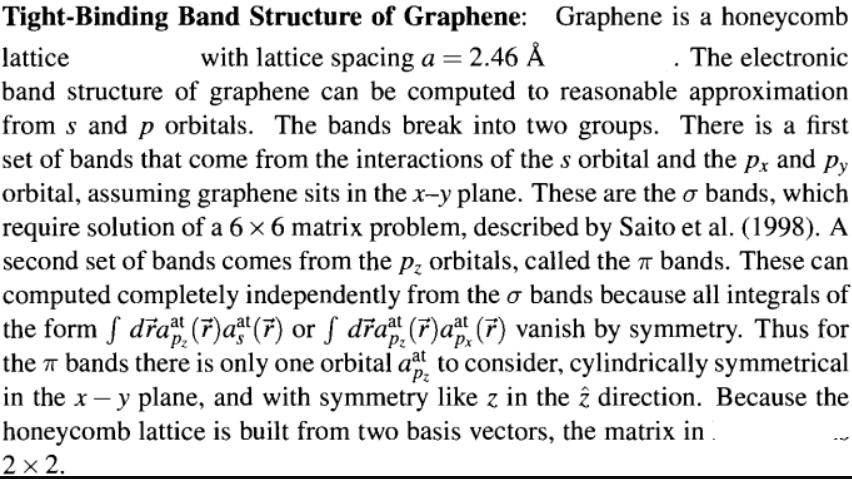
Tight-Binding Band Structure of Graphene: Graphene is a honeycomb with lattice spacing a = 2.46 The electronic lattice band structure of graphene can be computed to reasonable approximation from s and p orbitals. The bands break into two groups. There is a first set of bands that come from the interactions of the s orbital and the Px and Py orbital, assuming graphene sits in the x-y plane. These are the o bands, which require solution of a 6 6 matrix problem, described by Saito et al. (1998). A second set of bands comes from the p orbitals, called the bands. These can computed completely independently from the o bands because all integrals of the form f dra (7)a (7) or da (r)a (7) vanish by symmetry. Thus for the bands there is only one orbital at to consider, cylindrically symmetrical Pz in the x - y plane, and with symmetry like z in the 2 direction. Because the honeycomb lattice is built from two basis vectors, the matrix in . 2 x 2.
Step by Step Solution
3.53 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


