Question: Show transcribed image text VIDEO CASE Using Operations to Create Value at Crayola Crayola HALLMARK CON Operations processes are at the heart of Crayola, the
Show transcribed image text
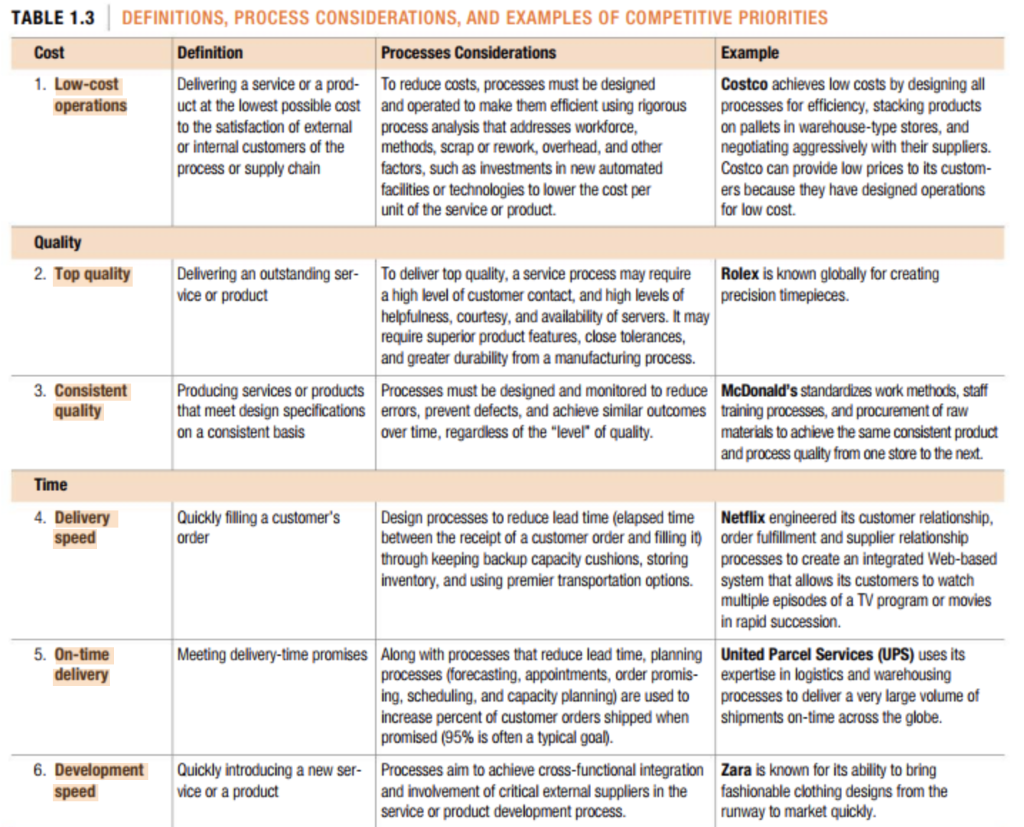
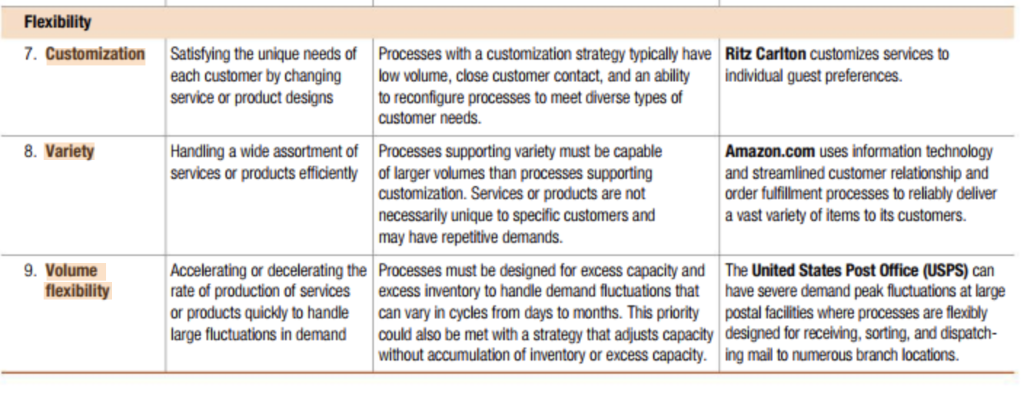
VIDEO CASE Using Operations to Create Value at Crayola Crayola HALLMARK CON Operations processes are at the heart of Crayola, the Easton, Pennsylvania maker of crayons, markers, and paints loved by children of all ages around the world. Since 1903, the company has been taking wax, dyes, and other raw materials and turning them into a colorful array of products sold through an extensive network of distributors and retailers such as Walmart and Target stores. Each day, the company produces 13 million crayons, 2 million mark- ers, 500,000 jars of paint, 170,000 pounds of modeling compounds, and 22,000 Silly Putty eggs from its three manufacturing plants. Crayola derives much of its own inspiration and creativity by asking, "What would a kid do?'especially when focusing on innovation. Not that kids have the knowledge to create complex systems and operational pro- cesses. Rather, the question leads to creative solutions by freeing employees to think about the company's competitive priorities in new ways. In the supply chain, the company maintains five "pillars of operational leadership. These pillars focus attention on differentiating the company on (1) innovation, (2) sustainability, (3) agility and resilience, (4) cost, and (5) quality and ethical responsibility. The company has a history of innovation. They were the first to introduce an art education program called Dream-Makers, into the nation's elemen- tary schools. Washable markers and crayons also were firsts for the indus- try and continue to be best-sellers for the company. Recently, the language on crayon paper packaging changed to include three languages-French, Crayola, headquartered in Pennsylvania, has become a leader in its industry by focusing on operational excellence and innovation. English and Spanishinstead of one. This change alone saved $400,000 in paper and printing costs since the packaging could now be used across multiple markets. In the area of sustainability, Crayola built a solar farm on a 20-acre site adjacent to its manufacturing plant in Easton. The farm produces manufacturing and distribution presences there. As you can imagine, this means operations managers must think about how to grow the current supply chain beyond the boundaries of existing domestic and international borders if additional expansion is to occur. enough energy to completely run the plant as well as the headquarters build- ing nearby. The 850 million colored pencils produced each year only use reforested wood, with one tree planted for every tree harvested. Sourcing for paraffin wax used in crayons recently moved from Louisiana to western Pennsylvania, saving 5,000 barrels of oil annually related to wax transporta- tion. All plastic components are made with recycled plastics. And any excess wax from the production of crayons is reintroduced into the manufacturing process so no waste is produced. The company is aggressively pursuing new markets outside the United States. China's market of children ages 0-14 is larger than all the other global markets combined, with more than half the world's child population. Yet only 14 percent of the company's total sales come from international markets. So, particular attention is being devoted to growing the company's QUESTIONS 1. Map Crayola's five pillars of operational leadership to the competitive priorities in Table 1.3. 2. Create an assessment of Crayola's competitive priorities as it relates to their Asian expansion plans. 3. Which of the competitive priorities might present the biggest challenge to Crayola as it expands internationally? TABLE 1.3 DEFINITIONS, PROCESS CONSIDERATIONS, AND EXAMPLES OF COMPETITIVE PRIORITIES Cost Definition Processes Considerations Example 1. Low-cost Delivering a service or a prod- To reduce costs, processes must be designed Costco achieves low costs by designing all operations uct at the lowest possible cost and operated to make them efficient using rigorous processes for efficiency, stacking products to the satisfaction of external process analysis that addresses workforce, on pallets in warehouse-type stores, and or internal customers of the methods, scrap or rework, overhead, and other negotiating aggressively with their suppliers. process or supply chain factors, such as investments in new automated Costco can provide low prices to its custom- facilities or technologies to lower the cost per ers because they have designed operations unit of the service or product. for low cost. Quality 2. Top quality Delivering an outstanding ser- To deliver top quality, a service process may require Rolex is known globally for creating vice or product a high level of customer contact, and high levels of precision timepieces. helpfulness, courtesy, and availability of servers. It may require superior product features, close tolerances, and greater durability from a manufacturing process. 3. Consistent Producing services or products Processes must be designed and monitored to reduce McDonald's standardizes work methods, staff quality that meet design specifications errors, prevent defects, and achieve similar outcomes training processes, and procurement of raw on a consistent basis over time, regardless of the "level" of quality. materials to achieve the same consistent product and process quality from one store to the next Time 4. Delivery Quickly filling a customer's Design processes to reduce lead time (elapsed time Netflix engineered its customer relationship, speed order between the receipt of a customer order and filling it) order fulfillment and supplier relationship through keeping backup capacity cushions, storing processes to create an integrated Web-based inventory, and using premier transportation options. system that allows its customers to watch multiple episodes of a TV program or movies in rapid succession. 5. On-time Meeting delivery-time promises Along with processes that reduce lead time, planning United Parcel Services (UPS) uses its delivery processes (forecasting, appointments, order promis- expertise in logistics and warehousing ing, scheduling, and capacity planning) are used to processes to deliver a very large volume of increase percent of customer orders shipped when shipments on-time across the globe. promised (95% is often a typical goal). 6. Development Quickly introducing a new ser- Processes aim to achieve cross-functional integration Zara is known for its ability to bring speed vice or a product and involvement of critical external suppliers in the fashionable clothing designs from the service or product development process. runway to market quickly. Flexibility 7. Customization 8. Variety Satisfying the unique needs of Processes with a customization strategy typically have Ritz Carlton customizes services to each customer by changing low volume, close customer contact, and an ability individual guest preferences service or product designs to reconfigure processes to meet diverse types of customer needs. Handling a wide assortment of Processes supporting variety must be capable Amazon.com uses information technology services or products efficiently of larger volumes than processes supporting and streamlined customer relationship and customization Services or products are not order fulfillment processes to reliably deliver necessarily unique to specific customers and a vast variety of items to its customers. may have repetitive demands. Accelerating or decelerating the Processes must be designed for excess capacity and The United States Post Office (USPS) can rate of production of services excess inventory to handle demand fluctuations that have severe demand peak fluctuations at large or products quickly to handle can vary in cycles from days to months. This priority postal facilities where processes are flexibly large fluctuations in demand could also be met with a strategy that adjusts capacity designed for receiving, sorting, and dispatch- without accumulation of inventory or excess capacity. ing mail to numerous branch locations. 9. Volume flexibility Competitive Priorities and Capabilities A customer-driven operations strategy requires a cross-functional effort by all areas of the firm to understand the needs of the firm's external customers and to specify the operating capabilities the firm requires to outperform its competitors. Such a strategy also addresses the needs of internal customers because the overall performance of the firm depends upon the performance of its core and support- ing processes, which must be coordinated to provide the overall desirable outcome for the external customer. Competitive priorities are the critical operational dimensions a process or supply chain must possess to satisfy internal or external customers, both now and in the future. Competitive priorities are planned for processes and the supply chain created from them. They must be present to maintain or build market share or to allow other internal processes to be successful. Not all competitive priori- ties are critical for a given process; management selects those that are most important. Competitive capabilities are the cost, quality, time, and flexibility dimensions that a process or supply chain actually competitive priorities The critical dimensions that a process or supply chain must possess to satisfy its internal or external customers, both now and in the future. competitive capabilities The cost, quality, time, and flexibility dimensions that a process or supply chain actually possesses and is able to deliver
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts